- Title
-
barx1 represses joints and promotes cartilage in the craniofacial skeleton
- Authors
- Nichols, J.T., Pan, L., Moens, C.B., and Kimmel, C.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Cartilage and dermal bone phenotypes present in barx1 mutant zebrafish. (A,B) Live 5 days post-fertilization (dpf) zebrafish larvae were imaged with transmitted light. Arrow indicates lower jaw divot. (C,D) 5 dpf zebrafish stained with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red to label cartilage and bone were imaged with transmitted light. Eyes were removed to allow visualization of skeleton. Arrow indicates lower jaw skeletal gap. (E,F) 4 dpf Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red stained skeletons were dissected and imaged with transmitted light. (G-J) Confocal projections of live 6 dpf larvae with chondrocytes transgenically labeled with EGFP (sox9a:EGFP, green), and bone labeled with Alizarin Red. (A-H) Lateral views, anterior is towards the left, dorsal is upwards. (I,J) Ventral views, anterior is towards the left, whereas left is upwards. Arch 1 elements include the pterygoid process (ptp), palatoquadrate (pq) and Meckel’s (mc) cartilages. The jaw joint (j) and the ectopic Meckel’s joint (mj) are described in cellular detail below. The independent elements resulting from the ectopic arch 1 joint are referred to as Meckel’s cartilage ventral (mv) and Meckel’s cartilage intermediate (mi). Arch 1-derived dermal bones indicated are the dentary (d), maxilla (mx) and entopterygoid (en). Arch 2-derived cartilages include the ceratohyal (ch) and hyosymplectic (hs), which are divided by the interhyal joints (ihj) and the ectopic ceratohyal joint (chj). Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
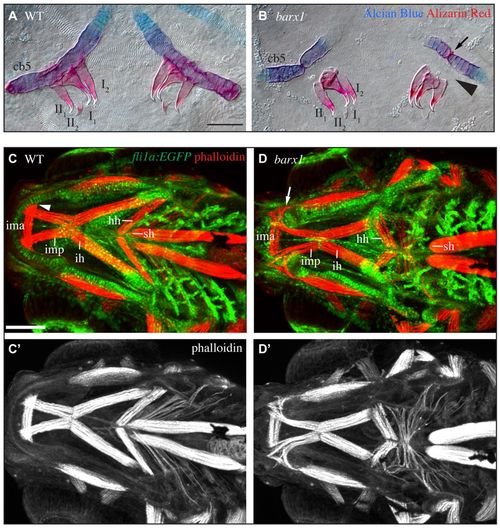
barx1 mutant zebrafish display tooth and muscle phenotypes. (A,B) 5 dpf Alcian Blue- and Alizarin Red-stained ceratobranchial 5 (cb5) and pharyngeal teeth (annotated I1-II2) were dissected and imaged with transmitted light. Arrow indicates ectopic joint in cb5. Arrowhead illustrates missing bone of attachment. Ventral view, anterior is upwards, right is towards the left. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C,D) Confocal projections of 5 dpf larvae with pharyngeal arch derivatives transgenically labeled with EGFP (fli1a:EGFP, green) and muscles stained with phalloidin (red). Ventral view, anterior is towards the left, left is upwards. Labeled muscles include the intermandibularis posterior (imp), intermandibularis anterior (ima), interhyoideus (ih), hyohyoideus (hh) and sternohyoideus (sh). Arrowhead indicates imp attachment site in wild types, arrow indicates disorganized imp invading the ectopic gap in Meckel’s cartilage in mutants. (C′,D′) Single channel phalloidin fluorescence. Scale bar: 100 μm. |
|
barx1 is excluded from differentiating joint cells but maintained in the subintermediate domain. (A-C′) In situ hybridization was carried out to reveal wild-type barx1 expression (red) in the context of sox9a expression (green). (D-E′′) Fluorescent in situ hybridization revealed wild-type barx1 expression (green) in the context of hand2 (red) and nkx3.2 (blue) expression. Labeled pharyngula period anatomy includes the stomodeum (s), pharyngeal arch 1 (a1), pharyngeal pouch 1 (p1) and pharyngeal arch 2 (a2). Labeled hatching period anatomy includes the Meckel’s (mc) and palatoquadrate cartilages (pq), which are divided by the jaw joint (jj). Arrowheads indicate barx1 expression distal to the jaw joint in the subintermediate domain. Arrows indicate overlap between barx1 and hand2. Asterisk in D marks the ventral-most aspect of hand2 expression. In all images, anterior is towards the left, dorsal is upwards. All images are single confocal sections. Scale bars: 100 μm. (F,G) Outlines of gene expression data in A-E′′. Intermediate (I), subintermediate (S) and ventral (V) domains, and Meckel’s cartilage intermediate (mi), subintermediate (ms) and ventral (mv) are indicated. |
|
