- Title
-
Tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol disrupt pancreatic organogenesis and gene expression in zebrafish embryos
- Authors
- Wilson, P.W., Cho, C., Allsing, N., Khanum, S., Bose, P., Grubschmidt, A., Sant, K.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Birth Defects Res
|
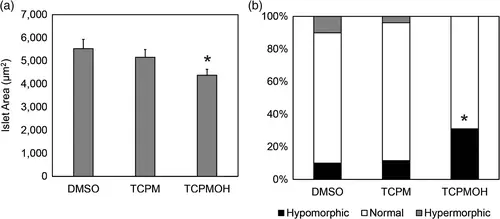
Islet area. Tg(insulin::GFP) zebrafish embryos were imaged and measured at 96 hpf following exposure to 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol (TCPMOH), 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane (TCPM), or 0.01% DMSO. Asterisks * designate statistically significant changes from controls (p < .05). n = 25–29 embryos per treatment group. (a) Mean islet area of embryos exposed to 50 nM TCPMOH and 50 nM TCPM were reduced by 20.8% and 6.8%, respectively, compared to controls. (b) The incidence of hypermorphic or hypomorphic islets was not statistically significant. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
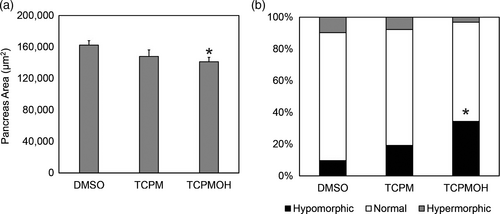
Exocrine pancreas area. Tg(ptf1a::GFP) zebrafish embryos were imaged and measured at 96 hpf following exposure to 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol (TCPMOH), 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane (TCPM), or 0.01% DMSO. Asterisks (*) designate statistically significant changes from controls (p < .05). n = 26–32 embryos per exposure group. (a) Mean exocrine pancreas area of embryos exposed to 50 nM TCPMOH and 50 nM TCPM were reduced by 13% and 8.8%, respectively, compared to controls. (b) Incidence of hypomorphic pancreases was significantly increased in TCPMOH-exposed embryos, accounting for one-third of those exposed. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
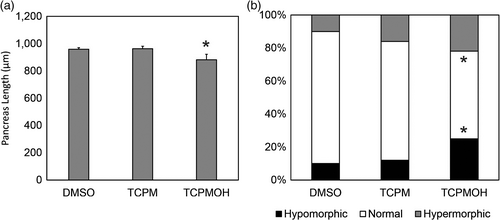
Pancreas length. Tg(ptf1a::GFP) Zebrafish embryos were imaged and measured at 96 hpf following exposure to 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol (TCPMOH), 50 nM tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane (TCPM), or 0.01% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Asterisks (*) designate statistically significant changes from controls (p < .05). n = 26–32 embryos per exposure group. (a) The mean pancreas length of embryos exposed to 50 nM TCPMOH was reduced by 6%, compared to controls. The mean pancreas length of embryos exposed to 50 nM TCPM was 2.7% larger than the controls. (b) The incidence of hypo- and hypermorphic pancreas lengths was increased to 25% (each) in embryos exposed to TCPMOH. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
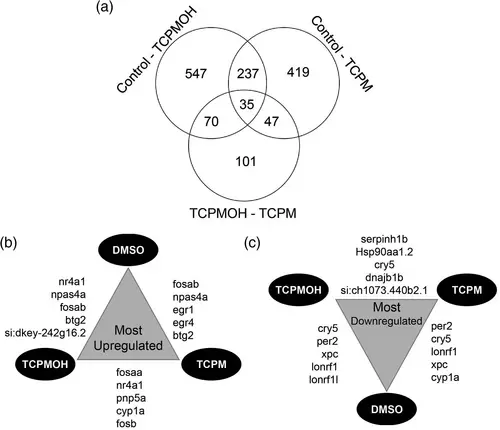
Gene expression summary. (a) Expression of 547 and 419 genes was significantly changed (p < .05) by tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol (TCPMOH) and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane (TCPM) exposure, respectively, with 237 genes significantly changed by both. A total of 101 genes were differentially expressed between TCPMOH and TCPM exposure and 35 genes were significantly altered across all group comparisons. (b) The top five upregulated genes by treatment group. (c) The top five down regulated genes by treatment group |
|
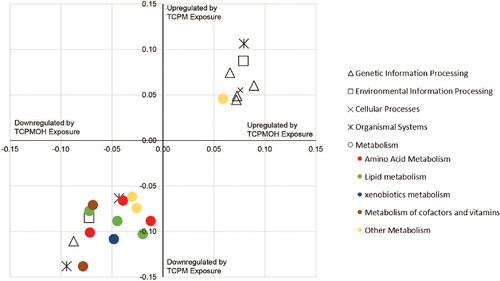
KEGG pathways changed by tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane (TCPM) or tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol (TCPMOH) exposure. Transcriptomic responses to TCPM and TCPMOH are correlated (R2 = .903). Pathways in the upper right quadrant are upregulated by exposure to TCPM and TCPMOH. Pathways in the lower left quadrant are downregulated by exposure to TCPM and TCPMOH. |