- Title
-
ClC-7 Regulates the Pattern and Early Development of Craniofacial Bone and Tooth
- Authors
- Zhang, Y., Ji, D., Li, L., Yang, S., Zhang, H., Duan, X.
- Source
- Full text @ Theranostics
|
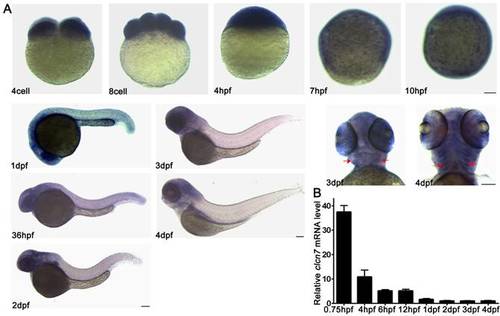
Spatial and temporal expression patterns of clcn7 during zebrafish early development. (A) WISH results. clcn7 was detected during cleavage stage (4 cell, 8 cell) in whole cells at blastula stage (4 hpf), especially in the enveloping layer at gastrula and bud stages (7 hpf, 10 hpf) in the head of embryos from 1dpf to 4dpf. Strong signaling appeared in pharyngeal arches from the ventral portion (3 dpf, 4 dpf). (B) Q-PCR results of clcn7. The red arrow indicates pharyngeal arches. dpf: days post-fertilization. hpf: hours post-fertilization. Error bars represent standard deviation. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
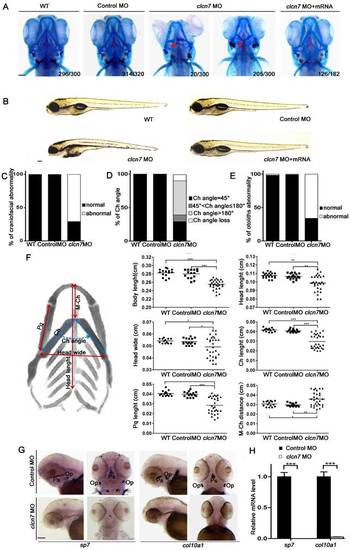
Craniofacial bone and cartilage abnormalities in clcn7 morphants. (A) Craniofacial phenotype comparison between control and clcn7 morphants. Cranial cartilages (blue) and mineralized bones (red) were stained with alcian blue and alizarin red in control and clcn7 morphants at 5 dpf, respectively. (A-C) Compared to WT and Control embryos, clcn7 morphants showed more malformed craniofacial skeletons, and clcn7 mRNA rescued the abnormalities in craniofacial region. (D, E) Abnormal ceratohyal (Ch) angle and altered location of otolith in clcn7 morphants. (F)Quantitative analysis of a series of changes of phenotypic indexes. clcn7 morphants showed obvious changes in the pattern of craniofacial structure. (G) WISH analysis showed the abolished expression of sp7 and col10a1 in cranial skeleton, most notably in the parasphenoid (Ps) and opercle (Op) bones in clcn7 morphants at 3 dpf. (H) Q-PCR analysis confirmed the reduced level of sp7 and col10a1. For A-E, WT n=300, Control MO n=320, clcn7 MO n=300, clcn7 MO + mRNA n=182. For H: Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The red arrow indicates abnormal Ch angle, and the white arrow points to abnormal otolith. Ch: ceratohyal. M: Meckel's. Op: opercle. Pq: palatoquadrate. Ps: parasphenoid. WT: wide type. Error bar represents the SD. The experiment was repeated at least thrice with the same conditions. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
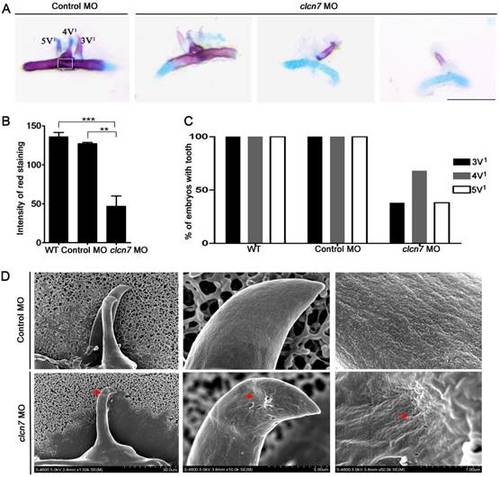
Defective tooth phenotypes in clcn7-deficient zebrafish. (A) Alcian blue and alizarin red staining results of 5thceratobranchial arch and teeth in control and clcn7 morphants at 5dpf. The malformed teeth were fewer with weak red staining clcn7 morphants. (B) Quantitative comparison of the extent of calcification among WT embryos, control and clcn7 morphants. (C) Comparison of embryonic tooth number. WT and control embryos had 3V1, 4V1 and 5V1 teeth, while clcn7 morphants showed 3V1, 4V1 and 5V1 fewer teeth. (D) Ultrastructure of tooth 4V1 in control and clcn7morphants. clcn7 morphants had malformed tooth and enameloid dysplasia. Red arrows point to the pits on the enameloid surface. For A, B, D: WT n=50, Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The white square in the first image of figure A is the region for measuring calcified content in panel B. Error bar represents the SD. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. The data in image C was one of the representative experimental results. WT n=300, Control MO n=320, clcn7 MO n=300. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
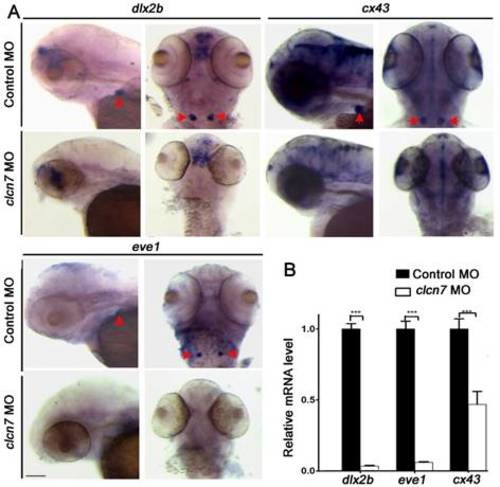
