Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240415-47
- Publication
- Fang et al., 2024 - Deficiency of the HGF/Met pathway leads to thyroid dysgenesis by impeding late thyroid expansion
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
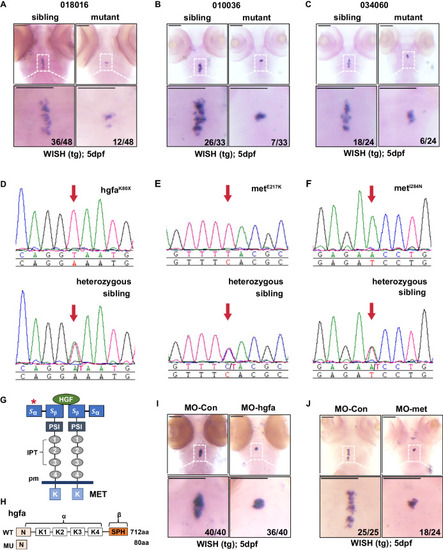
Identification of hgfa and met mutations from three zebrafish lines with abnormal thyroid morphology by whole-exome sequencing and positional cloning. |