- Title
-
slc7a6os Gene Plays a Critical Role in Defined Areas of the Developing CNS in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Benini, A., Cignarella, F., Calvarini, L., Mantovanelli, S., Giacopuzzi, E., Zizioli, D., Borsani, G.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
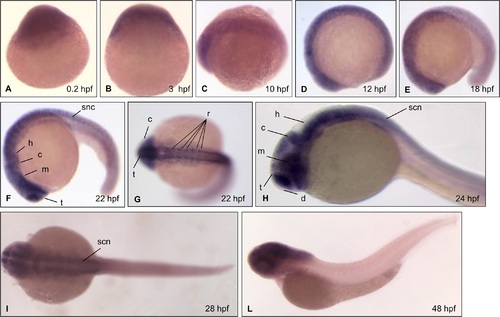
Expression of slc7a6os by whole-mount in situ hybridization at different stages during zebrafish development. Embryos at (A) 0.2 hpf (1–2 cell stage); (B) 3 hpf, (high stage); (C) 10 hpf (bud stage); (D) 12 hpf (6 somites), (E) 18 hpf (18 somites), (F)(G) 22 hpf (26 somites), (H) 24 hpf, (I) 28 hpf; (L) 48 hpf were examined by whole-mount in situ hybridization with an antisense slc7a6os riboprobe. The maternal origin of slc7a6os transcript is supported by its presence at 1–2 cells stage and high stage at the animal pole (A, B); at bud stage the hybridization signal is present in the midline (C). During early somitogenesis stages (D, E) the slc7a6os transcript is detectable ubiquitously in the rostral part of the embryo. At the end of somitogenesis the hybridization signal is more intense in structures of the developing central nervous system (F, G). A lateral view of embryos demonstrates the remarkable slc7a6os expression in defined brain regions at 24 hpf (H). Later on, at 28 (I) and 48 hpf (L) the gene expression is maintained in spinal cord neurons and in central nervous system structures. Abbreviations: d, diencephalon; m, midbrain; h, hindbrain; c, cerebellum; t, telencephalon; s, somites; scn, spinal cord neurons; r, rhombomeres. |
|
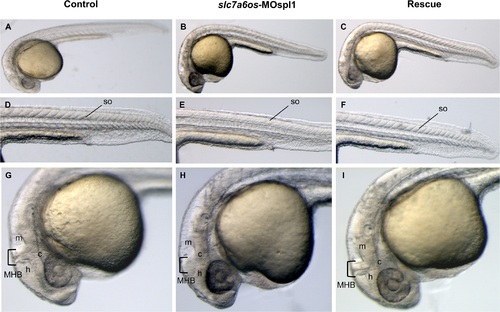
Morphological analysis of slc7a6os morphants and phenotypic rescue at 28 h. Embryos were injected at the two-cells stage with 6 ng/embryo of slc7a6os-MOspl1 splicing-inhibiting morpholino and examined at different developmental stages. At 28 hpf MO injected embryos exhibit alterations in somites structure and brain malformations (B, E, H) when compared to control embryos (A, D, G). Magnification of lateral views show undefined boundaries between brain subregions, especially at hindbrain and midbrain regions (H). The morphological differences observed in morphant embryos are rescued by expression of synthetic slc7a6os mRNA (C, F, I). Abbreviations: h, hindbrain; c, cerebellum; m, midbrain; MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; so, somites. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