Ectopic joint cells are present in barx1 mutant zebrafish. (A,B) All cells were stained with SYTO59 (red), and chondrocytes transgenically labeled with EGFP (sox9a:EGFP, green) in 4 dpf animals. (C,D) 66 hpf larvae were subjected to in situ hybridization to label cartilage (sox9a, green) and joint cells (chd, red). (E,F) Live larvae with chondrocyte cell membranes transgenically labeled with RFP (sox10:mRFP, red) and joint region cells labeled with EGFP (trps1:EGFP, green) were imaged. (G,H) 72 hpf larvae with chondrocytes transgenically labeled with EGFP (sox9a:EGFP, green) were stained with anti-collagen type II antibody (red). Skeletal elements are oriented and labeled as in Fig. 1F. Arrowhead indicates boundary between distinct chondrocyte populations. All images are single confocal sections. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
Ectopic barx1 represses the jaw joint. (A-D) Alcian Blue- (cartilage) and Alizarin Red- (bone) stained 4 dpf larval zebrafish skeletons were dissected and imaged with transmitted light. An asterisk indicates jaw joint loss. Skeletal elements are oriented and labeled and as in Fig. 1F. Anterior is towards the left; dorsal is upwards in all panels. Scale bar: 50 μm. (E-G′) 4 dpf larval zebrafish skeletons from animals injected with misexpression constructs and stained with Alcian Blue (cartilage) and Alizarin Red (bone) were imaged with transmitted light. Asterisks indicate joint loss. Scale bar: 50 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
hand2 is epistatic to barx1. (A-D) Alcian Blue- (cartilage) and Alizarin Red- (bone) stained 4 dpf larval zebrafish skeletons were dissected and imaged with transmitted light. An asterisk indicates jaw joint loss. Skeletal elements are oriented and labeled and as in Fig. 1F. Anterior is towards the left; dorsal is upwards in all panels. Scale bar: 50 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
barx1 negatively regulates hand2. (A-F′′) Wild-type and barx1 mutant animals were subjected to fluorescent in situ hybridization to reveal sox9a, nkx3.2 and hand2 expression during the pharyngula (A-B′′) and hatching (C-F′′) periods. Arrow indicates ventrally restricted hand2; arrowhead indicates expanded hand2 expression. All panels are single confocal sections. (G,H) Animals were subjected to in situ hybridization to reveal midline-restricted hand2 expression in wild type (arrow) and expanded hand2 expression in barx1 mutants (arrowhead). (I,J) hand2-expressing cells were transgenically labeled with E2Crimson (hand2:Crimson, red) and chondrocytes with EGFP (sox9a:EGFP, green), and imaged by time-lapse microscopy. Movie excerpts are z-projections from the ventral perspective. Arrow indicates downregulated hand2 reporter in differentiated cartilages; arrowhead indicates persistent hand2 reporter. Dorsal is upwards and anterior is towards the left in A-D; anterior is towards the top, while right is towards the left in E-J. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
hand2 regulates barx1 positively and negatively early and late, respectively. (A-D) barx1 expression was revealed by in situ hybridization and imaged with transmitted light. Labeled pharyngula period anatomy includes the stomodeum (s) and the eye (e). Labeled hatching period anatomy includes the mouth (m) and the eye (e). Arrow and arrowhead indicate reduced and expanded ventral barx1 expression, respectively. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
Skeletal phenotype variability in barx1 mutant zebrafish. (A-D) Zebrafish heterozygous for barx1fh330 and barx1fh331 alleles were crossed and offspring were stained with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red, dissected and imaged with transmtted light. Genotyped trans-heterozygotes displayed barx1-associated phenotypes revealing that these two alleles fail to complement. Anterior is towards the left; left is upwards. (E-P) Alcian Blue- and Alizarin Red-stained larvae were dissected and flat mounts imaged to reveal the range of phenotypic severity found in barx1 mutants. Anterior is towards the left; dorsal is upwards. Scale bar: 10 μm. |