- Title
-
dlx3b/4b are required for the formation of the preplacodal region and otic placode through local modulation of BMP activity
- Authors
- Esterberg, R., and Fritz, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
BMP activity is transiently increased during early somitogenesis in Dlx3b/4b morphants. (A,B) bmp4 expression is unaffected in Dlx3b/4b morphants prior to the onset of dlx3b/4b expression in 70% epiboly embryos. (C,D) At bud stage, the domain of bmp4 expression is expanded in the prechordal plate and tailbud of Dlx3b/4b morphants (D). Insets depict the increase of the prechordal domain. (E,F) Antibodies against PSMAD1/5/8 (red) reveal an increase in cells responding to BMP activity of Dlx3b/4b morphants (F). DAPI-stained nuclei are blue. Inset in (F) is a high magnification image depicting PSMAD1/5/8 co-localization with DAPI-stained nuclei. (G,H) bmp4 expression in Dlx3b/4b morphants is comparable to controls at 18-somites. All views are lateral views, with ventral to the left in (A,B), anterior to the left in (C–F), and anterior to the bottom in (G,H). Insets in (C,D) are dorsal views, with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Depletion of Chd reveals anti-BMP function of Dlx3b/4b. (A–D) Intermediate cell mass of the tail is increased in Dlx3b/4b morphants (B), reminiscent of a ventralization phenotype. Injection of a low dose of chd-mo results in a mild V1 ventralization phenotype (C). Knockdown of Chd and Dlx3b/4b increases the severity of ventralization (D). (E–M) Heightened BMP activity in Chd/Dlx3b/4b triple morphant embryos severely reduces otic expression of eya1 (E–G), pax2a (H–J), and tbx2b (K–M), while leaving expression in surrounding tissue intact. (A–D) are lateral views and (E–M) are dorsal views, with anterior to the left. All embryos are 24 hpf. |
|
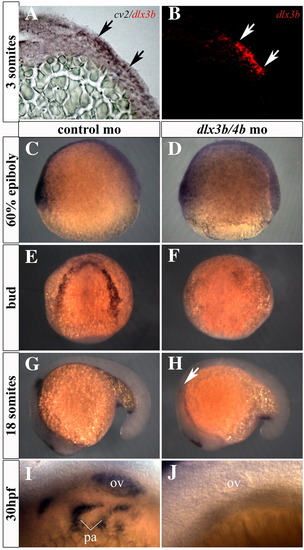
cv2 expression is lost from the PPR, otic placode, and pharyngeal arches in Dlx3b/4b morphants. (A,B) cv2 (purple) is co-expressed with dlx3b (red) in the ectoderm of the PPR. Transverse sections were taken through the neural plate of 3-somite embryos. (C,D) Prior to the onset of dlx3b/4b expression, cv2 expression is unaffected on the ventral side of 60% epiboly embryos. (E,F) cv2 expression is lost from the PPR in Dlx3b/4b morphants (F). (G,H) cv2 expression is lost from the otic placode in 18 somite Dlx3b/4b morphants (H). (I,J) cv2 expression is lost from the otic vesicle and pharyngeal arches in 30 hpf (hours post fertilization) embryos (J). ov, otic vesicle; pa, pharyngeal arches. All views are lateral except (E,F), which are dorsal views. |
|
dlx3b overexpression dorsalizes the zebrafish embryo. (A–D) Embryos ectopically expressing dlx3b mRNA display molecular read-outs consistent with reduced BMP activity. (A,B) bmp4 expression is reduced from the prechordal plate and tailbud of embryos ectopically expressing dlx3b (B). (C,D) Antibodies against PSMAD1/5/8 (red) reveal that BMP activity is reduced in embryos ectopically expressing dlx3b mRNA (D). (E,F) Riboprobes against krox20 and pax2a reveal a widening of the hindbrain in embryos ectopically expressing dlx3b mRNA (F). (G,H) Ectopic dlx3b DNA (red) can induce ectopic cv2 expression (purple). (I–N) Ectopic expression of dlx3b mRNA resembles the dorsalization seen in embryos ectopically expressing cv2. Knockdown of Cv2 can rescue the dorsalization seen in 81% (170/211) of embryos ectopically expressing dlx3b mRNA (L). (I–N) 30 hpf embryos; lateral views, with anterior to the left. Embryos were grouped into dorsalization categories based on previous classifications ([Kishimoto et al., 1997] and [Mullins et al., 1996]). (A–F) Bud stage embryos. Lateral views, with anterior to the left. (G,H) 80% epiboly embryos; lateral views, with ventral to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
dlx3b/4b and cv2 are required for PPR marker expression. (A–J) eya1 (A–E) and six4.1 (F–J) expression are reduced in the PPR of Dlx3b/4b (B,G) and Cv2 (C,H) morphants, but can be rescued when Bmp4 is knocked down (D,I) or when cv2 mRNA is ectopically expressed (E,J). (K,L) Ectopic dlx3b or cv2 (red) can induce ectopic eya1 (purple). (M) All cells ectopically expressing the uncleavable form of Cv2, cv2-CM (red), ectopically express eya1 (purple). (A–J) Bud stage embryos; dorsal views, with anterior to the top. (K–M) 80% epiboly embryos; lateral views, with ventral to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
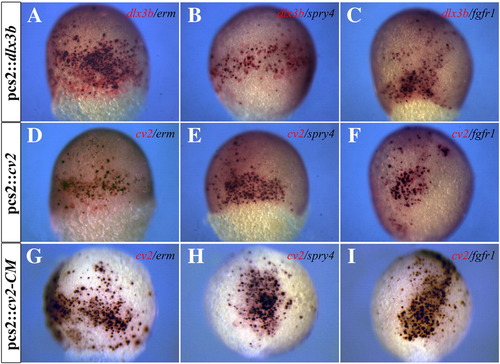
