- Title
-
TBC1D23 mediates Golgi-specific LKB1 signaling
- Authors
- Tu, Y., Yang, Q., Tang, M., Gao, L., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Liu, Z., Li, X., Mao, L., Jia, R.Z., Wang, Y., Tang, T.S., Xu, P., Liu, Y., Dai, L., Jia, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
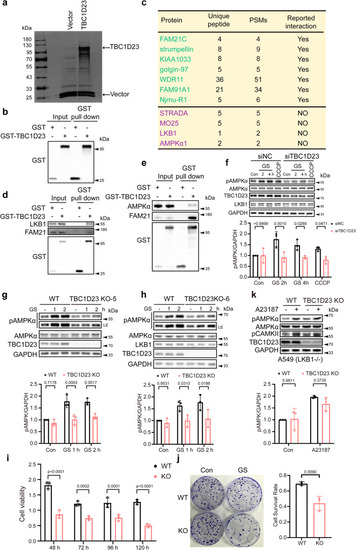
TBC1D23 is an interactor of LKB1 and is required for stress-induced AMPK activation. |
|
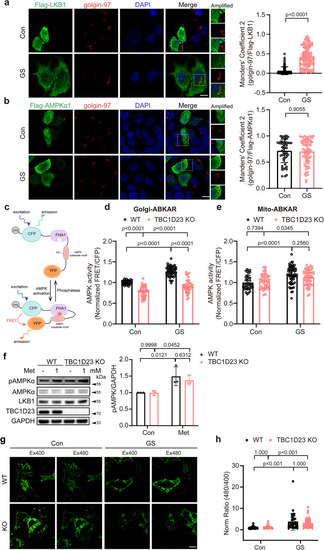
Deletion of TBC1D23 specifically impairs Golgi-AMPK activation. |
|
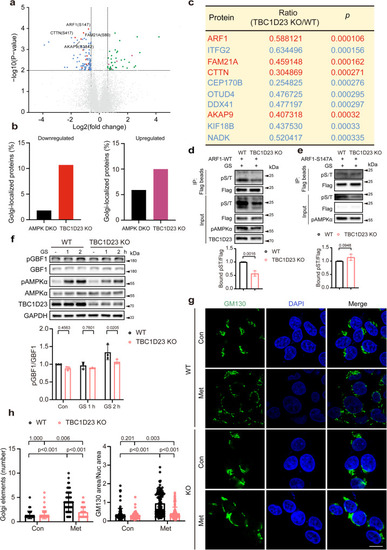
TBC1D23 preferentially regulates the phosphorylation of Golgi-localized proteins, and TBC1D23 loss prevents Golgi disassembly. |
|
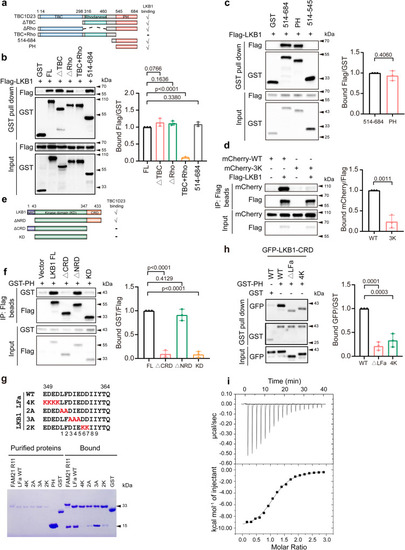
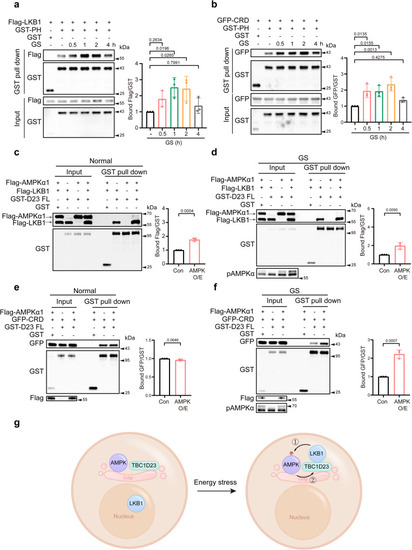
The PH domain of TBC1D23 directly interacts with LKB1 |
|
The interaction between TBC1D23 and LKB1 is dynamically regulated by AMPK activation. |
|
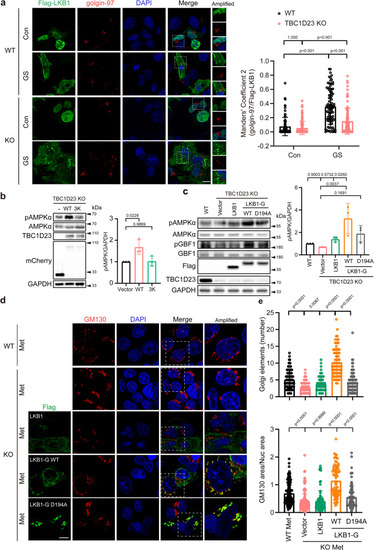
TBC1D23 and LKB1 cooperate to promote Golgi-AMPK activation. |
|
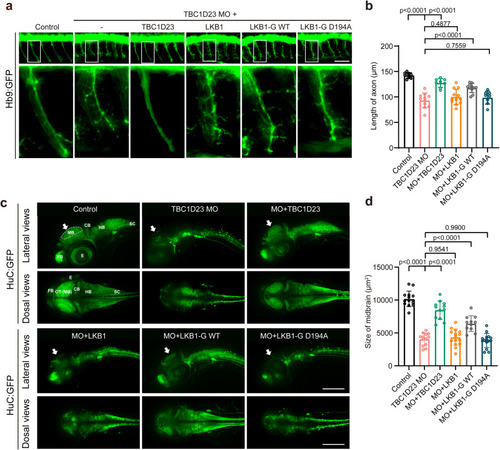
Golgi-targeted expression of LKB1 partially rescues TBC1D23 deficiency in zebrafish. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
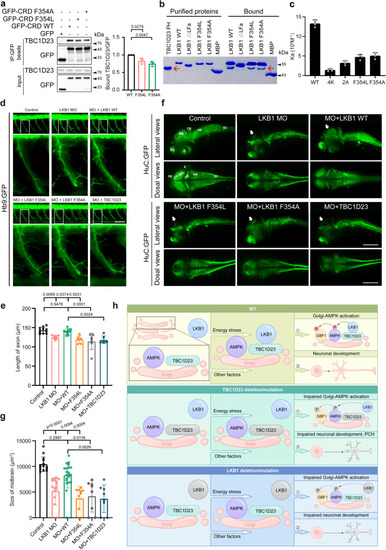
Interaction with TBC1D23 is required for LKB1 to promote neuronal development and brain growth. PHENOTYPE:
|