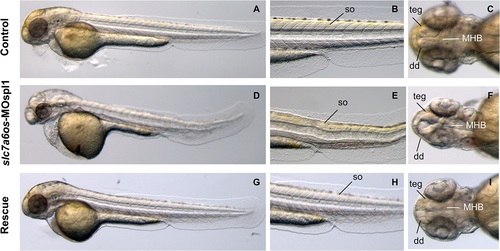
Morphological analysis of slc7a6os morphants and phenotypic rescue at 48 h. At 48 hpf, lateral view show that MO injected embryos have an evident pericardial and yolk-sac edema and the somite structures are not well-defined (D-E) when compared to controls (A, D). Dorsal view of morphants shows that the CNS abnormalities are more pronounced and reveals a severe disorganization of the following structures: midbrain–hindbrain boundary, dorsal diencephalon and tegmentum (F). Also at this developmental stage the expression of synthetic slc7a6os mRNA rescues the wild type phenotype in morphants (G-I). Abbreviations: so, somites; teg, tegmentum; dd, dorsal diencephalon; MHB, midbrain–hindbrain boundary. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
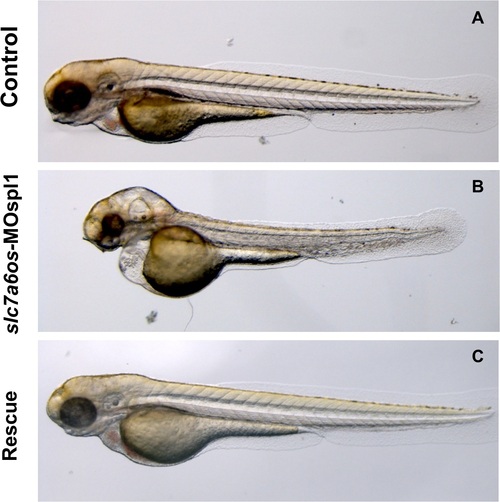
Morphological analysis of slc7a6os morphants and phenotypic rescue at 72 h. At 72 hpf, the pericardial and yolk-sac edema, CNS malformations and the general morphology alteration in MO injected embryos are more pronounced (B). Again the morphological differences seen in morphant embryos are rescued by the co-injection of synthetic slc7a6os mRNA (C). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
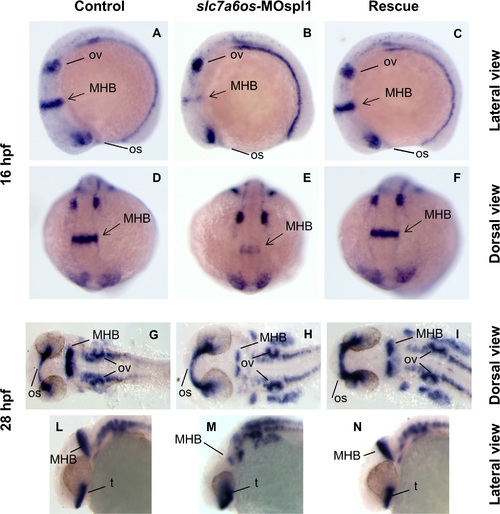
Analysis of pax2a expression in slc7a6os morphant embryos. Control and slc7a6os morphant embryos were analyzed by WISH for pax2a gene expression at different developmental stages. At 16 hpf expression of pax2a is down regulated in morphants: in particular a strong down-regulation for this marker was observed in the midbrain-hindbrain boundary (B, lateral view and E, dorsal view). No evident alterations were observed for otic vesicles and optic stalk in slc7a6os injected embryos compared to controls. At 28 hpf the defect in midbrain-hindbrain boundary is still clearly evident in morphants (H, flat mounted embryos). The midbrain-hindbrain boundary alteration is also evident in the embryo lateral view (M). Rescue experiments with synthetic slc7a6os mRNA confirmed the specificity of the phenotype observed (C, F, I, N). Abbreviations: MHB, midbrain–hindbrain boundary; op, optic stalk; ov, otic vesicles; t, telencephalon. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
