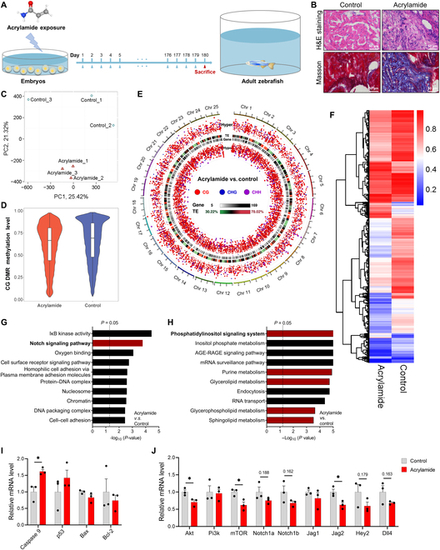
Chronic exposure to acrylamide induces HF in adult zebrafish. (A) Experimental design: embryos at 2 hpf exposed to 0.25 mM acrylamide for 180 d. (B) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson staining of adult zebrafish heart sections in control and acrylamide treatment (0.25 mM) groups. (C) The control and acrylamide-treated groups were completely distinguished by different colors in principal components analysis (PCA) plots based on WGBS analysis. (D) The global methylation level between the control and acrylamide-treated groups based on WGBS analysis. (E) Global methylation patterns in zebrafish hearts exposed to 0.25 mM acrylamide. (F) Heatmap showing differentially methylated changes in heart tissue between control and acrylamide-treated zebrafish based on CG pattern. (G and H) GO and KEGG analyses of WGBS data. (I) Relative mRNA expression of cardiac-apoptosis-related genes in control and acrylamide-treated zebrafish (n = 3 per group). (J) Relative mRNA expression of cardiac NOTCH and PI3K/AKT-related genes in control and acrylamide-treated zebrafish (n = 3 per group). Data are presented as the means ± SEM. Significance was calculated using 2-tailed P values by unpaired Student’s t test; *P < 0.05.
|

