- Title
-
The Role of TRiC-enhanced Actin Folding in Leber Congenital Amaurosis
- Authors
- Berger, S., D Currie, P., Berger, J.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res.
|
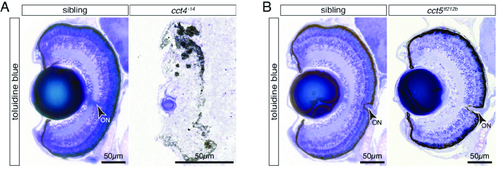
The eye develops in cct5tf121b but not cct4-14mutants. (A) Toluidine Blue-stained sections of six-dpf-old siblings revealed the typical layered structure of the retina. In contrast, the eye of TRiC loss-of-function cct4-14 mutants was severely degraded and only rudimentary structures of lens and pigmented retina were recognisable. (B) At six dpf, homozygotes of the missense mutant cct5tf121b featured a structured eye and the layering of the retina appeared comparable to siblings. Arrowheads indicate optic nerves (ON). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
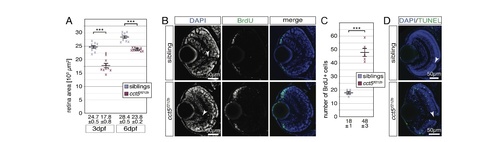
The retina of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏mutants is smaller and characterised by enhanced proliferation and apoptosis. (A) Quantification of the retina sizes revealed that the retinal area of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes was significantly smaller compared to siblings. The mean retinal area of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes was 17.8 ± 0.8 (×103 μm2) at three dpf and 23.8 ± 0.2 (×103 μm2) at six dpf compared to siblings that featured mean retinal areas of 24.7 ± 0.5 (×103 μm2) at three dpf and 28.4 ± 0.5 (×103 μm2) at six dpf; n = 10 per genotype and stage. (B) In contrast to three-dpf-old siblings, more BrdU-positive cells (green) were detected at the periphery of the retina within the ciliary marginal zone of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes. (C) Quantification of the number of BrdU-positive cells within individual retinas revealed that significantly more cells were proliferating within the ciliary marginal zone of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes at three dpf. Whereas cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 had 48 ± 3 BrdU-positive cells per retinal cross section, 18 ± 1 were proliferating in siblings (n = 5). (D) In contrast to the retina of three-dpf-old siblings, in which apoptotic cells were rarely labelled by the TUNEL assay (green), apoptosis was frequently observed throughout the entire retina of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏homozygotes. Data are mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t-test. Arrowheads indicate optic nerves (ON). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
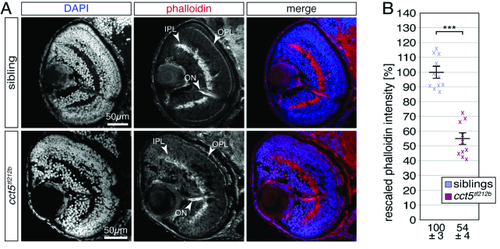
F-actin is significantly reduced in the retina of cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 mutants. (A) At three dpf, F-actin was labelled with phalloidin (red) on cross sections counterstained with DAPI (blue). Whereas the inner and outer plexiform layers of the retina (IPL and OPL, respectively) were prominently stained by phalloidin within siblings, the signal from cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes appeared weaker. Phalloidin also marked the optic nerve (ON). (B) Quantification of the brightness of the phalloidin signal within the IPL revealed that cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes showed a significant reduction in signal intensity to 54 ± 4% in relation to their siblings, which were rescaled to 100 ± 3%. Data are mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t-test; n = 10. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
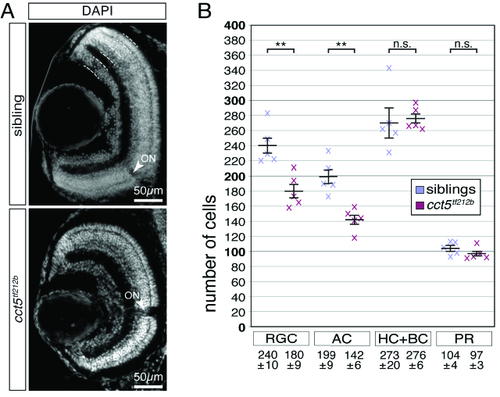
Retinal ganglion and amacrine cells are reduced in number in cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 mutants. (A) At six dpf, the retinal nuclei of siblings and cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 mutants were marked at the level of the optic nerve using the nuclear stain DAPI. Indicated by the dotted lines, the outer nuclear layer contains the photoreceptor cells (PR). The inner nuclear layer harbours the apical horizontal cells (HC) and the bipolar cells (BC) as well as the basally located amacrine cells (AC). The most basal layer contains the retinal ganglion cells (RGC). Arrowheads indicate optic nerves (ON). (B) Quantification of the cellularity of the different retinal layers within siblings and cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes at six dpf. The cell number of the RGC and the AC were significantly reduced in cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes. Per retinal cross section, siblings had 240 ± 10 RGC and 199 ± 9 AC in contrast to 180 ± 9 RGC and 142 ± 6 AC in cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes. The number of HC and BC as well as PR remained unchanged. Siblings had 273 ± 20 HC and BC as well as 104 ± 24 PR and cct5𝑡𝑓121𝑏 homozygotes had 276 ± 6 HC and BC as well as 97 ± 3 PR. Data are mean ± SEM; **P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test; n.s., not significant; n, 5. PHENOTYPE:
|