FIGURE
Fig. 8
Fig. 8
|
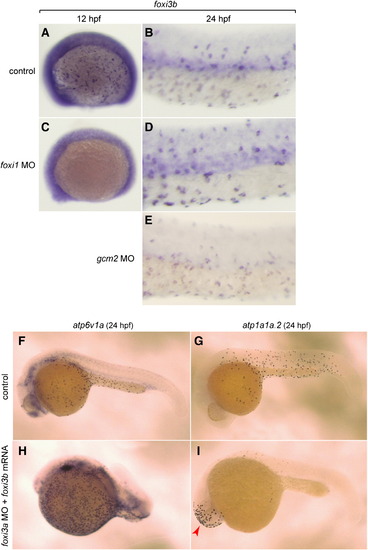
Complex interplay between the foxi1–foxi3a/gcm2 pathway and foxi3b. (A–E) Whole mount in situ hybridization, with a foxi3b probe, of control (A, B), foxi1 MO-injected (C, D), and gcm2 MO-injected (E) embryos. (F, H) Whole mount in situ hybridization, with an atp6v1a probe, of control embryo (F) and foxi3a morphant injected with foxi3b mRNA (H). (G, I) Whole mount in situ hybridization, with an atp1a1a.2 probe, of control embryo (G) and foxi3a morphant injected with foxi3b mRNA (L). foxi3b-induced formation of NaK-MRC was only observed ectopically in the head region (red arrow) in foxi3a morphants. |
Expression Data
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 329(1), Esaki, M., Hoshijima, K., Nakamura, N., Munakata, K., Tanaka, M., Ookata, K., Asakawa, K., Kawakami, K., Wang, W., Weinberg, E.S., and Hirose, S., Mechanism of development of ionocytes rich in vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase in the skin of zebrafish larvae, 116-129, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.