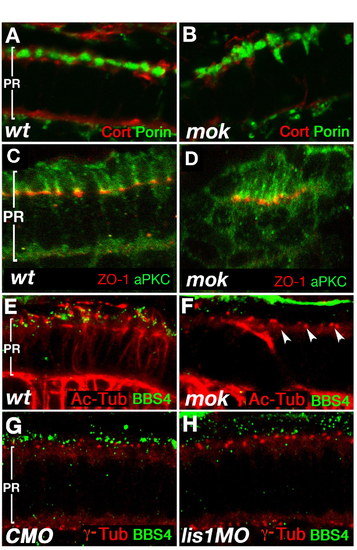
Photoreceptor Polarity and the Subcellular Distribution of the BBS4 Polypeptide. (A and B) Staining for a mitochondrial marker, Porin (green), and Actin-associated polypeptide Cortactin (red) at 3.25 dpf does not reveal obvious differences between wild-type (A) and mutant (B) cells. (C and D) Has/aPKC (green) and ZO-1 (red) polypeptides localize to narrow apical cell surface domains in the area of cell junctions, in wild-type cells (C) as well as in the clusters of elongated mutant photoreceptors (D). (E and F) Staining for BBS4 (green) and acetylated tubulin (red) in zebrafish photoreceptors at 3 dpf. In wild-type (E) but not mutant (F), BBS4 forms aggregates in the vicinity of connecting cilia (arrowheads). (G and H) Staining for BBS4 (green) and basal bodies (red) in zebrafish photoreceptors at 4 dpf. BBS4 staining is strongly reduced in lis1a morphants (H; compare with G). Cilia (E and F) and basal bodies (G and H) are visualized by using anti-acetylated tubulin and anti-g tubulin antibodies, respectively. In all panels, apical is up.
|

