- Title
-
brca2 in zebrafish ovarian development, spermatogenesis, and tumorigenesis
- Authors
- Shive, H.R., West, R.R., Embree, L.J., Azuma, M., Sood, R., Liu, P., and Hickstein, D.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
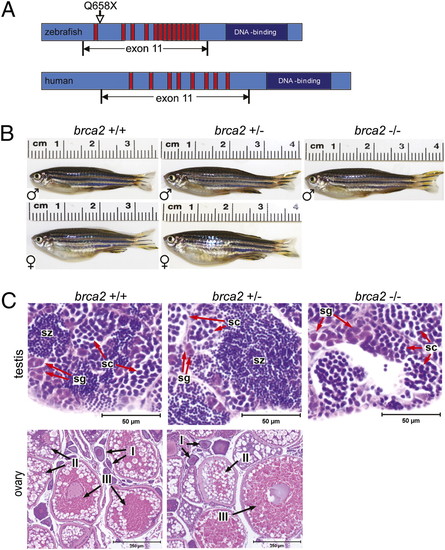
Zebrafish brca2 structure and zebrafish brca2Q658X mutation. (A) Schematic of zebrafish brca2 (Upper) compared with human BRCA2 (Lower). The zebrafish brca2 gene [National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) sequence NC_007126.4] has 16,583 base pairs with 27 exons and encodes a 2874-aa protein (NCBI sequence NP_001103864). Conserved domains include the Rad51-binding BRC repeats (red bars) and the DNA-binding domain (dark-blue box). The zebrafish brca2Q658X mutation (C1971T;Q658X) described herein is shown relative to its position within exon 11. (B) WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes exhibit distinctly male or female phenotypes, whereas brca2Q658X homozygotes are phenotypically male. (C) Gonads from zebrafish of each genotype reflect observed male or female phenotypes in B. Spermatogenesis is complete in testes from WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes. Testes from brca2Q658X homozygotes contain only spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes. Ovaries from WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes are similar and contain developing and mature oocytes. sg, spermatagonia; sc, spermatocytes; sz, spermatozoa; I, stage I oocyte; II, stage II oocyte; III, stage III oocyte. (Scale bars: 50 μm for sections of testis; 250 μm for sections of ovaries.) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
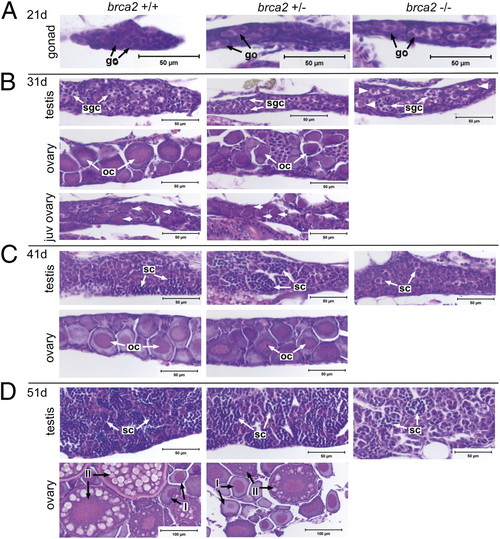
Failure of ovarian development occurs in brca2Q658X homozygotes during gonadal development. (A) Gonads from WT, brca2Q658X heterozygotes, and brca2Q658X homozygotes are indistinguishable at 21 dpf. (B) At 31 dpf, WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes exhibit juvenile ovaries, early testicular differentiation, or early ovarian differentiation, whereas brca2Q658X homozygotes exhibit only early testicular differentiation. Perinucleolar oocytes in juvenile ovaries are indicated by short arrows; putative premeiotic germ cells are indicated by arrowheads. (C and D) At 41 and 51 dpf, WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes exhibit continued maturation of testes or ovaries, whereas brca2Q658X homozygotes exhibit only testicular development. go, gonocyte; sgc, spermatogonial cyst; oc, oocyte; sc, spermatocyst; I, stage I oocyte; II, stage II oocyte. (Scale bars: 50 μm; 100 μm in 51 dpf ovaries.) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
