- Title
-
Loss of foxc1 in zebrafish reduces optic nerve size and cell number in the ganglion cell layer
- Authors
- Umali, J., Hawkey-Noble, A., French, C.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Vision Res.
|
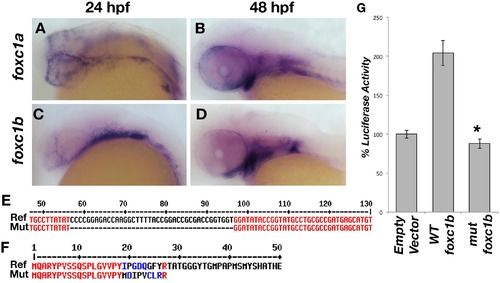
Zebrafish foxc1 genes. foxc1a is expressed in the neural crest and periocular mesenchyme at 24 hpf (A) and in the pharyngeal arches at 48 hpf (B). foxc1b is also expressed in the periocular mesenchyme and a small number of ocular progenitor cells at 24 hpf (C), and in the pharyngeal arches at 48 hpf (D). Partial alignment of the reference foxc1b coding sequence and the 40 base-pair deletion mutant sequence created by CRISPR genome editing (E). The zebrafish mutant strain deleted 40 nucleotides (57–96 of the open reading frame), resulting in a frameshift mutation and predicted premature protein truncation (F). Luciferase assays in HEK293 cells using a reporter with 6 copies of the consensus FOXC1 binding element demonstrates the zebrafish foxc1b 40 base pair deletion creates a null mutation, as no luciferase activity (above endogenous levels) is observed (G) p = 9 x 10-5. |
|
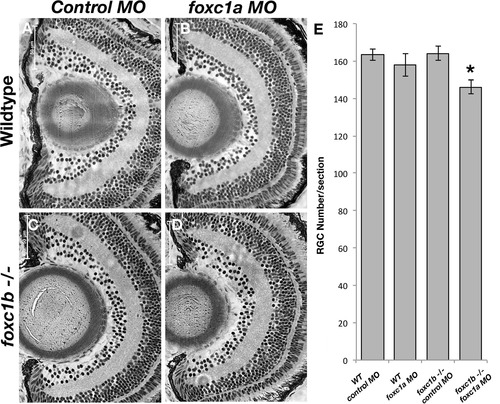
Loss of foxc1 function causes reduced cell number in the RGC layer. foxc1a morpholino injection into a foxc1b -/- background (D) reduced RGC number when compared to wildtype embryos injected with standard negative control morpholinos (A), wildtype embryos injected with foxc1a morpholinos (B), or foxc1b mutants injected with control morpholinos (C). This is statistically significant p = 0.013 (E, comparison of A-D). Data presented as mean ± SEM. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Loss of foxc1 function reduced optic nerve thickness. foxc1a morpholino injection into a foxc1b -/- background reduced optic nerve thickness (D) when compared to wildtype embryos injected with standard negative control morpholinos (A), wildtype embryos injected with foxc1a morpholinos (B), foxc1b mutants injected with control morpholinos (C) This is statistically significant (E, comparison of A–D, p = 0.03 (C). Data presented as mean ± SEM. Red line indicates area of measurement. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) PHENOTYPE:
|
|
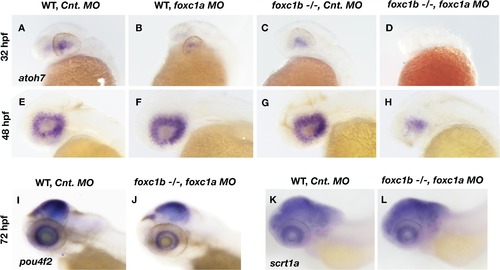
