- Title
-
Transcriptional regulation of a myeloid-lineage specific gene lysozyme C during zebrafish myelopoiesis
- Authors
- Kitaguchi, T., Kawakami, K., and Kawahara, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Mech. Dev.
|
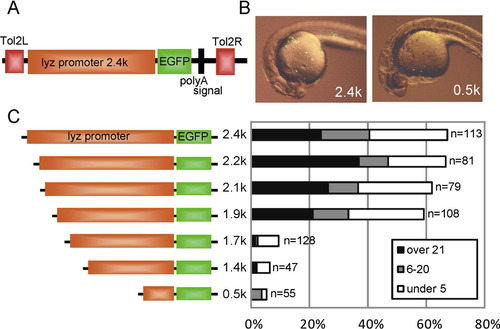
Promoter analysis of zebrafish lyz gene using Tol2 transient expression system. (A) Schematic map of pTol-lyzP (2.4 kb)-EGFP. Tol2L and Tol2R indicate minimal Tol2 transposable elements. (B) Transient EGFP expression at 24 hpf. Lateral view; anterior is left. The reporter construct (pTol-lyzP [2.4 kb]-EGFP or pTol-lyzP [0.5 kb]-EGFP; 25 pg each) was co-injected with synthetic Tol2 transposase mRNA (25 pg) into one- or two-cell stage embryos, and transient EGFP expression was examined by fluorescent microscopy. A large number of EGFP-positive cells were detected in the 2.4 kb lyz promoter construct-injected embryo, while a small number of EGFP-positive cells were detected in the 0.5 kb promoter construct-injected embryo. (C) Schematic map of the lyz promoter deletion constructs and the summary of EGFP transient expression assay. Indicated reporter constructs (25 pg) were co-injected with Tol2 RNA (25 pg) into one- or two-cell stage embryos and EGFP-positive cells were counted at 24–26 hpf. The embryos were classified by EGFP-positive cell number into three categories: over 21 positive cells (over 21), 6–20 positive cells (6–20), under five positive cells (under 5). The percentage of each category is shown in the bar graph. The number of injected embryo is indicated at the right side in the graph. |
|
Identification of the cis-elements important for myeloid-specific lyz expression. (A) Nucleotide sequence of lyz promoter region between -1.9 kb and -1.7 kb. The red boxes and blue box indicate C/ebp family (CCAAT enhancer) and Runx family putative binding sequences, respectively. The arrows show the start positions of each deletion constructs. (B) Summary of EGFP transient expression assay. The embryos are classified as explained in Fig. 1. (C) Schematic map of the lyz promoter constructs lacking putative binding sites for Runx family, C/ebp family or Ets/Pu.1 family and summary of EGFP transient expression assay. (D) DNA pull-down assay of EGFP-fused transcriptional factors by the biotinated 2.4 kb lyz promoter fragments. EGFP-fusion constructs were expressed in HEK293T cells (bottom panel). The biotinated lyz promoter or mutant promoter was incubated with cell lysates and subsequently incubated with streptavidin beads. EGFP-runx1 precipitated with the lyz 2.4 kb promoter (F), but not the runx site deletion promoter (ΔR; top left panel). EGFP-c/ebp1 strongly precipitated with the lyz promoter (F), while EGFP-c/ebp1 weakly precipitated with the mutant promoter lacking c/ebp1 site at -1.46 kb (ΔC; top middle panel). EGFP-pu.1, but not EGFP-IRF8 precipitated with the lyz 2.4 kb promoter (top right panel). |
|
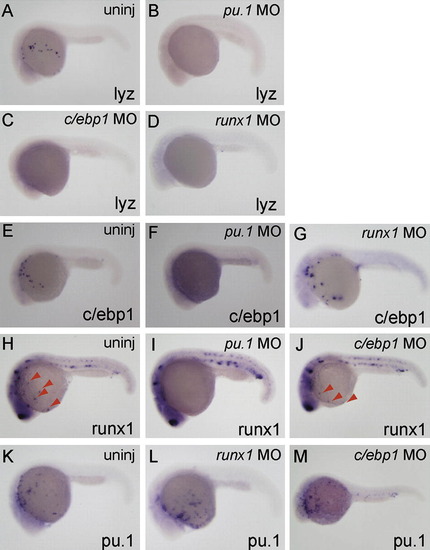
