FIGURE
Fig. 1
Fig. 1
|
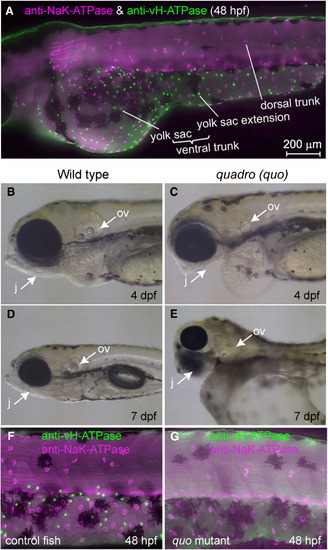
Distribution of two major types of MRC in the skin of zebrafish larvae and a mutant lacking one of them. (A) Double immunostaining of NaK-ATPase (magenta) and vH-ATPase (green) at 48 hpf, viewed from lateral side. (B–E) Phenotypes of quadro (quo) mutant. Defects are seen in otic and jaw development in quo mutant embryos (C, E). All panels show lateral views of live embryos with anterior to the left. j, jaw; ov, otic vesicle. (F, G) Double immunostaining with anti-vH-ATPase and anti-NaK-ATPase antibody at 48 hpf of wild-type control (F) and quo mutant (G). |
Expression Data
| Antibodies: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Days 7-13 |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 329(1), Esaki, M., Hoshijima, K., Nakamura, N., Munakata, K., Tanaka, M., Ookata, K., Asakawa, K., Kawakami, K., Wang, W., Weinberg, E.S., and Hirose, S., Mechanism of development of ionocytes rich in vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase in the skin of zebrafish larvae, 116-129, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.