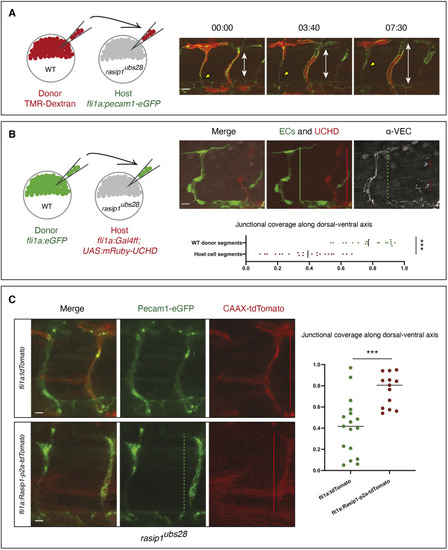
Autonomous requirement of Rasip1 during ISV formation. (A) Schematic showing transplantation of TMR-labeled donor wild-type (WT) cells into rasip1ubs28 mutant hosts with both donor and host cells expressing Pecam1-EGFP in endothelial cells. Time-lapse images of wild-type cells (red) in rasip1ubs28 mutant hosts showing that wild-type cells elongate and maintain junctional contacts (Movie 6). Double-headed arrows indicate the extent of the ISV between DA and DLAV. (B) Schematic showing transplantation of EGFP-labeled wild-type donor cells [Tg(flia:EGFP)y1] into rasip1 mutant host embryos [Tg(flia:Galff)ubs3; (UAS:UCHD-mRuby2)ubs20]. Immunofluorescence analysis of VE-cadherin in embryos at 32 hpf. Transplanted wild-type cells elongate and form multicellular tubes. Graph shows quantification of junctional coverage along the dorsal-ventral axis (ratio between the accumulated length of junctions to the length of the ISV) (analyzed WT donor segment n=20, host cell segment n=23). (C) Rescue by transient endothelial-specific rasip1 expression. Endothelial expression was achieved by DNA microinjection using a fli1a:Rasip1-p2a-tdTomato-CAAX construct or fli1a:tdTomato-CAAX as a control. Graph shows quantification of junctional coverage along the dorsal-ventral axis (analyzed ISVs in rasip1ubs28 mutant background n=17, rasip1 over-expression n=13). Scale bars: 20 μm. Analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Mann–Whitney test (***P<0.0001 in B, ***P<0.001 in C); error bars indicate s.d.
|