- Title
-
Primary cilia regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification through Notch signaling in zebrafish
- Authors
- Liu, Z., Tu, H., Kang, Y., Xue, Y., Ma, D., Zhao, C., Li, H., Wang, L., Liu, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
Ciliogenesis occurs in vascular endothelial cells (ECs) in AGM. |
|
Loss of cilia genes causes primary cilia defects in blood vessels in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region. |
|
Loss of cilia genes induces hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) defects. |
|
Blocking formation or function of primary cilia impairs hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) development. |
|
Cilia are required for hemogenic endothelium (HE) specification. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
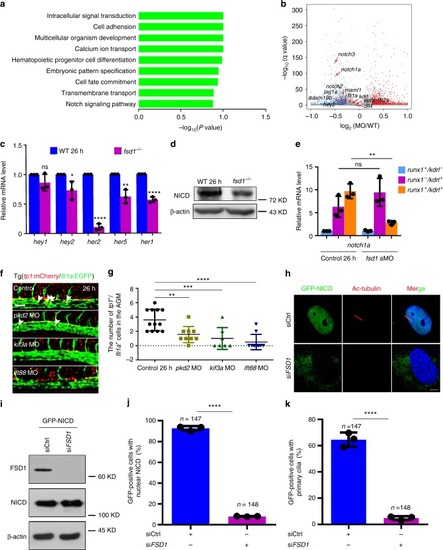
Notch signaling is downregulated in hemogenic endothelium (HE) cells in primary cilia-impaired embryos. |
|
Notch signaling acts downstream of primary cilia in regulating hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) specification. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|