- Title
-
The orphan G protein-coupled receptor 161 is required for left-right patterning
- Authors
- Leung, T., Humbert, J.E., Stauffer, A.M., Giger, K.E., Chen, H., Tsai, H.J., Wang, C., Mirshahi, T., and Robishaw, J.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
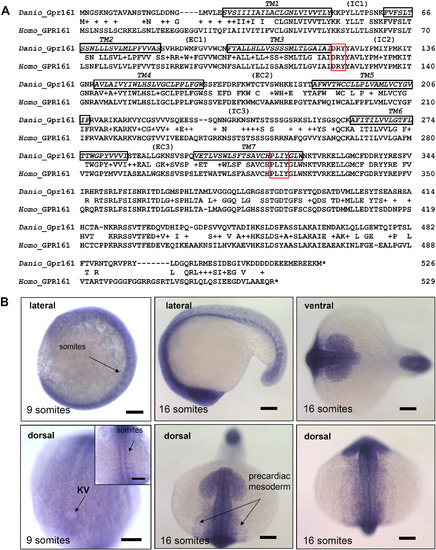
Sequence comparison and in situ expression analysis of zebrafish gpr161. (A) Genbank accession no. of human GPR161: NM_007369 (Homo); zebrafish gpr161: EU090912 (Danio). 7TM (black), DRY (red) and PxxY (red) motifs were boxed. (B) gpr161 expression in the developing embryos by whole mount in situ hybridization. Inset showed the expression in developing somites and expression surrounding the Kupffer's vesicle (KV) near the tail bud region at 9-somite stage. All scale bars were 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
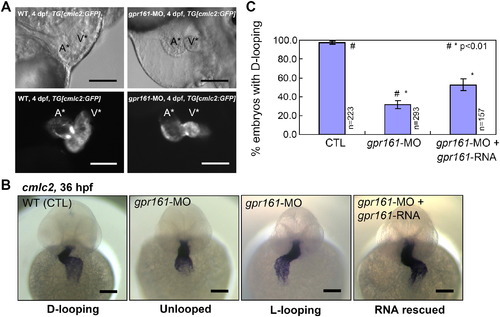
gpr161 knockdown disrupts cardiac looping morphogenesis. (A) Lateral view of zebrafish hearts at 4 dpf. Control and gpr161 knockdown in transgenic zebrafish embryos with cardiac specific GFP, TG[cmlc2:GFP], showing images of bright field (top panels) and fluorescent (bottom panels). A* labelled atrium, V* labelled ventricle. (B) Cardiac looping morphogenesis marked by cmlc2 expression in control (D-looping), gpr161 knockdown (unlooped and L-looping) and RNA rescued embryos. All scale bars were 100 μm. (C) Graphical summary of gpr161 knockdown disrupted normal cardiac D-looping morphogenesis at 36 hpf. Calculation as % of embryos with D-looping in control (97.8 ± 1.3%; n = 223), embryos injected with gpr161 morpholino (MO#36, 32.4 ± 4.1%; n = 293) and RNA rescue (gpr161 RNA without 5′UTR; 52.2 ± 3.4%; n = 157), n was number of total embryos and results were from 4 injection experiments. Error bars were ± SEM. t-test * and # indicated statistical significance, p < 0.01. |
|
gpr161 knockdown disrupts L–R identity in lateral plate mesoderm. (A) lefty2 expression in the left anterior lateral plate mesoderm (LPM) and lefty1 expression in the left diencephalon were disrupted in gpr161 knockdown embryos. (B) Graphical summary of control (99.3 ± 1.1%; n = 351), gpr161 morpholino (MO#24, 67.0 ± 4.7%; n = 348) and t-test (p < 0.01) results were from 11 injection experiments. (C) spaw expression in the left anterior lateral plate mesoderm (LPM) at 19.5 hpf in control and gpr161 knockdown embryos. ntl expression marked the midline as a reference. (D) Graphical summary of spaw expression in control (98.7 ± 1.4%; n = 311), gpr161 morpholino (MO#24, 63.4 ± 2.7%; n = 306) and t-test (p < 0.01) results were from 13 injection experiments. Error bars were ± SEM. All scale bars were 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
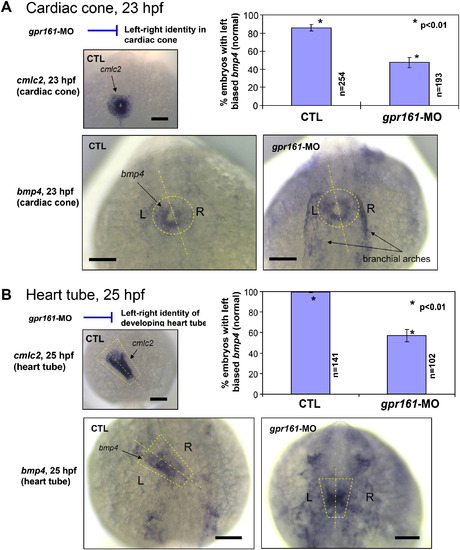