Ectopic dlx3b or cv2 expression can induce ectopic FGF activity. (A–C) Ectopic dlx3b expression (red) can induce ectopic expression of erm, spry4, and fgfr1 (purple). (D–F) Ectopic cv2 expression (red) can induce ectopic expression of erm, spry4, and fgfr1 (purple). (G–I) All cells ectopically expressing the uncleavable form of Cv2, cv2-CM (red), ectopically express erm, spry4, and fgfr1 (purple). (A–I) 80% epiboly embryos; lateral views. |
|
fgfr expression is lost from the otic placode and hindbrain of Dlx3b/4b morphants. erm and fgfr1-3 expression are lost from the otic placode and hindbrain of Dlx3b/4b morphants (B,E,H,K). Brackets in (B,K) depict reduction of erm (B) and fgfr3 (K) staining in the hindbrain. Arrows in (E,H) depict loss of fgfr1 staining (E) from the otic placode and loss of fgfr2 staining (H) from the hindbrain of Dlx3b/4b morphants. erm and fgfr1-3 expression can be restored to the otic placode and hindbrain when cv2 mRNA is ectopically expressed in Dlx3b/4b morphants (C,F,I,L). (A–P) 6 somite embryos; dorsal view with anterior to the top. MHB, midbrain–hindbrain boundary; r1, rhombomere 1; r2, rhombomere 2; r3, rhombomere 3; r4, rhombomere 4; r6, rhombomere 6; op, otic placode. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
pax2a expression in the otic placode requires Cv2. (A–E) pax2a expression is lost from the otic placode of Dlx3b/4b (B) and in 69% (27/39) of Cv2 (C,D) morphants. pax2a expression can be restored to the otic placode when cv2 mRNA is ectopically expressed in Dlx3b/4b morphants (E). (A–E) 6-somite embryos; dorsal view, with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Manipulation of PPR-inducing signals can rescue the otic phenotype of Dlx3b/4b morphants. (B) Dlx3b/4b morphants display a small, circular otic vesicle that lacks otoliths. (C,D) The otic phenotype of Cv2 morphants resembles that of Dlx3b/4b morphants (B), and is not significantly affected by the additional loss of Dlx3b/4b (D). (E,F) Ectopic expression of cv2 mRNA can rescue the Dlx3b/4b otic phenotype (F). (G–L) While heat shock of tBR embryos (G), knockdown of Bmp4 (I), or ectopic fgfr1 expression (K) does not affect ear morphology, each is able to partially rescue the otic phenotype of Dlx3b/4b morphants (H,J,L). All embryos are 30 hpf; lateral views, with anterior to the left. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
chd expression is reduced in Dlx3b/4b morphants, but can be rescued when cv2 is ectopically expressed. (A,B,E,F,I,J) chd expression is reduced in Dlx3b/4b morphants (B,F,J). At bud stage, chd expression is reduced in the anterior neural plate (B). At 6 somites, chd expression is reduced in the paraxial mesoderm (F) as well as rhombomeres 3 and 5 (J). (C,G,K) chd expression can be rescued when cv2 is ectopically expressed in Dlx3b/4b morphants. (D,H,L) Expression of the dominant negative form of cv2, cv2-N, causes a reduction of chd expression similar to Dlx3b/4b morphants. (A–D) Bud stage embryos. Dorsal views, with anterior to the top. (E–L) 6 somite stage embryos. (E–H) Caudal views, with dorsal to the top. (I–L) Lateral views, with anterior to the left. |
|
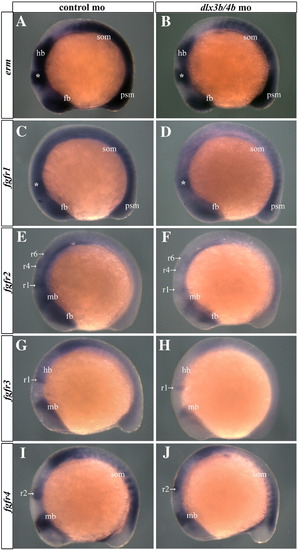
FGF activity is not compromised in Dlx3b/4b morphant embryos prior to the onset of somitogenesis. Bud stage embryos stained with riboprobes against erm, fgfr1, fgfr2, fgfr3, or fgfr4 show that expression is unchanged in Dlx3b/4b morphant embryos (B,D,F,H,J) when compared to controls (A,C,E,G,I). The arrow represents the otic placode. The arrowhead represents the notochord. The asterisk marks a region bordering the neural plate anterior to the otic placode. MHB, midbrain–hindbrain boundary; hb, hindbrain; r2, rhombomere 2; psm, presomitic mesoderm. (A–J) Bud stage embryos; dorsal views with anterior to the top. |
|
The reduction of FGF activity in Dlx3b/4b morphant embryos is transient, and begins to return to control levels by mid-somitogenesis. 12-somite embryos stained with riboprobes against erm, fgfr1, fgfr2, fgfr3, or fgfr4 show that expression is reduced in Dlx3b/4b morphant embryos (B,D,F,H,J) when compared to wild-type embryos (A,C,E,G,I). The asterisk marks the MHB. fb, forebrain; mb, midbrain; hb, hindbrain; r1, rhombomere 1; r2, rhombomere 2; r4, rhombomere 4; r6, rhombomere 6; som, somites; psm, presomitic mesoderm. (A–J) 12-somite embryos; lateral views with anterior to the left. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 325(1), Esterberg, R., and Fritz, A., dlx3b/4b are required for the formation of the preplacodal region and otic placode through local modulation of BMP activity, 189-199, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.