Differential requirement of myeloid-expressed transcription factor on the expression of c/ebp1, pu.1 and runx1. Whole-mount in situ hybridization with probes shown at bottom right of each panel. Injected morpholinos are indicated at top right. All embryos are around 24 hpf and lateral view; anterior is left. (A–D) lyz expression was inhibited in pu.1 MO-, runx1 MO- and c/ebp1 MO-injected embryos. (E–G) The expression of c/ebp1 in myeloid cells was suppressed in pu.1 morphants, but not in runx1 morphants. (H–J) The runx1 expression in myeloid cells (red arrowheads; H and J), but not in the ICM and Rohon-beard cells, was inhibited in pu.1 morphants, while injection of c/ebp1 MO did not affect runx1 expression. (K–M) pu.1 expression in myeloid cells was comparably detected in uninjected-, runx1 MO-injected and c/ebp1 MO-injected embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
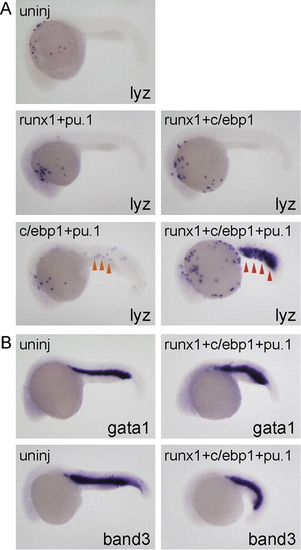
c/ebp1, pu.1 and runx1 coordinately regulate lyz expression. All embryos are around 24 hpf and lateral view; anterior is left. (A) Injection of mRNA mixture (runx1 [100 pg] + pu.1 [10 pg] or runx1 [100 pg] + c/ebp1 [100 pg]) did not affect lyz expression compared to uninjected embryos. lyz expression in the ICM (orange arrowhead) was weakly induced in the embryos injected with mRNA mixture (c/ebp1 [100 pg] + pu.1 [10 pg]). Injection of mRNA mixture (runx1 [100 pg] + c/ebp1 [100 pg] + pu.1 [10 pg]) strongly induced lyz expansion in the ICM (red arrowhead). (B) The expression of erythroid markers gata1 and band3 was comparable in both uninjected- and triple mRNA-injected embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Establishment of the lyz promoter-EGFP transgenic zebrafish, Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. All pictures show lateral view; anterior is left. (A, B and F–I) Fluorescent images. A stable transgenic fish line Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02 expressing EGFP driven by the 2.4 kb lyz promoter. (A and B) EGFP-positive cells in Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02 at 26 hpf (A) or 3 dpf (B). (C–E) Two-color in situ hybridization with probes of EGFP and lyz: EGFP expression stained by FITC (green) completely overlapped endogenous lyz expression stained by FastRed (red). (F–I) Effect of morpholinos (runx1 MO, pu.1 MO and c/ebp1 MO) and mRNAs (runx1 + pu.1 + c/ebp1) on EGFP expression in Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. Injected mRNAs or morpholinos are indicated at top right. The EGFP expression in Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02 was strongly suppressed in runx1 MO (0.5 ng)-injected, pu.1 MO (10 ng)-injected, or c/ebp1 MO (10 ng)-injected embryo compared to uninjected embryos (A). In contrast, the number of EGFP-positive cells increased in the embryos injected with mRNA (runx1 [100 pg] + c/ebp1 [100 pg] + pu.1 [10 pg]) in Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
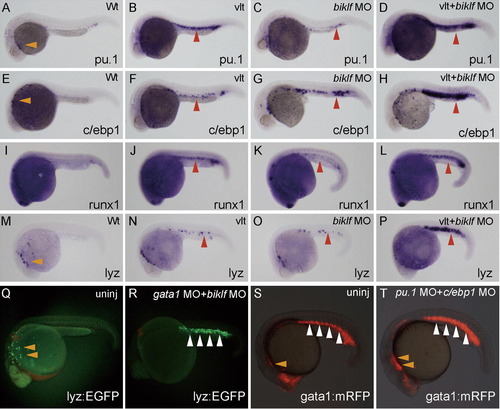