(A) bmp4 expression was predominantly on the left side of the cardiac cone in comparison to the uniform expression of cmlc2 (inset) which was disrupted in gpr161 knockdown embryos. Graphical summary of control (85.8 ± 3.7%; n = 254), gpr161 knockdown (MO#24, 47.5 ± 5.7%; n = 193) and t-test (p < 0.01) results were from 7 injection experiments. (B) bmp4 expression was predominantly on the left side of the heart tube in comparison to the uniform expression of cmlc2 (inset) was disrupted in gpr161 knockdown embryos. Graphical summary of control (99.5 ± 1.3%; n = 141), gpr161 knockdown (MO#24, 56.9 ± 5.9%; n = 102) and t-test (p < 0.01) results were from 4 injection experiments. Dashed lines were drawn over the cardiac cone and heart tube and the midline of the structures. n was number of total embryos. Error bars were ± SEM. All scale bars were 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
L–R asymmetry of visceral organs in zebrafish embryos. (A) foxa3 expression marks the gut primordium at 36 hpf showing the liver bud (left) and pancreatic bud (right) in control embryo. (B) Graphical summary of normal visceral asymmetry in control (97.8 ± 1.3%), gpr161 knockdown (32.4 ± 4.1%) and RNA rescued (52.2 ± 3.4%) embryos. t-test (p < 0.01) results were from 6 injection experiments. n was number of total embryos. Error bars were ± SEM. (C) foxa3 expression of liver and pancreatic buds in normal L–R asymmetric position in control, symmetric or heterotaxia in gpr161 knockdown and normal L–R asymmetry in RNA rescued embryos. All scale bars were 100 μm. |
|
gpr161 knockdown disrupts Ca2+ handling which is essential for establishment of L–R asymmetry. (A) Defective Ca2+ handling resulting in elevated intracellular Ca2+ in gpr161 knockdown embryos surrounding the Kupffer′s vesicle. Pseudocolour scale for the intracellular Ca2+ signal as normal, intermediate and high intensity. The percentage of embryos exhibited such level of Ca2+ signal was listed in control, gpr161 knockdown, ncx1- and pmca-RNA rescue of the gpr161 knockdown embryos. (B) Removal of excessive Ca2+ by over-expression of 1 pg of Ca2+ pump pmca or Na+/Ca2+ exchanger ncx1 can rescue gpr161 knockdown phenotype. Cardiac looping defect in gpr161-MO (MO#24, 54.1 ± 4.0%; n = 368), rescued by pmca-RNA (32.0 ± 6.0%; n = 238), rescued by ncx1-RNA (34.0 ± 4.8%; n = 144) and results were from 4 injection experiments. n was number of total embryos. Error bars were ± SEM. t-test * and # indicated statistical significance, p < 0.01. All scale bars were 100 μm. (C) A model of gpr161 involved in Ca2+ handling and essential for L–R asymmetry for cardiac morphogenesis and visceral asymmetry in developing zebrafish embryos. Blocking gpr161 function led to defect in Ca2+ handling and resulted in elevated free cytosolic Ca2+ and loss of cardiac looping and abnormal chamber morphogenesis. The gpr161 knockdown can be rescued by removing excessive cytosolic free Ca2+ using over-expression of Ca2+ pump pmca and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger ncx1. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
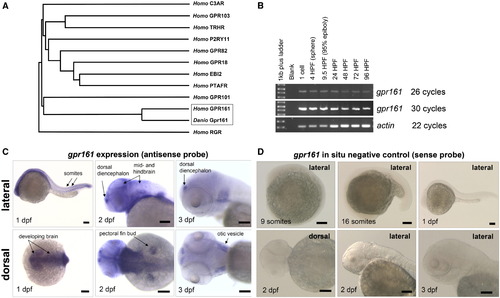
