- Title
-
Macrophage transplantation rescues RNASET2-deficient leukodystrophy by replacing deficient microglia in a zebrafish model
- Authors
- Rutherford, H.A., Candeias, D., Duncan, C.J.A., Renshaw, S.A., Hamilton, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
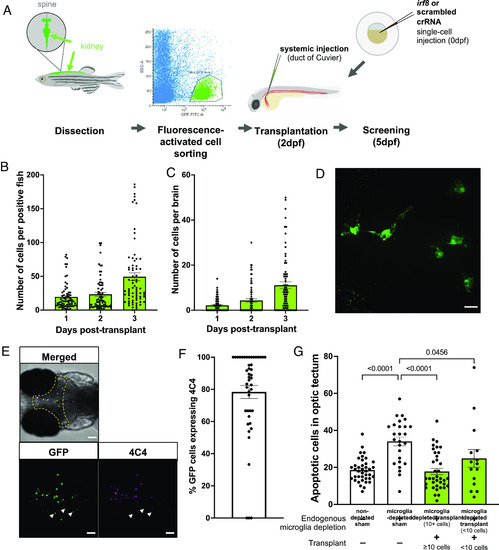
Macrophage transplantation successfully replaces microglia in WT zebrafish. ( |
|
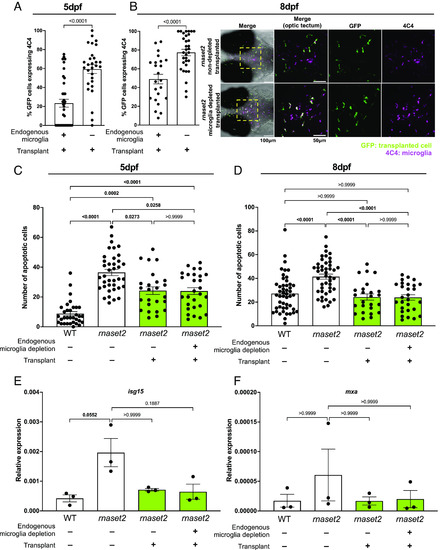
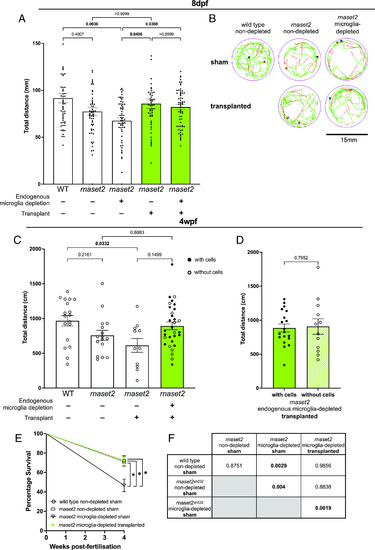
Macrophage transplantation reduces early neuropathology in |
|
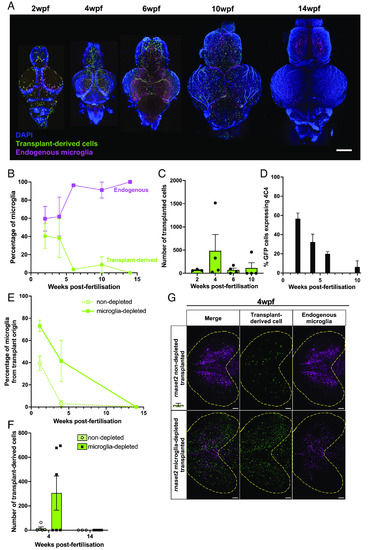
Transplanted cells persist in host brains throughout juvenile stages. ( |
|
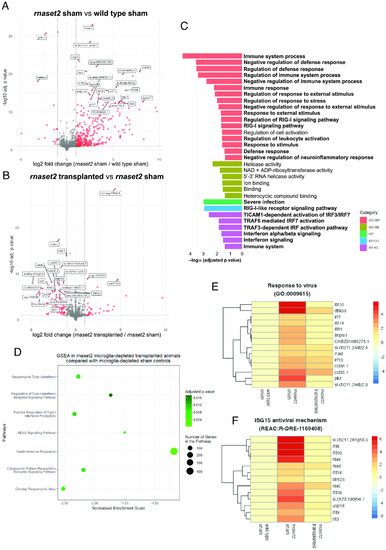
RNA sequencing reveals that microglia replacement rescues antiviral immune response in 4 wpf |
|
Transplantation rescues |