Suppression of erythroid-lineage factors biklf and gata1 strongly induces ectopic lyz expression in the ICM. (A–P) All embryos are around 24 hpf and lateral view; anterior is left. Morpholinos (biklf MO; 10 ng) were injected into one-cell stage embryos from wild-type or vlad tepes (vlt)/gata1 mutant, and the expression of myeloid markers was examined by whole-mount in situ hybridization; marker is shown at bottom right. Genome DNA was prepared from the stained embryos after taking pictures, and genotyping of vlt was performed. The myeloid markers, pu.1, c/ebp1, runx1 and lyz are expressed in myeloid cells over the yolk (orange arrowheads) (A, E and M). The expression of pu.1, c/ebp1, runx1 and lyz was weakly induced in the ICM (red arrowheads) in vlt embryos or biklf MO-injected embryos. When biklf MO was injected into vlt embryos, the markers (pu.1, c/ebp1, runx1 and lyz) were strongly induced in the ICM (red arrowheads). (Q and R) EGFP expression is detected in myeloid cells (orange arrowheads) in uninjected embryo from Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. EGFP expression at 23 hpf stage was significantly induced in the ICM (white arrowheads), when morpholinos (gata1 MO; 10 ng + biklf MO; 10 ng) were injected into one-cell stage embryos of Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. (S and T) mRFP expression in the ALPM (orange arrowheads) at 23 hpf stage was slightly increased, when morpholinos (pu.1 MO; 10 ng + c/ebp1 MO; 10 ng) were injected into one-cell stage embryos of Tg(gata1:mRFP)ko05. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
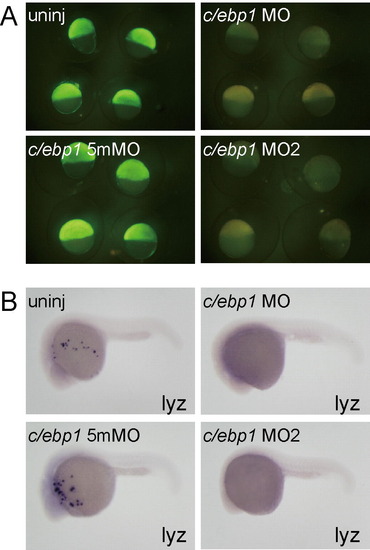
(A) Synthetic mRNA (250 pg) for C/ebp1-Nterminal-EGFP containing c/ebp1 MOs target sequences was injected into one blastomere of one- or two-cell stage embryos. Subsequently, morpholinos (c/ebp1 MO, 10 ng; c/ebp1 5mMO, 10 ng; c/ebp1 MO2, 2 ng) were injected into the yolk. The c/ebp1 5mMO is a 5 base mis-matched control morpholino for c/ebp1 MO. The expression of C/ebp1-Nterminal-EGFP at shield stage was effectively suppressed in c/ebp1 MO- and c/ebp1 MO2-injected embryos, but not in c/ebp1 5mMO-injected embryo. (B) lyz expression was inhibited in c/ebp1 MO- and c/ebp1 MO2-injected embryos, while c/ebp1 5mMO injection did not affect lyz expression. |
|
Expression of myeloid-lineage transcription factors in the isolated EGFP-positive cells from Tg(lyz:EGFP)ko02. EGFP-positive cells were isolated by a cell sorter and circulating blood cells were collected after tail transection. RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that runx1, cebp1 and pu.1, but not gata1, were detected in EGFP-positive cells. On the other hand, gata1 and runx1, but not c/ebp1 and pu.1, were detected in circulating blood cells dominantly composed of erythroid cells. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(5-6), Kitaguchi, T., Kawakami, K., and Kawahara, A., Transcriptional regulation of a myeloid-lineage specific gene lysozyme C during zebrafish myelopoiesis, 314-323, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.