Phylogram and RT-PCR analysis of the zebrafish gpr161. (A) Phylogram analysis revealed zebrafish Gpr161 protein is highly similar to the human counterpart within the purine receptor cluster branch of the δ-group of RHODOPSIN receptors. The protein sequences were aligned using T-coffee (http://igs-server.cnrs-mrs.fr/Tcoffee/tcoffee_cgi/index.cgi) and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Treetop program with a bootstrap value of 100and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Treetop program with a bootstrap value of 100 (http://www.genebee.msu.su/services/phtree_reduced.html). Genbank accession numbers for human C3AR (NP_004045), human GPR103 (NP_937822), humanTRHR (NP_003292), human P2RY11 (NM_002566), human GPR82 (NP_543007), human GPR18 (CAI14306), human EBI2 (P32249), human PTAFR (NP_000943), human GPR101 (NP_473362), human GPR161 (CAI22623), human RGR (AAI01111) and zebrafish Gpr161 (EU090912).(B) RT-PCR detection of the maternal zebrafish gpr161 transcript at 1 cell stage and zygotic transcript at sphere stage (4 hpf) onward to 96 hpf, for 26 and 30 PCR cycles. actin RT-PCR was used as RNA loading control, for 22 PCR cycles. (C) gpr161 expression in 1 dpf to 3 dpf zebrafish embryos. (D) Negative control of using sense probe of gpr161. All scale bars were 100 μm. |
|
Translational blocking by gpr161-MO morpholino detected by in vitro cell lysate assay. (A) Two translational blocking morpholinos, targeted against the 5′UTR upstream of the ATG start codon of zebrafish gpr161 open-reading frame, which was fused to V5-6xHistidine epitope. (B,C) Dose dependent inhibition of Gpr161 translation by two independent gpr161 morpholinos (gpr161-MO#36 and gpr161-MO#24) using in vitro cell lysate. No inhibition by 5-base mismatch control morpholino (mismatch-MO#28). Anti-V5 antibody was used to detect the in vitro translation (B) of Gpr161-V5 fusion protein and band intensity (C) was quantitated as % translation compared to control in the graph. No morpholino as control (100%), 10 μM MO#24 (7%), 1 μM MO#24 (56%), 0.1 μM MO#24 (84%), 10 μM MO#28 (79%), 1 μM MO#28 (92%), 0.1 μM MO#28 (79%), 10 μM MO#36 (0%), 1 μM MO#36 (13%) and 0.1 μM MO#36 (40%). (D) Both gpr161 morpholinos (MO#24 and MO#36) gave similar cardiac looping defect. All scale bars were 100 μm. |
|
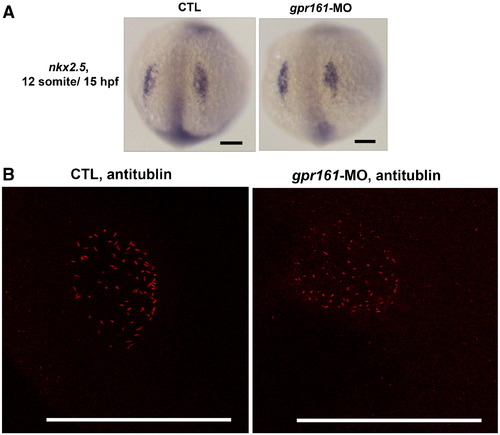
(A) nkx2.5 expression in control and gpr161 knockdown embryos. (B) Confocal imaging of microcilia in Kupffer's vesicle. Anti-tubulin staining (red) of microcilia of control and gpr161 knockdown embryos in the Kupffer's vesicle at 14 hpf. All scale bars were 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
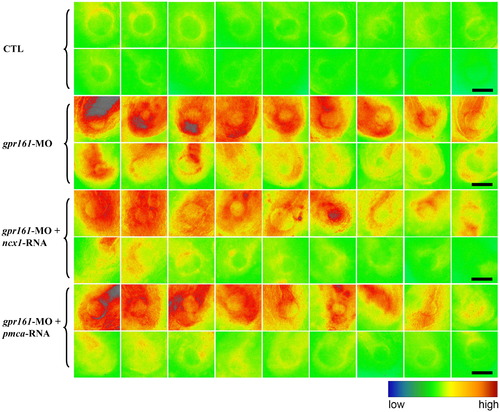
Ca2+ green imaging of intracellular Ca2+ in zebrafish embryos. Pseudocolour of fluorescent images of Ca2+ signal in posterior mesoderm near the Kupffer's vesicle of control, gpr161 knockdown, ncx1-RNA rescue and pmca-RNA rescue of gpr161 knockdown embryos at 14 hpf. Each group contains 18 different embryos organized as decreasing order of Ca2+ green intensity. All scale bars were 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 323(1), Leung, T., Humbert, J.E., Stauffer, A.M., Giger, K.E., Chen, H., Tsai, H.J., Wang, C., Mirshahi, T., and Robishaw, J.D., The orphan G protein-coupled receptor 161 is required for left-right patterning, 31-40, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.