Fig. 7
|
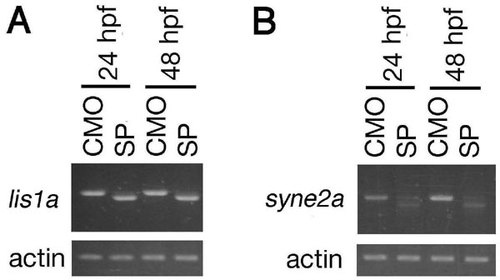
RT-PCR analysis of knockdown efficiency for splice-site targeted morpholinos. (A) A morpholino knockdown reduces the expression of the lis1a wild-type transcript to a nearly undetectable level at 24 and 48 hpf. Sequencing of the lis1a mRNA from SP morphants reveals a deletion of 29 bp followed by a frameshift. This defect eliminates the entire lis1a coding sequence with the exception of the first methionine. It is most likely caused by an activation of a cryptic donor splice site. (B) A knockdown reduces the expression of the syne2a wild-type transcript to a nearly undetectable level at 24 and 48 hpf. Sequencing of the shortened syne2a mRNA present at a low level in morphants reveals a deletion of 52 bp, followed by a frameshift. This lesion eliminates 184 C-terminal amino acids, including the KASH domain from the Syne2a sequence. The predicted truncated polypeptide lacks the transmembrane domain and most likely is not functional. CMO, control morpholino; SP, splice-site targeted morpholino. In all experiments, actin was used as a loading control (lower panels). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Long-pec |