Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221114-8
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2021 - atg7-Based Autophagy Activation Reverses Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
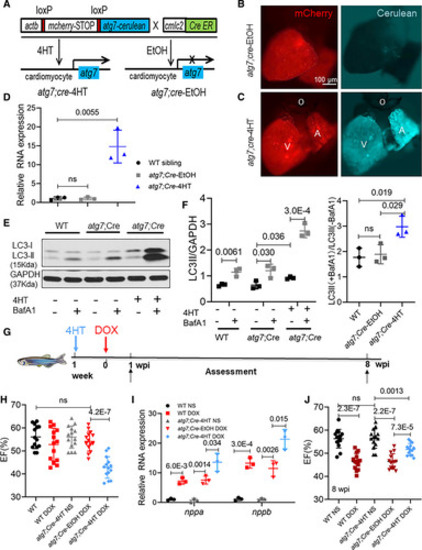
atg7 overexpression (OE) activates autophagy and exerts deleterious effects in the early phase of adult anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (aAIC). A, Schematics of the atg7 conditional transgenic line. B and C, Fluorescence images of hearts in fish at 1 wk after 24-h treatment with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4HT) or ethanol. Signals in the cerulean channel represent cardiomyocyte-specific atg7 OE after conditional gene activation. D, Relative transcript level of atg7 RNA in a wild-type (WT) sibling and zebrafish with atg7 OE and with and without 4HT treatment. E, Representative Western blot showing increased LC3-II (microtubule-associated protein light chain 3II) levels in a zebrafish with atg7 OE and control-treated with bafilomycin A1 (BafA1; n=3/treatment). F, Quantification of LC3-II and the ratio of LC3-II between the hearts treated with and without BafA1 in E. G, Schematics of the experimental procedure for activating atg7 in the early phase of aAIC. H and J, High-frequency echocardiography was performed at the indicated times to quantify cardiac function. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test was used. I, Evaluation of nppa and nppb gene transcript expression by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. n=3. Kruskal-Wallis test was used followed by post hoc Tukey test in D, F, and I. A indicates atrium; DOX, doxorubicin; EF, ejection fraction; LC3, light chain 3; NS, normal saline; O, outflow tract; V, ventricle; and wpi, wk postinjection. |