- Title
-
Histone deacetylase 1 is essential for oligodendrocyte specification in the zebrafish CNS
- Authors
- Cunliffe, V.T., and Casaccia-Bonnefil, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Mech. Dev.
|
Histone deacetylase 1 is required for specification of oligodendrocytes in the zebrafish hindbrain and for expression of sox10 in neural progenitor cells of the ventral hindbrain. (A–D) dorsal views of hindbrains of wild-type (A,C) and hdac1 mutant (B,D) embryos, anterior is uppermost. (E,F) Transverse sections through hindbrain of (E) wild-type and (F) hdac1 mutant embryos at the level of rhombomere 5. A symmetrically distributed population of dispersed cells expressing the oligodendrocyte differentiation marker plp1b is present in the hindbrain of wild-type sibling embryos (A) but completely absent in hdac1 mutants (B), at 4.5 days post-fertilization (dpf). Likewise, sox10-positive neural progenitors are readily visible throughout the ventral medial part of the wild-type hindbrain (C,E) but absent in the hindbrain of hdac1 mutant embryos (D,F), at 50 hpf. |
|
Expression of olig2 in the ventral hindbrain is mediated by hedgehog signalling and strictly dependent on hdac1 function. (A–J) Expression of olig2 in hindbrain of (A,C,E,G,I) wild-type sibling, (B) smoothened (smoh) mutant and (D,F,H,J) hdac1 mutant embryos at (A,B) 32 hpf, (C,D,E,F) 28 hpf and (G,H,I,J) 50 hpf. Panels A–D and G,H show transverse sections through the hindbrain of embryos at the level of rhombomere 5, panels E,F,I,J show dorsal views of (E,I) wild-type and (F,J) hdac1 mutant hindbrain, demonstrating that early expression of olig2 in r5/r6 and later expression throughout the ventral medial hindbrain is strictly hdac1-dependent. |
|
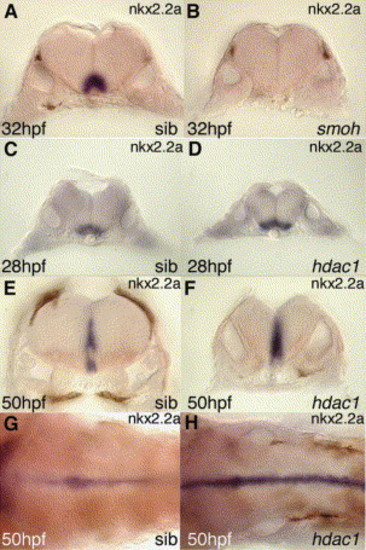
Expression of nkx2.2a in the ventral hindbrain is smoothened-dependent but up-regulated in hdac1 mutant embryos. (A–H) Expression of nkx2.2a in hindbrain of (A,C,E,G) wild-type sibling, (B) smoothened (smoh) mutant and (D,F,H) hdac1 mutant embryos at (A,B) 32 hpf, (C,D) 28 hpf, (E,F,G,H) 50 hpf. Panels A–F show transverse sections through the hindbrain of embryos at the level of rhombomere 5 and panels G,H show dorsal views of (G) wild-type and (H) hdac1 mutant hindbrain, demonstrating that expression of nkx2.2a in the ventral medial hindbrain is stably increased by loss of hdac1 function. |
|
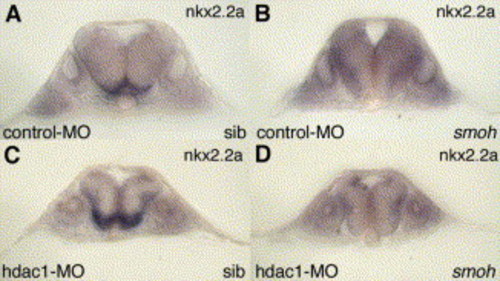
