Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080424-19
- Publication
- Whitlock et al., 2003 - Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (gnrh) cells arise from cranial neural crest and adenohypophyseal regions of the neural plate in the zebrafish, Danio rerio
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
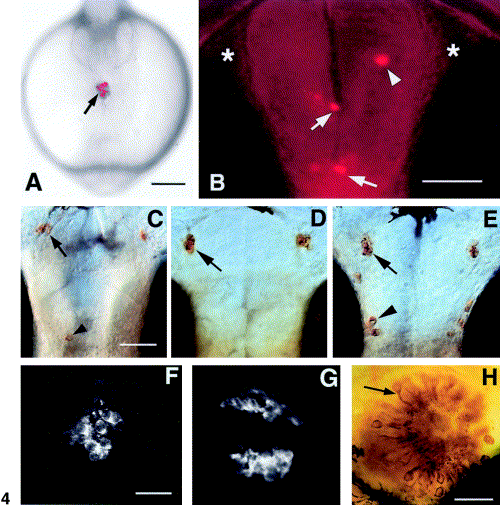
H-GnRH cells develop in association with the anterior pituitary placode. (A) Live embryo at 6-7 somites (∼ 13 h); frontal view showing DiI (arrow) label. (B) Ventral view of a live embryo at 56 h; labeled cells appear in the olfactory bulb (arrowhead), anterior commissure and post optic commissure (arrows). There are no labeled cells in the olfactory organs (asterisks). (C–E) Ventral view of anti-GnRH labeling in whole-mount you-too embryos at 56 h. (A) In mutants animals showing a partial pituitary (F) there are occasional H-GnRH cells (arrowhead); the TN-GnRH cells are present. (D) In animals lacking the pituitary, the H-GnRH cells are missing; the TN-GnRH cells remain unaffected (arrow). (E) TN-GnRH cells (arrow) and H-GnRH cells (arrowhead) are present in the wild-type siblings. (F) Anti-ACTH labeling in homozygous mutants showing a diminished, abnormal pituitary. (G) Anti-ACTH staining in the pituitary showing normal pattern of labeling. (H) Anti-calretinin labeling of the olfactory epithelium showing differentiated neurons (arrow) in the you-too mutant. Scale bars: (A) 200 μm; (B) 50 μm, (C–E) 50 μm; (F–G) 30 μm; (H) 30 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 257(1), Whitlock, K.E., Wolf, C.D., and Boyce, M.L., Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (gnrh) cells arise from cranial neural crest and adenohypophyseal regions of the neural plate in the zebrafish, Danio rerio, 140-152, Copyright (2003) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.