PUBLICATION
Klebsiella pneumoniae alters zebrafish circadian rhythm via inflammatory pathways and is dependent on light cues
- Authors
- Ding, H., Chen, X.C., Wan, L., Zhang, Y.Y., Rui, X.H., He, T., Liu, J., Shang, Z.B.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-240521-7
- Date
- 2024
- Source
- Heliyon 10: e30829e30829 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Keywords
- Circadian rhythm, Inflammation, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Light
- MeSH Terms
- none
- PubMed
- 38770281 Full text @ Heliyon
Abstract
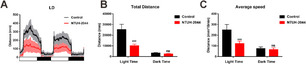
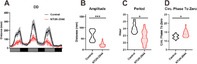
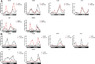
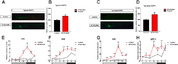
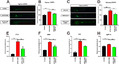
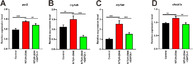
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen causing severe infections. The circadian rhythm is the internal rhythm mechanism of an organism and plays an important role in coping with changes in the 24-h circadian rhythm. Disruption of the circadian rhythm can lead to immune, behavioral, mental, and other related disorders. Whether K. pneumoniae can disrupt the circadian rhythm after infection remains unclear. Here, we examined the effects of K. pneumoniae NTUH-K2044 infection on biological rhythm and inflammation in zebrafish using behavioral assays, quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR, neutrophil and macrophage transgenic fish, and drug treatment. The results showed that K. pneumoniae infection decreased the motor activity of zebrafish and reduced the circadian rhythm amplitude, phase, and period. The expression of core circadian rhythm-associated genes increased under light-dark conditions, whereas they were downregulated under continuous darkness. Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated inflammation using Tg(mpx:EGFP) and Tg(mpeg:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish, expressing fluorescent neutrophils and macrophages, respectively, showed increased induction of inflammatory cells, upregulated expression of inflammatory factor genes, and stronger inflammatory responses under light-dark conditions. These effects were reversed by the anti-inflammatory drug G6PDi-1, and the expression of clock genes following K. pneumoniae treatment was disrupted. We determined the relationship among K. pneumoniae, inflammation, and the circadian rhythm, providing a theoretical reference for studying circadian rhythm disorders caused by inflammation.
Genes / Markers
Expression
Phenotype
Mutations / Transgenics
Human Disease / Model
Sequence Targeting Reagents
Fish
Orthology
Engineered Foreign Genes
Mapping