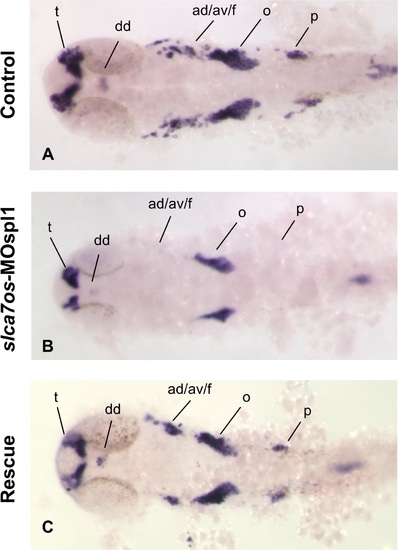
neurod expression is affected in slc7a6os morphants at 24 hpf. The expression of the neural marker neurod was analyzed by WISH at 24 hpf in control and slc7a6os morphants. In MO injected embryos no expression of neurod was detected in anterior and posterior ganglia while a down-regulation was observed in dorsal diencephalon, telencephalon and octave statoacustic ganglia (B, flat-mounted embryos). The altered expression pattern of neurod seen in morphants embryos is rescued by the expression of synthetic slc7a6os mRNA. Abbreviations: ad/av/f, anterodorsal/anteroventral lateral line/ facial placodes/ ganglia; dd, dorsal diencephalon; o, octaval/statoacustic ganglia; p, posterior lateral line ganglia; t, telencephalon. |
|
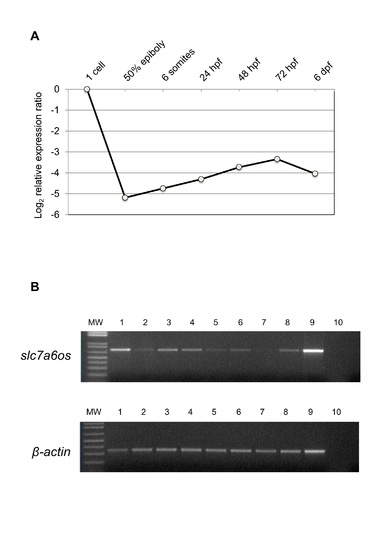
RT-PCR expression analysis of slc7a6os embryonic and adult zebrafish. (A) Real-Time PCR expression analysis of slc7a6os throughout Danio rerio development. All reactions were run in triplicate. The relative expression levels, represented as the mean±SEM in log2 scale, were determined with respect to the 1-cell stage and normalized to elongation factor 1α (ef1α). (B) RT-PCR expression analysis of slc7a6os in adult zebrafish tissues. Beta-actin was also amplified as housekeeping gene internal control. 1: brain; 2: intestine; 3: eye; 4: heart; 5: kidney; 6: swim bladder; 7: branchias; 8: testis; 9: ovary; 10: negative control. |
|
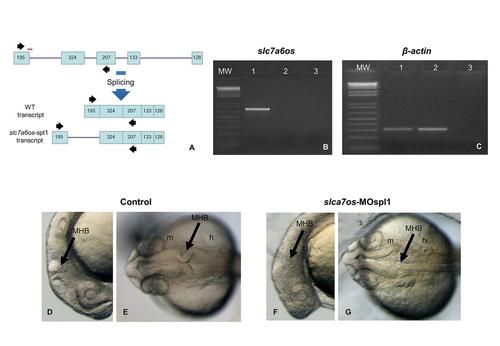
The phenotypic effects of slc7a6os loss-of-function become evident at 24 hpf. To knockdown the expression of a functional slc7a6os protein, the slc7a6os-MOspl1 splice blocking morpholino was synthesized targeting the exon1-intron1 boundary (A, red bar). RT-PCR experiments were performed on RNA extracted from slc7a6os-MOspl1-injected and control embryos with slc7a6os oligonucleotides on exon 1 and 3 (black arrows in A). The expected wild-type 681 bp PCR fragment is present only in control embryos (B, lane 1) and not detectable in slc7a6os-MOspl1 morphants (B, lane 2). The injection of slc7a6os-MOspl1 is expected to cause insertion of intron 1, leading to the production of a mature mRNA with several