The up-regulation of nkx2.2a expression in the ventral hindbrain that is caused by loss of hdac1 function is strictly smoothened-dependent. Expression of nkx2.2a at 25 hpf in hindbrain of (A) wild-type sibling embryo microinjected with an hdac1 control-MO, (B) homozygous smoothened mutant embryo microinjected with hdac1 control-MO, (C) wild-type sibling embryo microinjected with an hdac1-specific MO and (D) homozygous smoothened mutant embryo microinjected with an hdac1-specific MO. Panels show transverse sections through the hindbrain of 25 hpf embryos at the level of rhombomere 5. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
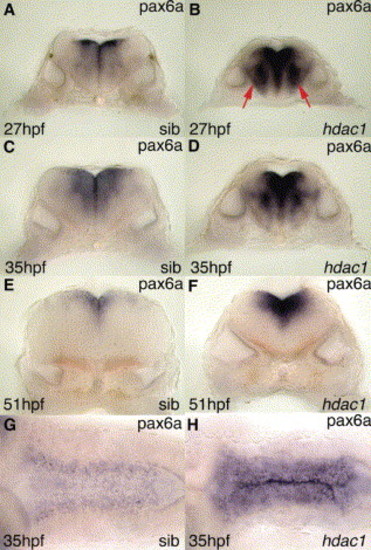
Expression of pax6a is up-regulated in the hindbrain of hdac1 mutant embryos. (A–H) Expression of pax6a in hindbrain of (A,C,E,G) wild-type sibling, (B,D,F,H) hdac1 mutant embryos at (A,B) 27 hpf, (C,D,G,H) 35 hpf and (E,F) 51 hpf. Panels A–F show transverse sections through the hindbrain of embryos at the level of rhombomere 5; panels G,H show dorsal views of (G) wild-type and (H) hdac1 mutant hindbrain, demonstrating that expression of pax6a is up-regulated throughout the length of the hindbrain as a consequence of the hdac1 mutation. Particularly strong ectopic expression of pax6a can be seen in dorso-medial and ventro-lateral (arrows in B) territories of rhombomere 5 in the hdac1 mutant hindbrain. |
|
Defective down-regulation of sox2 expression in the developing hdac1 mutant CNS. Transverse sections through rhombomere 5 in the hindbrain showing that sox2 expression is restricted to the ventricular zone in wild-type embryos at (A) 28 hpf, (C) 39 hpf, (E) 50 hpf. In hdac1 mutants, expression of sox2 encompasses both the ventricular zone and ventro-lateral (arrows) hindbrain territories at 28 hpf (B). At 39 hpf (D) the sox2 expression domain is thickened in the hdac1 mutant hindbrain and the size of the sox2-negative ventro-lateral domain is much reduced. At 50 hpf, sox2 expression remains strong in the dorsal ventricular zone of the hdac1 mutant hindbrain (F), and there is a persistent major deficit of sox2-negative cells ventrally. |
|
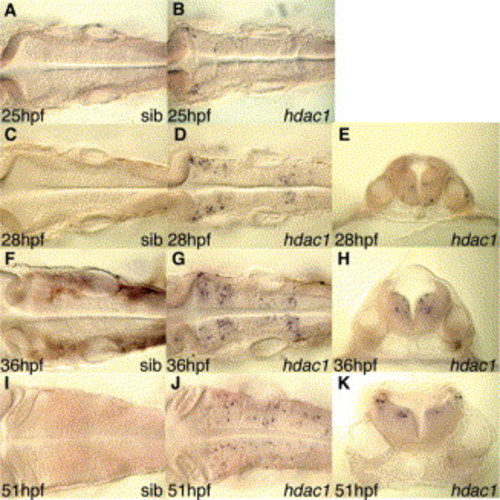
Hindbrain neural progenitors of hdac1 mutant embryos exhibit a dynamic pattern of apoptosis. TUNEL analysis of apoptosis in (A,C,F,I) wild-type sibling and (B,D,E,G,H,J,K) hdac1 mutant embryos at (A,B) 25 hpf, (C–E) 28 hpf, (F–H) 36 hpf, (I–K) 51 hpf. Views are dorsal except for panels E,H,K, which show transverse sections at the level of rhombomere 5 through the hindbrain specimen shown in D,G,J, respectively. |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 123(1), Cunliffe, V.T., and Casaccia-Bonnefil, P., Histone deacetylase 1 is essential for oligodendrocyte specification in the zebrafish CNS, 24-30, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.