- Title
-
Control of dynamic cell behaviors during angiogenesis and anastomosis by Rasip1
- Authors
- Lee, M., Betz, C., Yin, J., Paatero, I., Schellinx, N., Carte, A.N., Wilson, C.W., Ye, W., Affolter, M., Belting, H.G.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
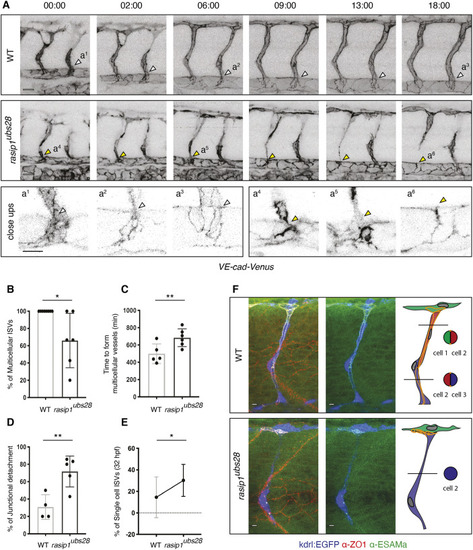
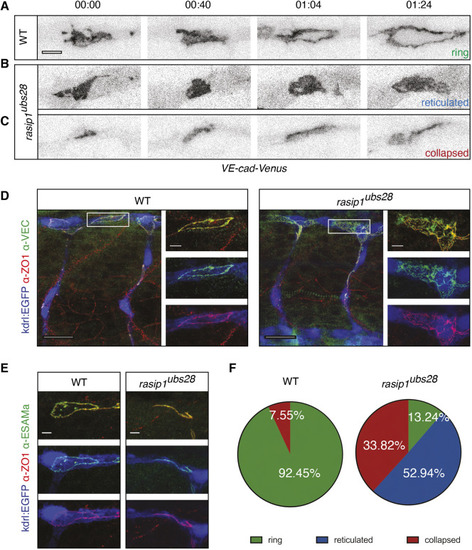
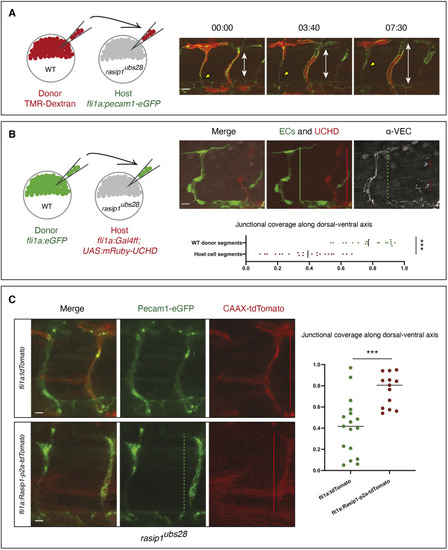
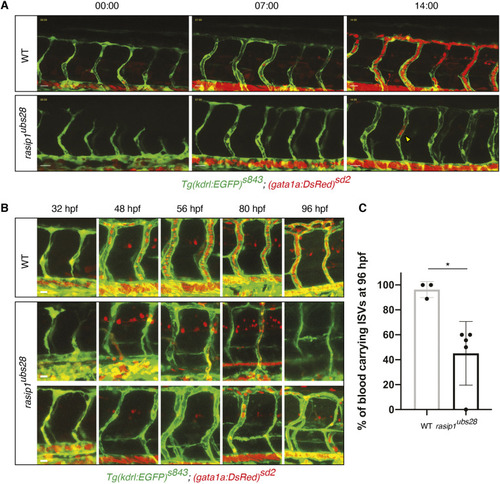
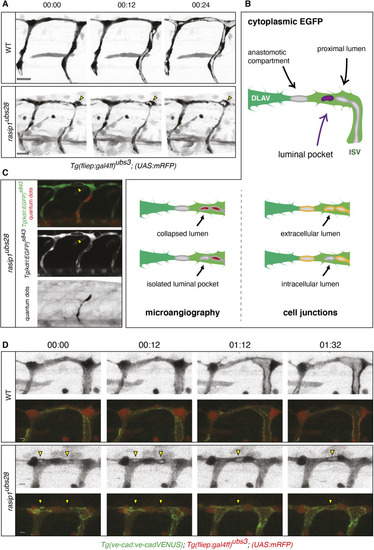
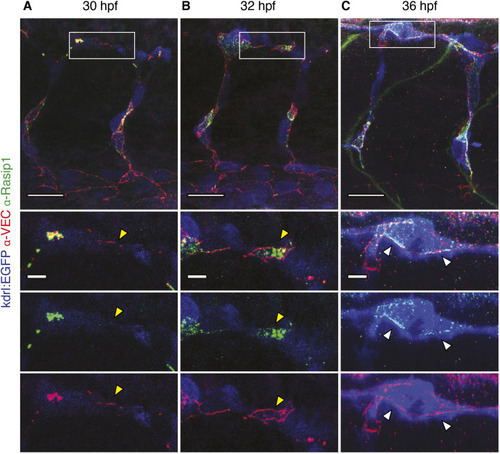
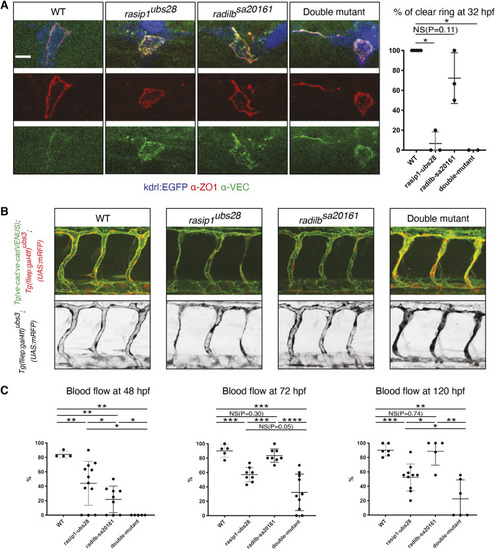
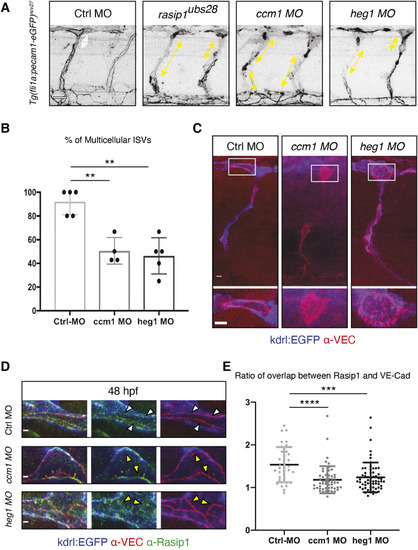
Formation of multicellular vessels is impaired in rasip1 mutants. (A) Still images of time-lapse movies showing endothelial cell junctions (Cdh5-Venus) in wild-type (WT) and rasip1ubs28 embryos (Movies 1 and 2). White arrowheads show maintained junctional contacts in wild-type ISV sprouts. Yellow arrowheads indicate junction detachment in mutant embryos. Bottom row shows close-ups (a1-a3: wild type; a4-a6: mutant) showing junctional detachment in a4 and a5. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B-E) Quantification of junctional and cellular configuration during ISV formation in wild-type and rasip1ubs28 mutant embryos. (B) Percentage multicellular tubes at 48 hpf (WT n=8, mutant n=6). (C) Speed of multicellular tube formation (WT n=5, mutant n=6). (D) Percentage of ISVs per embryo showing junctional detachment (WT n=4, mutant n=5). (E) Percentage of single-cell ISVs at 32 hpf (WT n=8, mutant n=8). Quantifications were performed by counting ISVs showing the respective phenotypes, averaged by total ISVs analyzed per embryo. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and Esama in Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 at 32 hpf. Schematics on the right show the different cellular configurations of multicellular (WT) and unicellular (rasip1 mutant) ISVs. Scale bars: 5 μm. The data were analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Mann–Whitney test (*P<0.1, **P<0.01); error bars indicate s.d. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
|