Fig. S4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080604-11
- Publication
- Postel et al., 2008 - Zebrafish integrin-linked kinase is required in skeletal muscles for strengthening the integrin-ECM adhesion complex
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
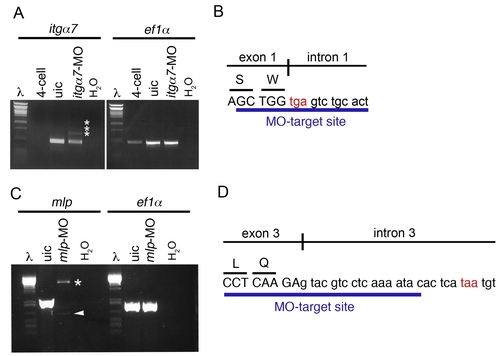
Controls for morpholino mediated knock-down of itgα7 and mlp. A,C) RTpcr on cDNA of itgα7-splice MO (A) or mlp-splice MO (B) injected embryos shows severe reduction of the amount of wt transcript compared to uninjected control embryos (uic). As a control for the amount of cDNA, RT-PCR for ef1α was performed. Larger transcript are observed in both the itgα7- splice MO and mlp- splice MO injected embryos (asterisk). Sequencing of these larger PCR product confirmed the defective splicing of both transcripts resulting in a introduction of a premature stop codon. The arrowhead indicates an nonspecific PCR product. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage Range: | 1-cell to Adult |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 318(1), Postel, R., Vakeel, P., Topczewski, J., Knöll, R., and Bakkers, J., Zebrafish integrin-linked kinase is required in skeletal muscles for strengthening the integrin-ECM adhesion complex, 92-101, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.