- Title
-
Nexmifa Regulates Axon Morphogenesis in Motor Neurons in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Zheng, Y.Q., Suo, G.H., Liu, D., Li, H.Y., Wu, Y.J., Ni, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Mol. Neurosci.
|
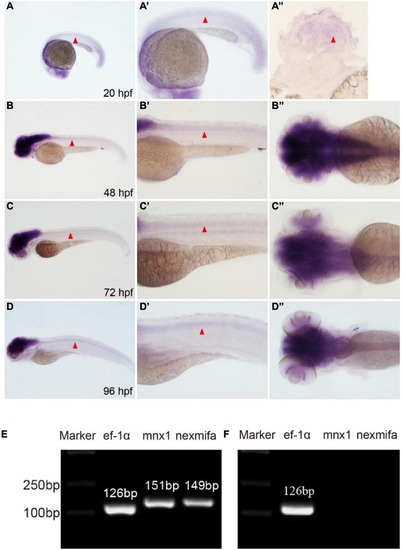
Nexmifa expression analysis in spinal cord and motor neurons. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
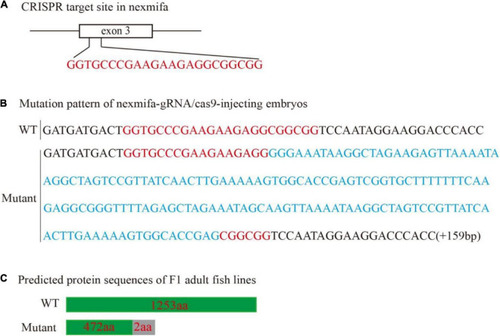
Generation of the zebrafish nexmifa mutant using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. |
|
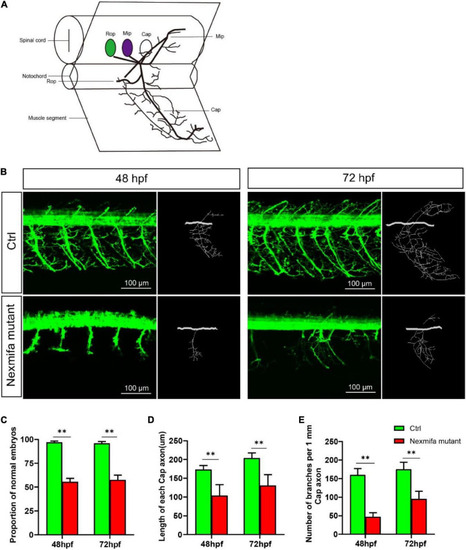
Nexmifa affects motor neuron morphogenesis in nexmifa mutant zebrafish embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
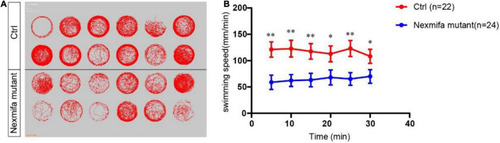
Motor defects in nexmifa mutant zebrafish embryos at 7 dpf. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
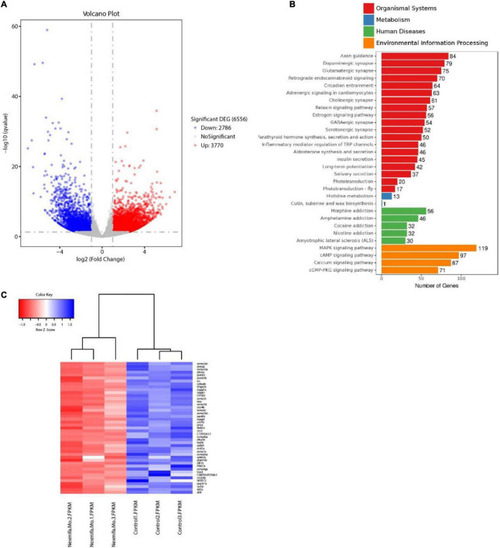
Transcriptomics profiling in nexmifa morphant and wild-type zebrafish. |
|
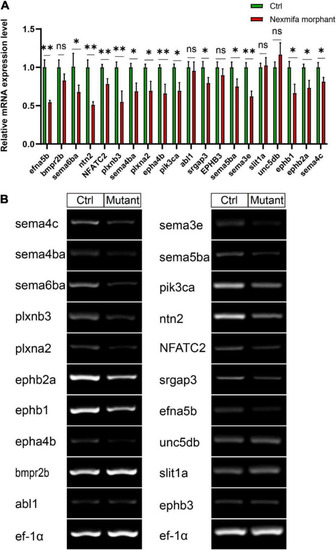
The expression of 20 down-regulated DEGs. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
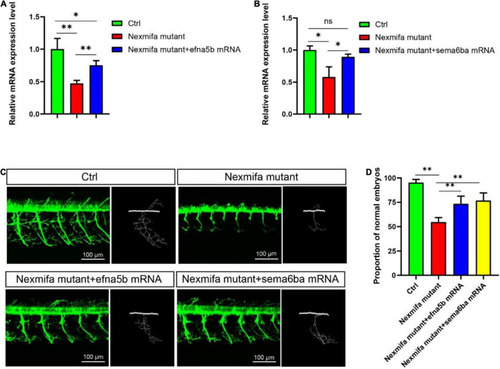
Efna5b and sema6ba overexpression rescues motor neuron defects in nexmifa morphant embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
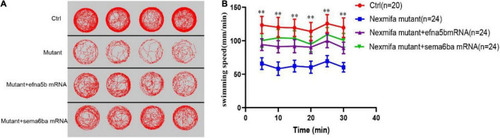
Efna5b and sema6ba overexpression rescues the impaired motility in nexmifa mutant embryos at 7 dpf. PHENOTYPE:
|