- Title
-
A transcriptomics analysis of the Tbx5 paralogues in zebrafish
- Authors
- Boyle Anderson, E.A.T., Ho, R.K.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Tbx5b mutants phenocopy Tbx5b morphants. (a) tbx5b expression in the eyes (asterisk) and lateral plate mesoderm (arrow) of 21 hpf embryos. (b) The indel for the tbx5b-2A mutant (red) embryos is located in the beginning of the first intron. Uppercase letters are the protein coding sequence while lowercase letters are the untranslated regions and introns. (c) The mutation would produce a prematurely truncated protein with a frameshift resulting in incorrect amino acids starting at AA53 and a premature stop codon after 16 incorrect amino acids (red). (d-e) Embryos at 3 dpf. Arrows point to the heart and pectoral fins. Siblings from a Tbx5b in-cross display normal heart (d) and fin (d’) development while mutant siblings have affected hearts (e) and fins (e’) which phenocopy the defects seen in the heart (f) and fins (f’) of embryos injected with a Tbx5b morpholino. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Effects of Tbx5 paralogues on vasculature. (a-a”’) Dorsal view of sox7 expression at 18 hpf showing misexpression in Tbx5a-deficient embryos (a’), Tbx5b-deficient embryos (a”) and double-deficient embryos (a”’) compared to normal wildtype expression (a). (b-b”’) Dorsal view of hhex expression at 21 hpf displaying mild misexpression in Tbx5a-deficient embryos (b’) and more severe misexpression in Tbx5b-deficient embryos (b”) and double-deficient embryos (b”’) compared to wildtype (b). (c-c”’) Lateral view of cox6b1 expression at 18 hpf in the developing pronephric duct. Arrowheads mark the anterior limit of expression. Expanded expression is present in the surrounding tissue of Tbx5a-deficient (c’) and double-deficient (c”’) embryos, while expression is decreased throughout the embryo in Tbx5b-deficient embryos (c”). (d-d”’) Lateral view of the Tg(fli1a::EGFP)y1 line displays increased branching in the intersomitic vessels of both Tbx5b-deficient (d”) and double-deficient embryos (d”’) (see arrowheads) compared to either wildtype (d) or Tbx5a-deficient embryos (d’). (e-e”’) Dorsal view of the Tg(fli1a::EGFP)y1 line. The subintestinal vessels are marked with a bracket in 3 dpf embryos. There is a decrease in size of the subintestinal vasculature in Tbx5b-deficient (e”) and double-deficient (e”’) embryos compared to either wildtype (e) or Tbx5a-deficient embryos (e’). Scale bars are 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Effects of Tbx5 Paralogues on the Somites. All views are lateral, see text for details. hsp90aa1.2 expression at 18 somite stage is expanded in Tbx5b-deficient (a”) and double-deficient (a”’) embryos compared to wildtype (a). phlda2 expression at 18 hpf is consistent in the somites in wildtype (b), Tbx5a-deficient (b’) and Tbx5b-deficient (b”) embryos, but mostly absent in double-deficient embryos(b”’). Expression of aimp1 at the 21 hpf stage is decreased in Tbx5a-deficient (c’), Tbx5b-deficient (c”) and double-deficient (c”’) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (c). In 21 hpf embryos, obsl1a expression is increased in the somites of Tbx5a-deficient (d’) and double-deficient (d”’) embryos compared to wildtype (d) embryos. Tbx5b-deficient embryos show a decrease in expression in the trunk somites (d”) but an increase in the more posterior somites (S4F” Fig) compared to wildtype embryos. Expression of ryr1b is increased slightly in the Tbx5a-deficient (e’) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (e) and most strongly in the double-deficient embryos especially in the ventral somites(e”’). Expression of ryr1b in the Tbx5b-deficient embryos (e”’) is more similar to wildtype than to Tbx5a-deficient embryos. Scale bar is 100 μm. (f) Somite count of embryos at 25 hpf. Tbx5a-deficient (n = 16), Tbx5b-deficient (n = 12), and double-deficient (n = 15) showed no significant difference in somite count compared to wildtype (n = 15). (g) Somite length measured along the AP axis of wt (n = 104), Tbx5a-deficient (n = 110), Tbx5b-deficient (n = 66) and double-deficient (n = 96). Both Tbx5b-deficient and double-deficient embryos showed a significant decrease in somite size compared to wt embryos. (g-f) significance was tested using ANOVA and Tukey HSD test, *p<0.05, ***p<0.0001. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
