- Title
-
CRISPR/Cas9-based QF2 knock-in at the tyrosine hydroxylase (th) locus reveals novel th-expressing neuron populations in the zebrafish mid- and hindbrain
- Authors
- Altbürger, C., Holzhauser, J., Driever, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Neuroanat.
|
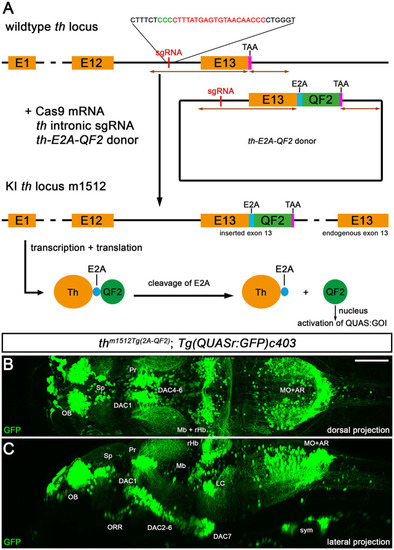
Knock-in of QF2 into the |
|
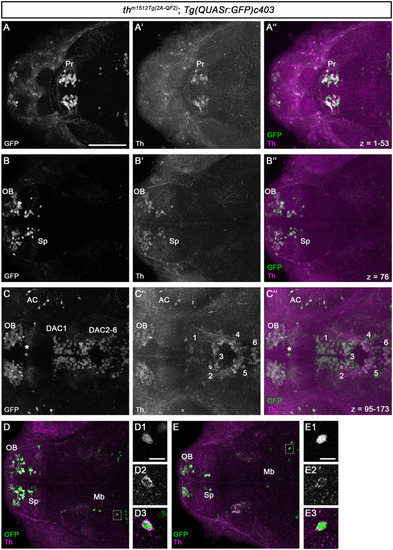
QF2-driven GFP expression highly coincides with endogenous Th. |
|
Midbrain and rHb GFP+ cells do not express other monoaminergic/catecholaminergic markers. |
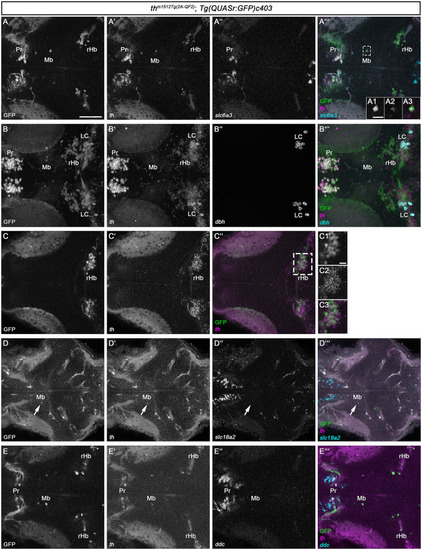
|
HCR RNA-FISH does not reveal coexpression of catecholaminergic markers except |
|
Th/ |