- Title
-
Enhancer trap lines with GFP driven by smad6b and frizzled1 regulatory sequences for the study of epithelial morphogenesis in the developing zebrafish inner ear
- Authors
- Baldera, D., Baxendale, S., van Hateren, N.J., Marzo, M., Glendenning, E., Geng, F.S., Yokoya, K., Knight, R.D., Whitfield, T.T.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Anat.
|
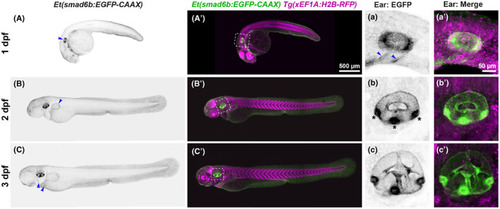
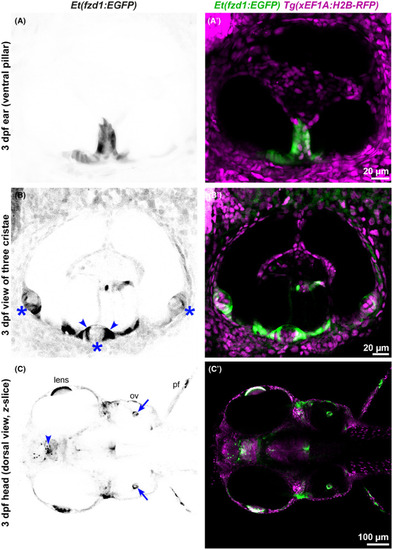
Expression of the |
|
|
|
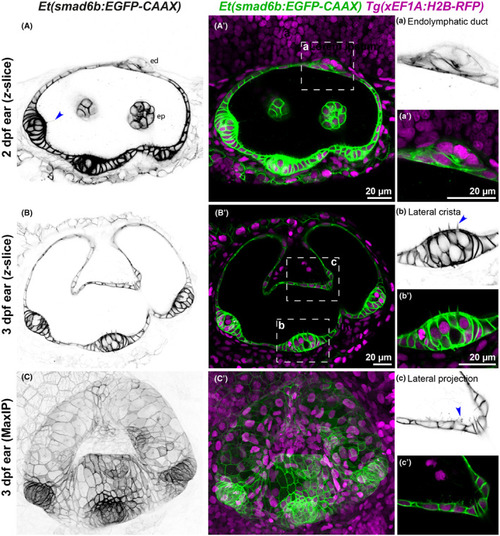
Comparison of |
|
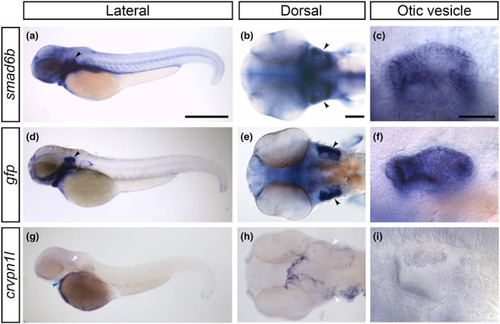
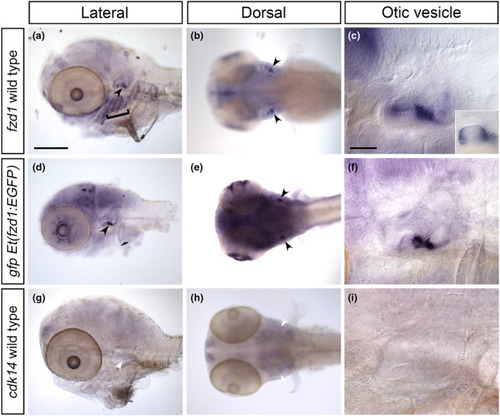
Expression of the |
|
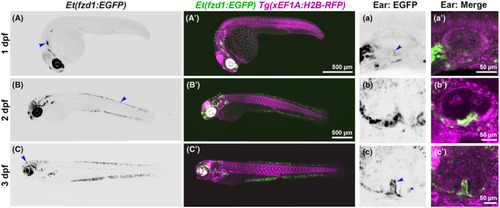
Expression of the |
|
Comparison of |
|
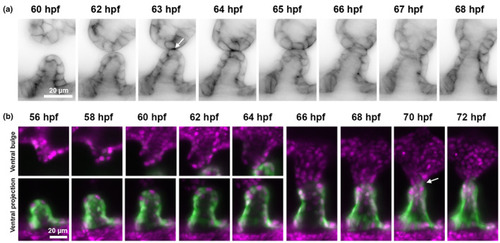
Imaging of ventral pillar formation in |