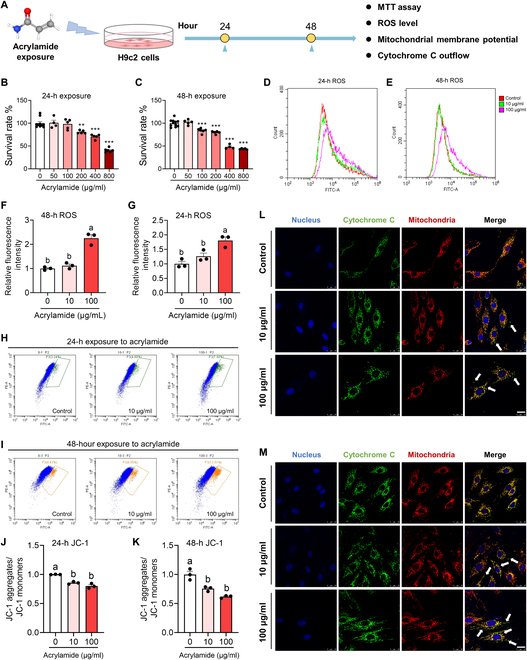
Fig. 5 Acrylamide induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis with ROS accumulation, cytochrome C outflow, and dropped mitochondrial membrane potential in H9c2 cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell study. (B and C) Survival rates of H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively. The viability of cells was determined by the 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di-phenytetrazoliumromide (MTT) assay. (D and E) Accumulation of ROS was observed at 24 and 48 h by 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) probe after acrylamide treatment. (F and G) Quantification of ROS accumulation in H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively (n = 3 per group). (H and I) Mitochondrial membrane potential was evaluated at 24 and 48 h by JC-1 probe after acrylamide treatment. (J and K) Quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential in H9c2 cells after 24- and 48-h acrylamide exposure, respectively (n = 3 per group). (L and M) Cytochrome C outflow was observed by colocalizing mitochondria (red) and cytochrome C (green) fluorescently, while cell nucleus was dyed by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) with acrylamide exposure for 24 and 48 h, respectively. The white arrows point out the occurrence of cytochrome C outflow. Data are presented as the means ± SEM. Significance was calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; groups labeled with different letters differed significantly (P < 0.05). FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Research (Wash D C)