|
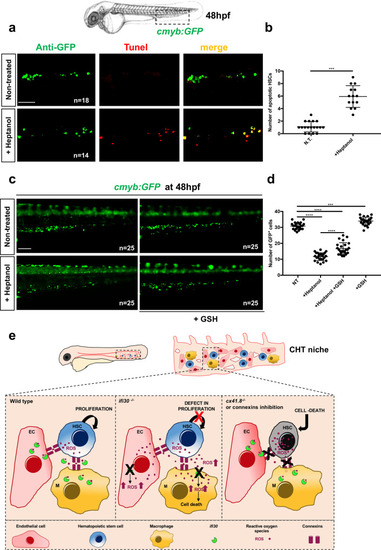
Loss of HSPCs after connexin inhibition with drug treatment can be rescued by GSH treatment.a Anti-GFP and TUNEL staining of NT and heptanol-treated cmyb:GFP embryos. b Quantification of the number of apoptotic HSPCs in both conditions. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired two-tailed t test ***P < .001. Center values denote the mean and error values denote s.e.m. c Fluorescence imaging of NT and heptanol-treated (50 μM) cmyb:GFP embryos and after GSH treatment. d Quantification of cmyb:GFP+ cells. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Tukey–Kramer post hoc tests, adjusted for multiple comparisons, ***P = 0007; ****P < .0001. Center values denote the mean and error values denote s.e.m. e HSPCs directly communicate with ECs and macrophages (MΦ) in the embryonic niche through connexin channels. Under normal conditions ifi30 reduces oxidized glutathione GSSG into reduced GSH, maintaining low levels of ROS in the CHT/HSPCs. The deficiency of ifi30 increases GSSG levels and increases ROS in the CHT niche, generating a defect of HSPC proliferation. The connexin-deficient embryos (cx41.8 mutants or treated with connexin inhibitors) present ROS accumulation directly in HSPCs, inducing their cell death. Scale bars: 100 μm (a–c).
|