- Title
-
Endodermal pouch-expressed dmrt2b is important for pharyngeal cartilage formation.
- Authors
- Li, L., Mao, A., Wang, P., Ning, G., Cao, Y., Wang, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Open
|
Expression of dmrt2b in the developing endodermal pouches. (A–D) Analysis of dmrt2b expression at different stages. (E,F) Endodermal cells were absent from sox32 morphants. Expression of endodermal marker sox17 (E), endodermal pouch marker nkx2.3 (E) and dmrt2b (F) were examined by in situ hybridizations at the indicated stages in wild-type embryos injected with 8 ng control MO (cMO) or sox32 MO. (G) Expression of dmrt2b in endodermal pouches. At 36 hpf, Tg(sox17:GFP) transgenic embryos were stained for dmrt2b mRNA with Dr-dmrt2b-C3 probe (red), and then immunostained with anti-GFP antibody (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The six endodermal pouches are labeled in the left two panels. EP, endodermal pouch; ov, otic vesicle. Scale bar: 50 µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Depletion of dmrt2b impairs cranial cartilage development. (A) Generation of dmrt2b mutant using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The dmrt2b mutant has a four base deletion that results in expression of a truncated protein lacking the DM domain. (B,C) Morphological defects in dmrt2b mutants at the indicated stages. (D) Anatomy of the pharyngeal arches and head skeleton in dmrt2b mutants. Red arrowheads indicate branchial arches. (E,F) Alcian Blue staining of head cartilages at 96 hpf. Cartilage defects in dmrt2b mutants and morphants were abrogated by injection of dmrt2b mRNA (F). (G) Anatomy of the pharyngeal arches and head skeleton in embryos injected with indicated shRNA expression plasmids. Red arrowheads indicate branchial arches. (H) Alcian Blue staining of head cartilages in shRNA expression plasmid injected embryos. Scale bar: 100 µm. ac, auditory capsule; not, notochord; pc, parachordal; abc, anterior basicranial commissure; ep, ethmoid plate; tc, trabeculae cranii; m, Meckel's cartilage; bh, basihyal; ch, ceratohyal; pq, palatoquadrate; hs, hyosymplectic; cb, ceratobranchial. Scale bars: 200 µm (B,C), 100 µm (D–H). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
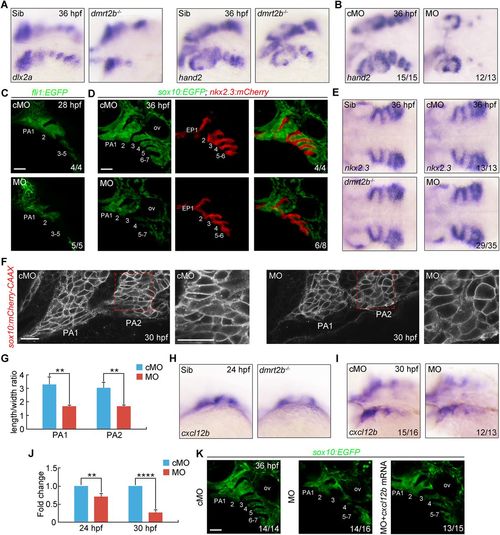
dmrt2b functions in CNC cell condensation. (A,B) Depletion of dmrt2b resulted in fewer CNC cells in the pharyngeal arches. dmrt2b mutants (A) and morphants (B) were harvested at 36 hpf for in situ hybridization with dlx2a and hand2 probes. Lateral views of embryos presented with anterior to the left. (C) Live confocal images of Tg(fli1:EGFP) transgenic embryos injected with 4 ng cMO or dmrt2b MO at 24 hpf. The pharyngeal arches are numbered. (D) Live confocal images of endodermal pouches and CNC cells in the pharyngeal regions of Tg(nkx2.3:mCherry; sox10:EGFP) transgenic embryos at 36 hpf. (E) The expression of endodermal pouch marker nkx2.3 in dmrt2b mutants and morphants. Dorsal views with anterior to the left. (F) Changes in cell shape in the leading edge of the first and second pharyngeal arches in Tg(sox10:mCherry-CAAX) embryos injected with 4 ng dmtr2b MO. The boxed areas are presented at a higher magnification