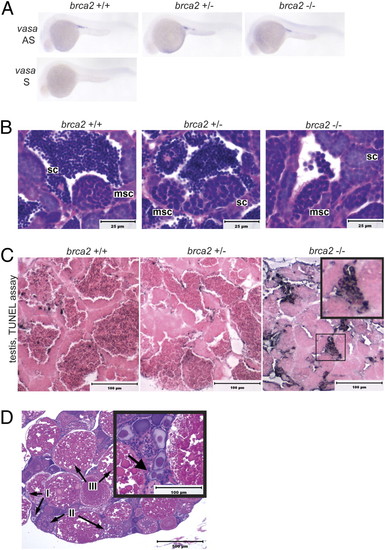
Germ cell specification, development, and survival in embryonic and adult brca2Q658X homozygotes. (A) WISH with antisense (AS) and sense (S) RNA probes for vasa indicates appropriate migration and colonization of the gonadal ridge in WT, brca2Q658X heterozygous, and brca2Q658X homozygous embryos. (B) Testes from WT, brca2Q658X heterozygotes, and brca2Q658X homozygotes show spermatocysts containing meiotic spermatocytes. (C) TUNEL staining of testes from WT, brca2Q658X heterozygotes, and brca2Q658X homozygotes. Multiple clusters of apoptotic spermatocytes are present in testes from brca2Q658X homozygotes (Inset). (D) Homozygous tp53M214K mutation rescues ovarian development in brca2Q658X homozygotes, but female brca2Q658X homozygous;tp53M214K homozygous zebrafish develop binucleate oocytes (Inset). sc, spermatocyst; msc, meiotic spermatocyst; I, type I oocyte; II, type II oocyte; III, type III oocyte. (Scale bars: 25 μm in B, 100 μm in C, and 500 μm in D.) |
|
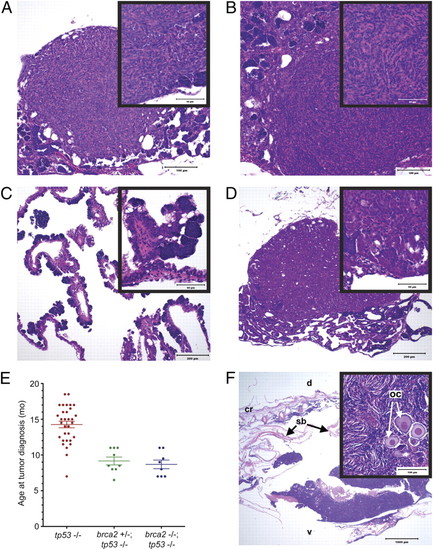
brca2Q658X homozygotes are predisposed to testicular neoplasias, and brca2Q658X and tp53M214K mutations have collaborative effects on tumorigenesis. (A) Undifferentiated stromal cell tumor from a brca2Q658X homozygote. (B) Undifferentiated stromal cell tumor from a brca2Q658X homozygote with irregular bundles around poorly defined small tubular structures (Inset). (C) Papillary cystadenoma from a brca2Q658X homozygote. (D) Seminoma from a brca2Q658X homozygote. (E) Age at tumor onset is significantly lower in both brca2Q658X homozygous;tp53M214K homozygous zebrafish and brca2Q658X heterozygous;tp53M214K homozygous zebrafish compared with the tp53M214K homozygous zebrafish parent line. (F) The ovary is a primary site for tumor development in brca2Q658X heterozygous;tp53M214K homozygous zebrafish, with oocyte entrapment (Inset). oc, oocyte; cr, cranial; d, dorsal; v, ventral; sb, swim bladder. (Scale bars: 100 μm in A and B; 200 μm in C and D; 1,000 μm in F; 50 μm in the Insets in A, B, C, and D; 100 μm in the Inset in F.) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