Molecular changes in the teeth of clcn7-deficient zebrafish. (A-B) WISH and Q-PCR analysis results. The fair expression of dlx2b, cx43, and eve1 in the teeth of clcn7 morphants at 3 dpf were diminished compared to that in control morphants. The data in image B was one of the representative experimental results. Error bar represents the SD. Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
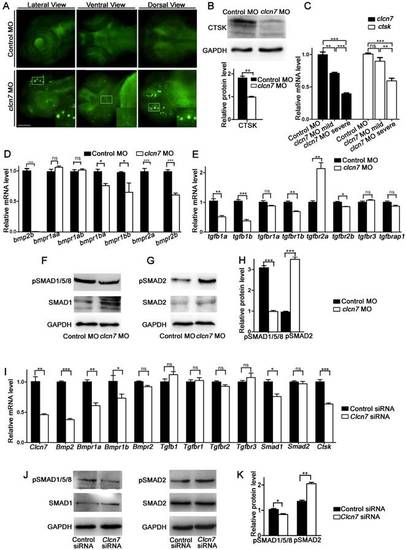
clcn7 deficiency led to lysosomal storage, reduced Cathepsin K expression and imbalanced TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway. (A) LysoTracker staining revealed lysosomal storage in the brain and jaw in clcn7 morphants at 3dpf compared to control morphants. The insets showed higher magnification of the white boxed areas in clcn7morphants. (B) Western blot and quantification analysis showed that CTSK protein was markedly decreased in clcn7morphants at 3dpf. (C) Comparison of clcn7 and ctsk level using Q-PCR detection. The mRNA level of clcn7 and ctskshowed a dose-dependent parallel downregulation with severe craniofacial changes. (D, E) Q-PCR analysis results. Transcript levels of bmp2b and bmpr1ba, bmpr1bb, bmpr2a, bmpr2b were decreased, the levels of tgfb1a, tgfb1bwere declined and that of tgfbr2a was increased in clcn7 morphants compared to controls at 3dpf. (F, G and H)Western blots results. The protein levels of pSMAD1/5/8 proteins were significantly reduced, while pSMAD2 levels were increased compared to control. (I) Q-PCR results of BMSCs. Compared to controls, the transcript levels of Bmp2 and Bmpr1a, Bmpr1b, Smad1 and Ctsk were decreased in Clcn7 siRNA group. (J, K) Western blot analysis showed that Clcn7 siRNA increased the protein levels of pSMAD2, while pSMAD1/5/8 levels were reduced compared to controls. For B-H: Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50, clcn7 MO mild n=50, clcn7 MO severe n=50. All data represent mean ±SD. The experiment was repeated at least thrice with the same conditions. ns: not significant difference. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
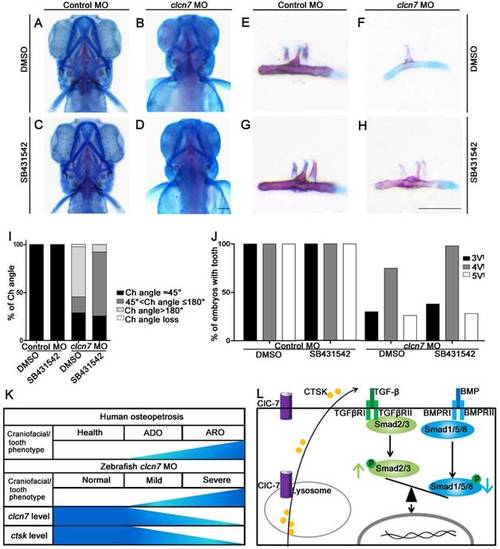
Inhibition of TGF-β signaling partially rescues craniofacial abnormalities in clcn7 deficient zebrafish. (A-D)Ventral views of 5dpf zebrafish with alcian blue and alizarin red staining. Control zebrafish treated with DMSO (A) or 10 μM SB431542 (C) showed no obvious changes of Ch angle. (B) clcn7 knockdown zebrafish treated with DMSO showed abnormal Ch angle, and 10 μM SB431542 partially rescued Ch angle, showing significant differences (D, I). (E-H) Comparison of embryonic tooth number among controls and clcn7 morphants treated with DMSO or 10 μM SB431542. (J) clcn7 morphants treated with 10 μM SB431542 showed the higher eruption rate of 4V1 tooth. (K)Schematic correlation between the amount of ClC-7 and craniofacial/tooth phenotypes in humans and zebrafish. ARO showed more and severe craniofacial/tooth phenotypes than ADO. The more severe the craniofacial phenotypes in clcn7 morphants, the lower level of clcn7 and ctsk, which further results in the imbalance between TGF-β and BMP signals, affecting the craniofacial and tooth development. (L) Schematic representation of ClC-7- and CTSK-mediated TGF-β/BMP pathway in zebrafish. clcn7 deficiency led to impaired lysosomal function and reduced CTSK expression. TGF-β-like Smad2 signals are elevated and BMP-like Smad1/5/8 signals are reduced in clcn7 knockdown zebrafish, which may contribute to the imbalance in TGF-β/BMP signaling during craniofacial and tooth development. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. The data in image J was one of the representative experimental results. For A-J: Control MO DMSO n=210, Control MO SB431542 n=198, clcn7 MO DMSO n=158, clcn7MO SB431542 n=134. Scale bars: 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|