Loss of foxc1 affects markers of RGC differentiation.Expression of atoh7 is induced in the nasal-ventral domain of the retina at 32 hpf (A), and encompasses the entire retina by 48 hpf (E) in wildtype embryos injected with a control morpholino. Loss of foxc1a on its own through morpholino inhibition (B and F) had no effect on atoh7 initiation at 32 hpf, nor its expression throughout the retina at 48 hpf. Similarly, no change in atoh7 expression is observed in foxc1 −/− injected with control morpholinos at either 32 hpf (C) or 48 hpf (G). Injection of foxc1a morpholinos into a foxc1b −/− background impaired the initiation of atoh7 expression at 32 hpf (D), and reduced expression throughout the retina at 48 hpf (H). pou4f2is expressed throughout the RGC layer at 3 dpf (I), and is reduced in foxc1b -/- injected with foxc1a morpholinos (J). A marker of Amacrine cells, scrta1, is not affected (K and L). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
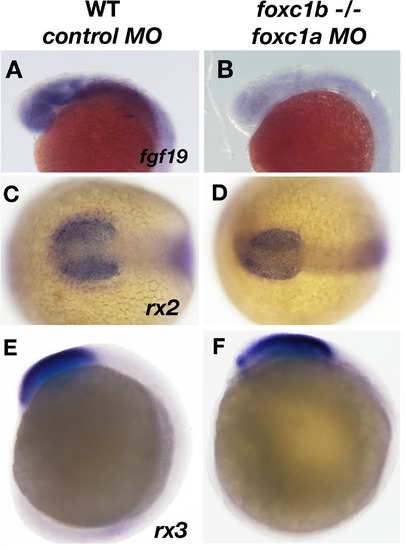
Expression of fgf19 is disrupted due to loss of foxc1function. fgf19 expression is found ubiquitously in the head at 20 hpf (A), and is reduced in foxc1b −/− injected with foxc1amorpholinos (B). The expression of two early retinal homeoboxgenes (rx2 and rx3) is not altered in these embryos (rx2, 16 somites C, D, rx3, 10 somites, E, F). Lateral views (A, B, E, F) and dorsal views (C, D). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
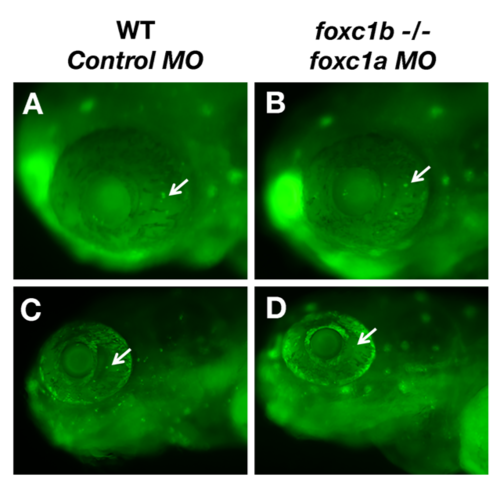
Injection of foxc1a morpholinos into foxc1b -/- mutants does not cause cell death in the eye. A small number of apoptotic cells identified by acridine orange staining are identified in wildtype eyes at 48 hpf and 72 hpf (A and C). No difference in the number of apoptotic cells are observed due to loss of foxc1 function (B and D). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
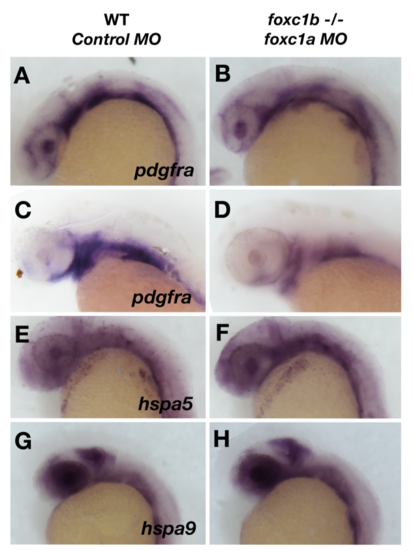
Loss of foxc1 function has minimal effects on oxidative response genes in the eye. Loss of foxc1 function results in a subtle reduction of expression of pdgfra at 24 hpf in the lens and neural crest cells (A and B), and this reduction is more pronounced at 48 hpf when pdgfra expression is confined to the pharyngeal arches (C and D). No change is observed in the expression of heat shock protein genes in the eye such as hspa5 (E and F) and hspa9 (G and H). |
Reprinted from Vision Research, 156, Umali, J., Hawkey-Noble, A., French, C.R., Loss of foxc1 in zebrafish reduces optic nerve size and cell number in the ganglion cell layer, 66-72, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Vision Res.