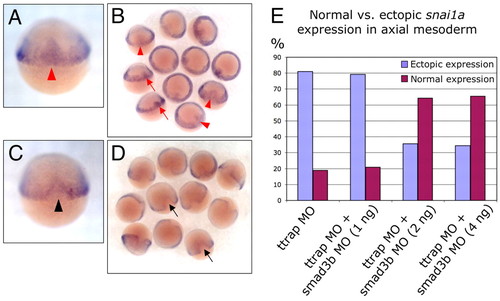
Knockdown of Ttrap induces ectopic snai1a in the shield and DFCs. (A-D) WISH for snai1a, 60% epiboly. (A,B) snai1a transcripts are found in the margin and paraxial mesoderm in TtrapMO embryos, but are also present ectopically in the presumptive axial mesodermal region within the shield (red arrowheads and arrows). (C,D) Rescued Ttrap and Smad3b MO double-knockdown embryos display normal snai1a domain, particularly, the exclusion of snai1a from the shield (black arrowhead and arrows). Dorsal views, anterior at top. (E) Derepression of snai1a in axial mesoderm of TtrapMO embryos is mediated by Smad3. Graph depicts partial rescue of TtrapMO-induced snai1a phenotype in Ttrap and Smad3 double knockdowns. y-axis represents percentage of embryos exhibiting either snai1a exclusion from axial mesoderm (purple bars) or ectopic expression in axial mesoderm (blue bars), at 60% epiboly. x-axis represents types of MO treatment. 81% of TtrapMO embryos display abnormal snai1a domain, whereas simultaneous knockdown of Ttrap and Smad3 reverts up to 58% of these embryos back to the wild-type domain (purple bars).
|

