Fig. S5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131031-20
- Publication
- Jao et al., 2013 - Efficient multiplex biallelic zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR nuclease system
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
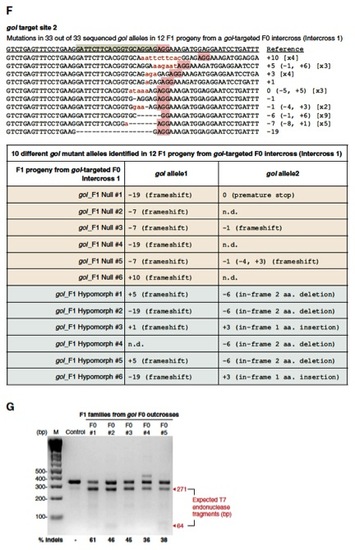
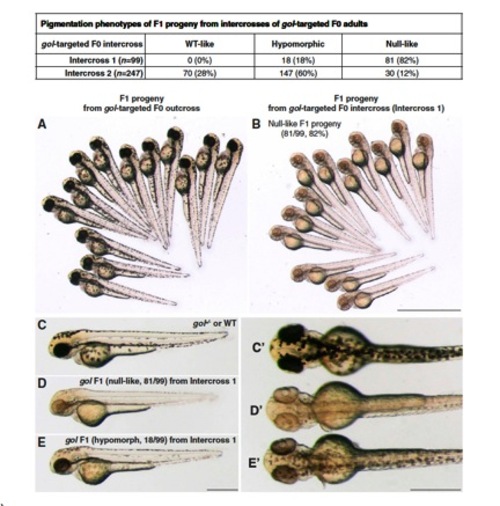
Germ-line transmission of Cas9-induced mutations at the gol locus. (A–E) Two pairs of gol-targeted founders were intercrossed (intercross 1 and intercross 2) to generate F1 progeny. At 2 dpf, 81 of 99 (82%) F1 embryos from intercross 1 were phenotypically null (B, D, and D2) and the rest 18 of 99 (18%) F1 embryos were hypopigmented (E). Lack of F1 progeny with wild-type pigmentation suggested that the germ line of both gol-targeted founders from intercross 1 had <100% biallelic disruption of gol loci. In intercross 2, 72% of the F1 progeny were either null-like or hypopigmented, indicating that the majority of the gol loci in the germ line of these two founders was also biallelically disrupted. (F) Sequences of the gol target region of 12 F1 progeny (6 nulllike, 6 hypopigmented) from intercross 1. All sequences (33 of 33) had indels near the gol target. Because only 10 different gol mutant alleles were recovered from 12 F1 siblings and 7 of these 10 alleles were recovered multiple times, the germ line of each gol-targeted founder from intercross 1 likely had only limited numbers of gol mutant alleles. Note that all of the null-like F1 progeny had either a frameshift or a nonsense mutation at both gol alleles, whereas all of the hypopigmented F1 embryos had either a 6 or a +3 small in-frame indel in one of the gol alleles. ND, not determined. (G) Screening five gol-targeted founders by outcrossing followed by T7EI assays to detect gol mutations in the F1 progeny. All five gol-targeted founders transmitted gol mutations to their progeny as indicated by the presence of two expected T7EI fragments. |