in frame termination codons after the coding sequence of exon 1. As anticipated, we failed to observe the predicted 3368 bp product in the RT-PCR analysis (B, lane 2) likely due to both the large size of the fragment to be amplified and the rapid degradation of the aberrant mRNA operated by the nonsense mediated decay mechanisms. A RT-PCR amplification was carried with β-actin primers as a quality control for both cDNAs. The lane 3 in panels B and C correspond to a RT-PCR reaction performed with no cDNA. At 24 hpf slc7a6os MO injected embryos exhibit CNS malformations with unclear boundaries between developing brain regions, especially at midbrain-hindbrain and hindbrain-midbrain boundaries (F, lateral view; G, dorsal view). The arrowheads indicate the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. Abbreviations: h, hindbrain; m, midbrain, MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
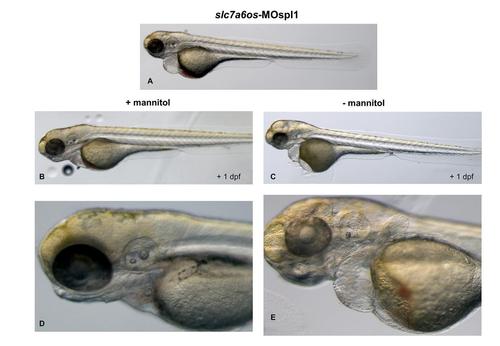
Treatment with mannitol reduces the pericardial and yolk-sac edema in slc7a6os morphants. slc7a6os morphants with severe pericardial and yolk-sac edema at 72 hpf (A) were exposed to 250 mM mannitol. After one day treated embryos showed a strong reduction of the edema (B, D) when compared to untreated embryos (C, E). |
|
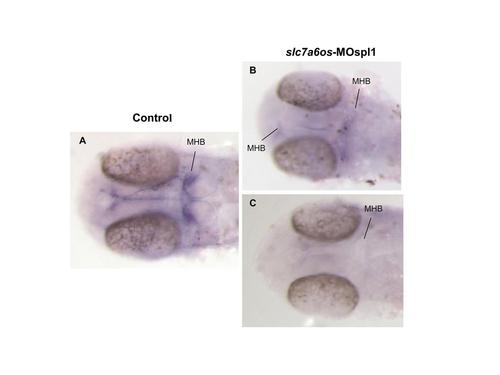
Loss of function of slc7a6os leads to severe defects in MHB region. Control (n = 37) and slc7a6os morphant embryos (n = 33) were analyzed by WISH for wnt1 gene expression. At 24 hpf expression in the midbrain-hindbrain boundary is strongly affected in morphants compared to controls (A). Two categories of phenotypes are present in morphants: a mild phenotype (B) observed in two third of the embryos and a more severe one present in the remaining third (C). Abbreviations: MHB: midbrain-hindbrain boundary. |
|
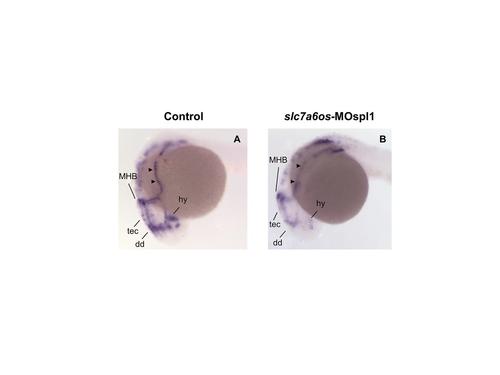
Patterning of the embryonic lateral line appears to be altered in slc7a6os morphants. Control (n = 58) and slc7a6os morphant embryos (n = 53) were analyzed at 24 hpf by WISH with lef1 probe. The morphants embryos show altered deposition of interneuromast cells expressing lef1, indicated by arrowheads, compared to control embryos. Abbreviations: MHB: midbrain-hindbrain boundary; dd, dorsal diencephalon; hy, hypothalamus; tec, tectum. |