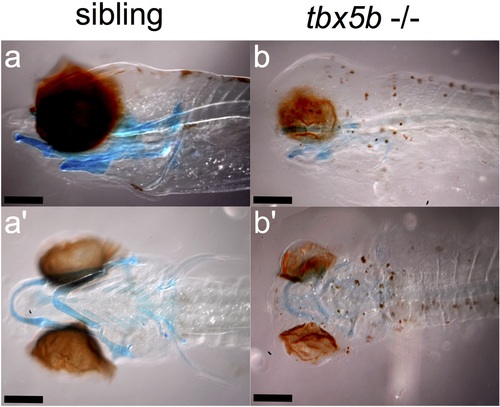
Alcian blue staining in the jaw at 6 dpf. Wildtype siblings show a more protruding lower law that extends beyond the eye as can be seen both from a lateral (a) and ventral (a’) view. Affected tbx5b -/- mutant embryos have a rounder head and a jaw that does not protrude beyond the eyes, as seen from both a lateral (b) and ventral (b’) view. Scalebar is 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
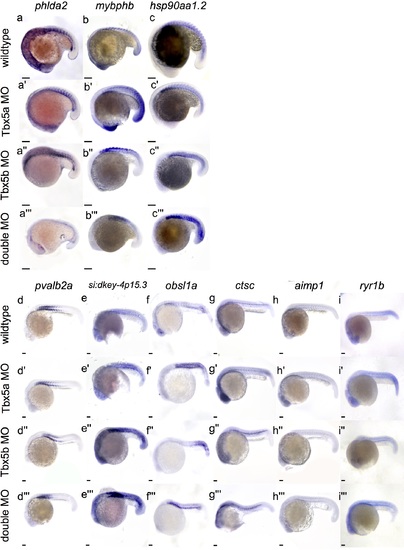
Complete somite differential expression. In situ hybridization of all genes differentially expressed in the somites. (a-a”’) At 18hpf, phlda2 is upregulated in Tbx5a-deficient (a’) and Tbx5b-deficient (a”) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (a’), but downregulated in the double-deficient embryos (a”’). At 18hpf, mybphb shows upregulation in Tbx5a-deficent (b’) and double-deficient (b”’) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (b). At 18hpf, hsp90aa1.2 is upregulated in Tbx5a-deficient (c’), Tbx5b-deficient (c”) and double-deficient (c”’) embryos compared to wildtype (c) embryos, especially in the anterior somites. At 21 hpf, pvalb2 expression is increased in Tbx5b-deficient (d”) and double-deficient (d”’) embryos compared to wildtype (d) but not Tbx5a-deficient embryos (d’). At 21 hpf, si:dkey-4p:15.3 expression is increased in Tbx5a-deficient (e’), Tbx5b-deficient (e”) and double-deficient (e”’) embryos. At 21 hpf, obsl1a expression is upregulated in Tbx5a-deficient (f’), Tbx5b-deficient (f”) and double-deficient (f”’) embryos compared to wildtype (f) embryos. At 21 hpf, ctsc expression is expanded in Tbx5a-deficient (g’) and Tbx5b-deficient (g”) embryos compared to wildtype (g) embryos. At 21 hpf, aimp1 expression is decreased in Tbx5a-deficient (h’), Tbx5b-deficient (h”) and double-deficient (h”’) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (h). At 21 hpf, ryr1b expression is increased in both Tbx5a-deficient (i’) and double-deficient (i”’) embryos compared to wildtype (i) embryos. (j-k) Comparison of length between Tbx5b mutant embryos and siblings, n = 10, measurements in μm. (j) Tbx5b-deficient embryos at 3 dpf are significantly shorter than their siblings. (k) Somite size is not significantly different at 3dpf between Tbx5b-deficient embryos and their wildtype siblings. Since somite size varies along the AP axis, measurements were taken of the more anterior somites only. (l) At 25 hpf, there is a significant difference in somite number between wildtype and Tbx5b morpholino injected embryos. Scale bar is 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
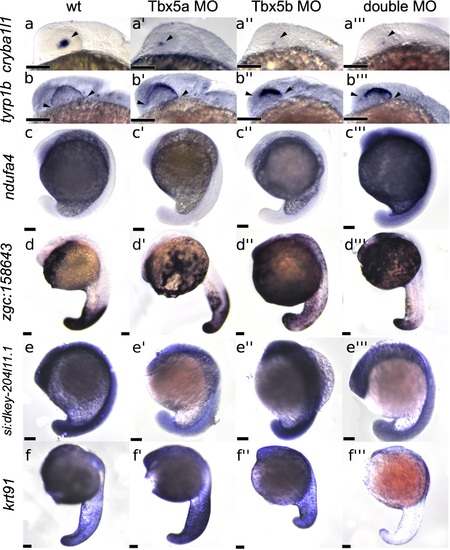
Differential expression in other tissues. All views are lateral. At 21 hpf, cryba1l1 is downregulated in Tbx5a-deficient (a’), Tbx5b-deficient (a”), and double-deficient (a”’) embryos compared to wildtype (a) embryos in the eye. Arrowheads mark the expression. At 21 hpf, tyrp1b expression is expressed at higher levels in Tbx5a-deficient(b’), Tbx5b-deficient (b”) and double-deficient (b”’) eyes compared to wildtype (b) eyes. Arrowheads mark the limits of the expression domain. At 18 hpf, ndufa4 is upregulated in the double-deficient embryo (c”’) compared to wildtype (c) embryos. Expression of zgc158642 at 21 hpf is upregulated in Tbx5b-deficient (d”) and double-deficient (d”’) embryos compared to wildtype embryos (d). At 18 hpf, si-dkey-204l11.1 expression is downregulated in Tbx5a-deficient (e’) and double-deficient (e”’) embryos compared to wildtype (e) embryos. At 21 hpf, expression of krt91 is downregulated in double-deficient embryos (f”’) compared to wildtype embryos (f). Note f” has normal tail length, but it is bent out of focus of this image. Scale bars are 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|