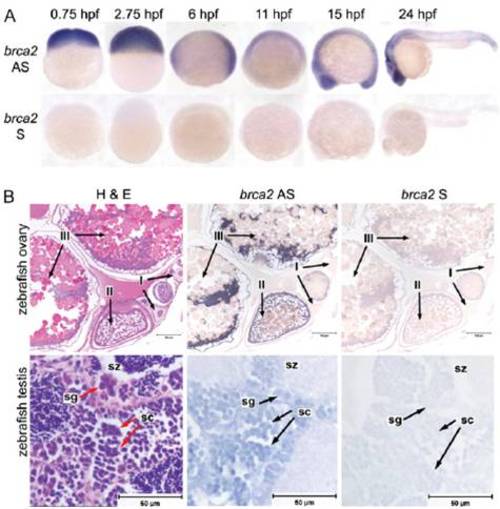
brca2 expression in WT embryonic and adult zebrafish. (A) WISH for brca2 expression in zebrafish embryos with antisense (AS; Upper) and sense (S; Lower) probes at the indicated stages demonstrates expression of brca2 throughout embryogenesis. (B) In situ hybridization for brca2 expression in sections of adult zebrafish ovary and testis with AS (Middle) and S probes (Right) indicates that brca2 is expressed in oocytes, spermatogonia, and spermatocytes (arrows). H&E-stained sections of ovary (Left, Upper) and testis (Left, Lower) are provided for anatomic reference. I, stage I oocyte; II, stage II oocyte; III, stage III oocyte; sg, spermatogonia; sc, spermatocytes; sz, spermatozoa. (Scale bars: 100 μm for ovary; 50 7mu;m for testis.) |
|
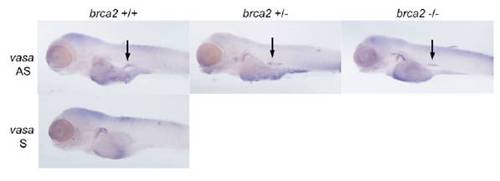
Germ cell specification and localization at 4 dpf. WISH for the germ cell marker vasa indicates similar numbers and localization of PGCs at 4 dpf in zebrafish embryos of each brca2 genotype. Arrows indicate vasa-expressing PGCs. AS, antisense RNA probe; S, sense RNA probe. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
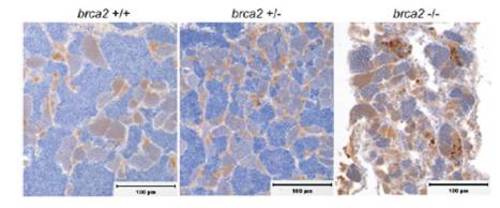
Immunohistochemistry for cleaved caspase-3 in testes from WT, brca2Q658X heterozygous, and brca2Q658X homozygous zebrafish. Multiple clusters of apoptotic spermatocytes are present in testes from brca2Q658X homozygotes, whereas few individual apoptotic cells are present in testes from WT and brca2Q658X heterozygotes. (Scale bars: 100 μm.) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
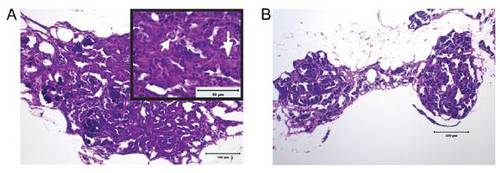
Hyperplastic, dysplastic, and degenerative changes in H&E-stained sections of testes from adult brca2Q658X homozygous zebrafish. (A) Testicular tubules are lined by numerous germ cells that form multicellular layers (Inset, long arrow). Multifocally, dysplastic germ cells with large nuclei, vacuolated chromatin, and prominent nucleoli are seen (Inset, short arrow). (B) Testes from brca2Q658X homozygotes show segmental degeneration, with loss of spermatocytes in testicular tubules. (Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 200 μm in B; 50 μm in the Inset in A.) PHENOTYPE:
|