in the right panels. (G) Quantitation of length/width ratio of CNC cells in the leading edge of the pharyngeal arches. All data are presented as the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars represent s.d. Significance was analyzed using unpaired t-tests. **, P<0.01. (H,I) The expression of cxcl12b in the developing pouches of dmrt2b mutants (H) and morphants (I) at the indicated stages. (J) The expression of cxcl12b in the head of dmrt2b morphants were examined by qRT-PCR at the indicated stages. All data are presented as the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars represent s.d. Significance was analyzed using unpaired t-tests. **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001. (K) Live confocal images of CNC cells in the pharyngeal regions of Tg(sox10:EGFP) transgenic embryos at 36 hpf. EP, endodermal pouch; ov, otic vesicle; PA, pharyngeal arch. Scale bars: 50 µm (C,D,K), 20 µm (F). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
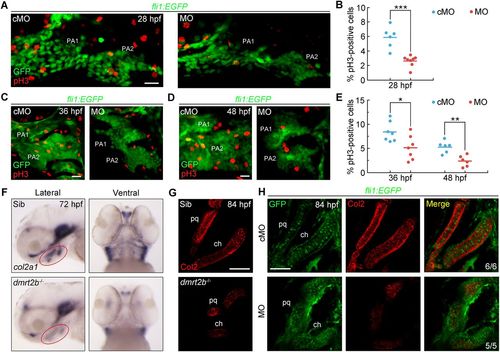
dmrt2b facilitates CNC cell proliferation and differentiation. (A,C,D) Representative confocal sections of pH3-positive cells in the first and second pharyngeal arches at the indicated stages. (B,E) Percentage of pH3-positive cells among GFP-positive CNC cells. n≥6 embryos for each condition. Significance was analyzed using unpaired t-tests. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (F) Expression levels of col2a1 mRNA at 72 hpf. Red circles indicate the pharyngeal region. The left panels are lateral views with anterior to the left and the right panels are ventral views with the anterior to the top. (G,H) Immunostaining of Col2 protein in pharyngeal cartilages at 84 hpf. dmrt2b mutants (G) and Tg(fli1:EGFP) embryos injected with 4 ng dmrt2b MO (H) were stained with the indicated fluorescent antibodies. PA, pharyngeal arch; pq, palatoquadrate; ch, ceratohyal. Scale bars: 20 µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
dmrt2b maintains BMP signaling in the pharyngeal region by inhibiting cv2 expression. (A) Expression of BRE-driven EGFP in the pharyngeal region of Tg(BRE:EGFP;sox10:mCherry-CAAX) transgenic embryos injected with 4 ng cMO or dmrt2b MO at 36 hpf. (B,C) p-Smad1/5/8 levels were decreased in the pharyngeal region of dmrt2b mutants (B) and morphants (C) at 36 hpf. Embryos were stained with the indicated antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (D,E) The expression of cv2 in dmrt2b morphants were examined by in situ hybridization (D) and qRT-PCR (E). All data are presented as the mean of three independent experiments. Error bars represent s.d. Significance was analyzed using unpaired t-tests. **P<0.01. (F) Co-injection of 100 pg cv2 MO with 4 ng dmrt2b MO partially rescued the EGFP expression in Tg(BRE:EGFP;sox10:mCherry-CAAX) transgenic embryos. (G) p-Smad1/5/8 levels were partially rescued in the pharyngeal region of dmrt2b mutants co-injected with 100 pg cv2 MO at 36 hpf. Embryos were stained with the indicated antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). ov, otic vesicle; p-S1/5/8, phosphorylated Smad1/5/8. Scale bars: 50 µm (A–C,F), 20 µm (G). |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |