- Title
-
The gonadal soma controls ovarian follicle proliferation through Gsdf in zebrafish
- Authors
- Yan, Y.L., Desvignes, T., BreMiller, R., Wilson, C., Dillon, D., High, S., Draper, B., Buck, C.L., Postlethwait, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
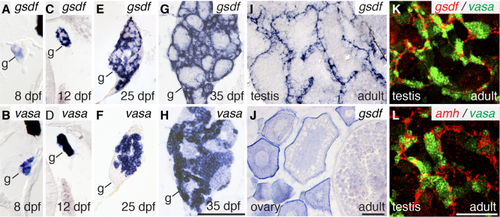
Expression of gsdf in somatic cells (A,C,E,G) and vasa in germ cells (B,D,F,H) of 8 dpf (A,B), 12 dpf (C,D), 25 dpf (E,F), and 35 dpf (G,H) animals. Expression of gsdf in 8 mpf adult testis (I) and ovary (J). Two color in situ hybridization on adult testis (K) for gsdf (red) and vasa (green) and (L) amh (red) and vasa (green). Black scale bar in H for A–H; black scale bar in J for I,J; white scale bar in L for K,L. All scale bars = 100 μm. |
|
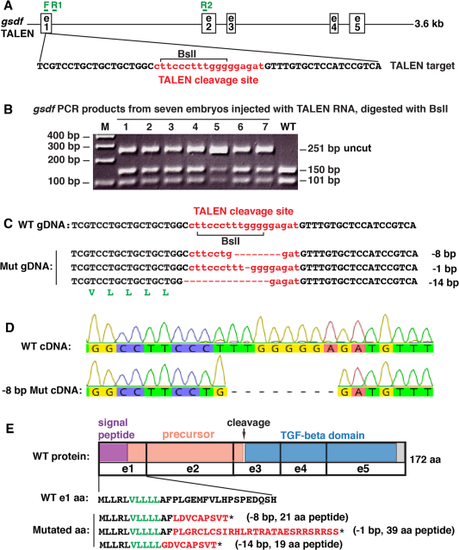
Mutagenesis. A: A 3.6 kb genomic region of gsdf including exons (e) 1–5 with the TALEN target sequence: TALEN cleavage site (small letters in red), TALEN binding sites in black and BslI restriction site (bracket), along with genotyping primer sites (F, R1 and R2 in green). B: PCR analysis of seven G0 injected embryos at 1 dpf using genotyping primers F and R1 shows a 251 base pair (bp) fragment in wild-types (WT) that digests with BslI to produce fragments of 150 bp and 101 bp. Seven injected embryos (1–7) contained a substantial load of mutations that destroyed the BslI site, leaving the 251 bp fragment undigested, in addition to the WT bands. C: Raising injected embryos and subsequent breeding produced stable lines carrying -8 bp, -1 bp, and -14 bp deletions. Talen cleavage site shown in red. A translated portion of gsdf (in green letters) appears below the -14 bp sequence. D: To verify transcription of the -8 bp deletion, we amplified a 275 bp fragment using primer F in exon-1 and R2 in exon-2 shown in A; results verified the 8 bp deletion, which confirmed the genomic sequence in C. E: TALEN-induced mutations are predicted to result in premature stop codons (*). The translated portion of Gsdf (in black and green letters) indicates the wild-type sequence, while red letters indicate the predicted frame-shifted sequences in gsdf mutants. Protein coding domains: purple, signal peptide; salmon, precursor; blue, TGFB-family domain; gray, C-terminus; e, exons; arrow, cleavage site. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
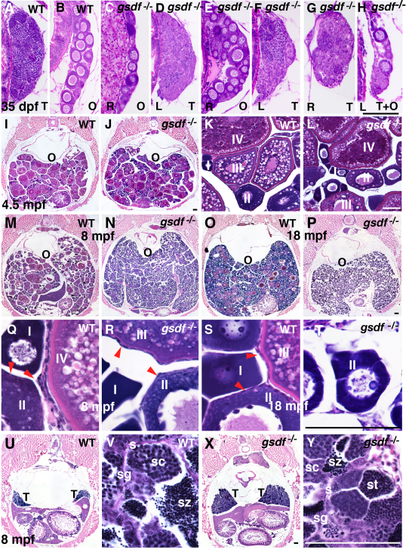
Gonad histology. A–H: Histological sections of 35 dpf wild-type fish showed only ovary or testis (A,B), but six of 22 gsdf mutant fish (27%) at 35 dpf contained either one ovary and one testis, like the two fish in C–F, or individual gonads containing both ovary and testis like the one fish in G and H. O, ovary; T, testis; R, right gonad; L, left gonad. I–T: Adult female ovaries showing low (I,J,M–P), and high (K,L,Q–T) magnification. Cross-sections of 4.5 mpf of wild-types (I,K) and gsdf mutants (J,L) that contained maturing (stage-I, II) and vitellogenic (stage-III and -IV) follicles. The 8-mpf-old wild-type females had gonads filled with maturing (stage-I, -II) and vitellogenic (stage-III and -IV) follicles (M,Q), as well as follicle cells on the surface of oocytes (red arrow heads in panel Q). N,R: Cross-sections of an 8 mpf gsdf mutant female showed an excess of immature follicles (stage-I and -II), a few early vitellogenic follicles (stage-III), but no late vitellogenic follicles (stage-IV). Follicle cells surround oocytes (red arrow heads, panel R) in mutants as in wild-types. (M,Q). Cross section of an old (18 mpf) female wild-type with many immature follicles, a few normal vitellogenic follicles (O,S), and an 18 mpf female gsdf mutant female with many young follicles (stage-I and -II) but no mature stages (P,T). U,V,X,Y: Cross-sections of 8 mpf wild-type (U,V) and gsdf mutant (X,Y) males at low (U,X) and high magnification (V,Y). Although male gsdf mutants had larger testes than wild-types, both genotypes formed all spermatogenic stages O, ovary; s, sertoli cells; sc, spermatocytes; sg, spermatogonia; st, spermatids; sz, spermatozoa; T, testis. Black scale bar in H for A–H; black scale bar in J for I, J; white scale bar in L for K, L; black scale bar in P for M–P; Black scale bar in T for Q–T; black scale bar in X for U, X; white scale bar in Y for V, Y. All scale bars = 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
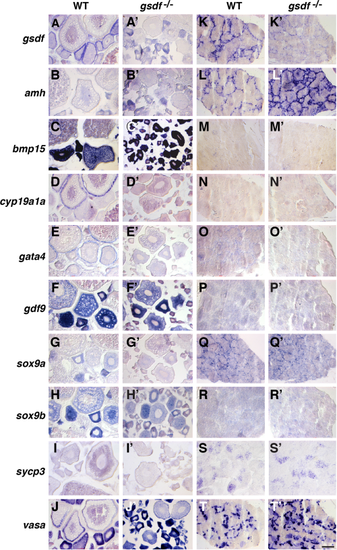
Gene expression patterns in adult gonads at 8 mpf. A–J: Wild-type ovaries. A′–J′: gsdf mutant ovaries. K–T: Wild-type testis. K′–T′: gsdf mutant testis. In situ hybridization for gsdf (A,A′,K,K′), amh (B,B′,L,L′), bmp15 (C,C′,M,M′), cyp19a1a (D,D′,N,N′), gata4 (E,E′, O,O′), gdf9 (F,F′,P,P′), sox9a (G,G′, Q,Q′), sox9b (H, H′,R,R′), sycp3 (I,I′,S,S′), vasa (J,J′,T,T′). Little gsdf transcript was apparent in mutant gonads. Transcript of cyp19a1a and gata4 was less abundant in mutant ovarian follicles and amh and vasa was more abundant in mutant testis. Scale bar = 100 μm in T′. |
|
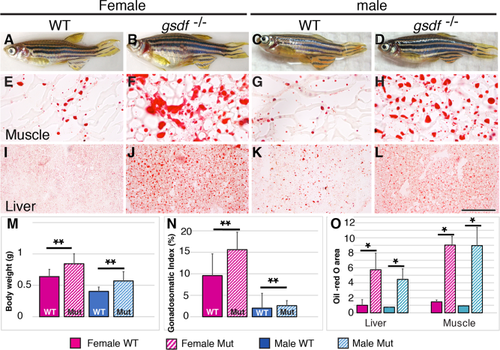
Body size and lipid homeostasis. A–D: Adult 8 mpf zebrafish: wild-types (A, female; C, male) and gsdf mutants (B, female; D, male), showing enlarged abdomens in mutants. E–L: Histological sections showing lipid stained with Oil Red O in trunk muscle (E–H) and hepatopancreas (liver; I–L). Mutants accumulated more and larger lipid droplets than wild-types. M: Body weight (g). N: Gonadosomatic index (%). O: Oil-red O area. Solid boxes, wild-types; striped boxes, mutants; red boxes, females; blue boxes, males. *0.05 < P < 0.01; **0.01 < P < 0.001. Scale bar = 100 μm in L. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|