Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240716-25
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2024 - Habitual Daily Intake of Fried Foods Raises Transgenerational Inheritance Risk of Heart Failure Through NOTCH1-Triggered Apoptosis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
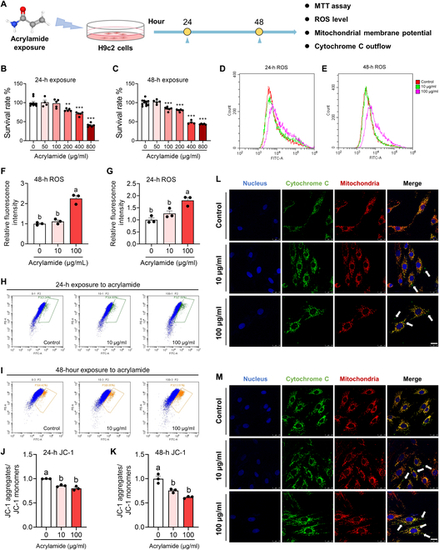
Acrylamide induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis with ROS accumulation, cytochrome C outflow, and dropped mitochondrial membrane potential in H9c2 cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell study. (B and C) Survival rates of H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively. The viability of cells was determined by the 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) assay. (D and E) Accumulation of ROS was observed at 24 and 48 h by 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) probe after acrylamide treatment. (F and G) Quantification of ROS accumulation in H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively (n = 3 per group). (H and I) Mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated at 24 and 48 h by JC-1 probe after acrylamide treatment. (J and K) Quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential in H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively (n = 3 per group). (L and M) Cytochrome C outflow was observed by colocalizing mitochondria (red) and cytochrome C (green) fluorescently, while cell nucleus was dyed by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) with acrylamide exposure for 24 and 48 h, respectively. The white arrows point out the occurrence of cytochrome C outflow. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. Significance was calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; groups labeled with different letters differed significantly (P < 0.05). FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate. |