Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221114-11
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2021 - atg7-Based Autophagy Activation Reverses Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
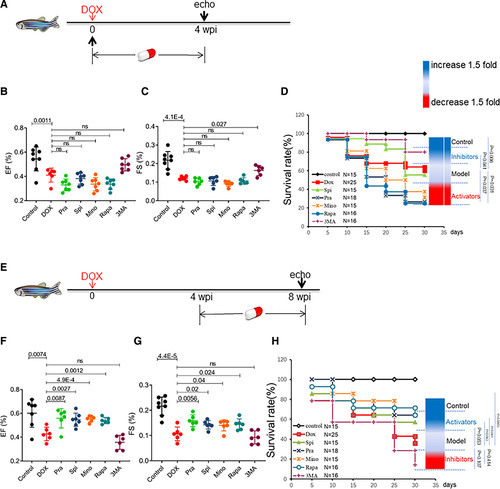
Top-ranking Food and Drug Administration–approved autophagy activators used with the embryonic anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC) model exerted therapeutic effects in the zebrafish adult AIC (aAIC) model in a time-dependent fashion. A, Schematics of the experimental procedure for drug administration in the early phase of aAIC. B and C, High-frequency echocardiography was performed to evaluate cardiac function. D, Kaplan-Meier survival curves showing the survival of doxorubicin (DOX)-stressed adult fish after drug administration in the early phase. n=15–25. E, Schematics of the experimental procedure for drug administration in the late phase of aAIC. F and G, High-frequency echocardiography was performed 8 wk postinjection (wpi) to evaluate cardiac functions. H, Kaplan-Meier survival curves showing the survival of DOX-stressed adult zebrafish after drug administration in the late phase. n=15–25. Log-rank test was used in D and H for comparisons; one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test in B, C, F, and G. echo indicates echocardiography; EF, ejection fraction; FS, fraction shortening; Mino, minoxidil; Pra, pravastatin; Rapa, rapamycin; Spi, spironolactone; and 3-MA,3-methyladenine. |