Fig. 10
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120522-24
- Publication
- Das et al., 2012 - Bmps and id2a act upstream of twist1 to restrict ectomesenchyme potential of the cranial neural crest
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
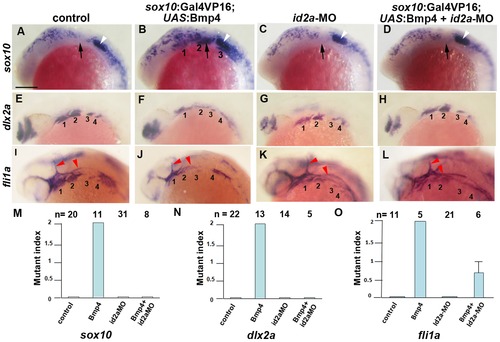
Reduction of Id2a rescues the ectomesenchyme defects caused by Bmp4 misexpression. (A–L) Colorimetric in situs show ectopic sox10 arch expression at 18 hpf and reductions of dlx2a and fli1a arch expression at 24 hpf in sox10:Gal4VP16; UAS:Bmp4 embryos but not sox10:Gal4VP16 control or id2a-MO-injected embryos. sox10:Gal4VP16; UAS:Bmp4 embryos injected with id2a-MO showed complete rescue of sox10 and dlx2a expression and partial rescue of fli1a expression. Arches are numbered and arrows denote the second arch, white arrowheads the developing ear, and red arrowheads the vasculature. Scale bar = 50 μm. (M–O) Quantification of gene expression defects. The mutant index is based on the following: 0 = normal, 1 = partially defective, 2 = fully defective. Fully defective was defined as gene expression being of equal intensity to that seen in un-injected sox10:Gal4VP16; UAS:Bmp4 embryos. For sox10, partially defective was defined as a reduction in the number of expressing cells and/or the intensity of arch expression compared to un-injected sox10:Gal4VP16; UAS:Bmp4 embryos. For fli1a and dlx2a, partially defective was defined as a level of arch expression intermediate between un-injected sox10:Gal4VP16; UAS:Bmp4 and sox10:Gal4VP16 control embryos. The rescue of Bmp4 misexpression defects with id2a-MO injection was statistically significant for all genes based on a Tukey-Kramer HSD test (α = 0.05). Standard errors of the mean are shown. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 14-19 somites to Prim-5 |