- Title
-
ccdc80-l1 Is Involved in Axon Pathfinding of Zebrafish Motoneurons
- Authors
- Brusegan, C., Pistocchi, A., Frassine, A., Della Noce, I., Schepis, F., and Cotelli, F.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
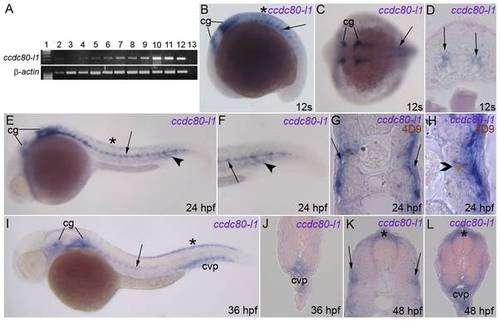
Expression of ccdc80-l1 analyzed by RT-PCR and WISH. (A) RT-PCR performed on different embryonic stages and adult tissues; the expression of ccdc80-l1 and β-actin are shown. Lanes are: ladder (lane 1), ovary (lane 2), 2–4 cells stage (lane 3), 64–1000 cells stage (lane 4), 30% epiboly (lane 5), 60–70% epiboly (lane 6), somitogenesis (lane 7), 24 hpf (lane 8), 30 hpf (lane 9), 48 hpf (lane 10), 72 hpf (lane 11), adult muscle (lane 12) and negative control (lane 13) in the absence of cDNA. (B–J) WISH performed on zebrafish embryos at several stage of development. (B, C) During somitogenesis ccdc80-l1 was expressed by cranial ganglia (cg), dorsal dermis (asterisk), adaxial cells and muscle pioneers at the level of the horizontal myoseptum (arrow). (D) ccdc80-l1 expression in a transverse section of the trunk of an embryo at 12 somites stage (arrows). (E–H) At 24 hpf, the hybridization signal was detectable in cranial ganglia (cg), dermis (asterisk), adaxial cells (arrow) and ventral somites (arrowhead). (F) Higher magnification of the tail at 24 hpf. (G) Transversal section of an embryo at 24 hpf. (H) Transversal section showing that at 24 hpf ccdc80-l1 hydridization signal co-localized with the nuclear labeling of 4D9 antibody, corresponding to the engrailed-positive muscle pioneers population (open arrowhead). (I, J) At 36 hpf, the signal of ccdc80-l1 probe was detected in cranial ganglia (cg), migrated adaxial cells (arrow), dorsal dermis (asterisk) and caudal vein plexus region (cvp). (K, L) At 48 hpf, ccdc80-l1 was detected in dorsal dermis (asterisk), external adaxial cells (arrows in K) and caudal vein plexus region (cvp in L). (B, E, F, I) Lateral views; dorsal is up, anterior is left; (C) dorsal view, anterior is left; (D,G, H, J–L) transversal sections, dorsal is up. |
|
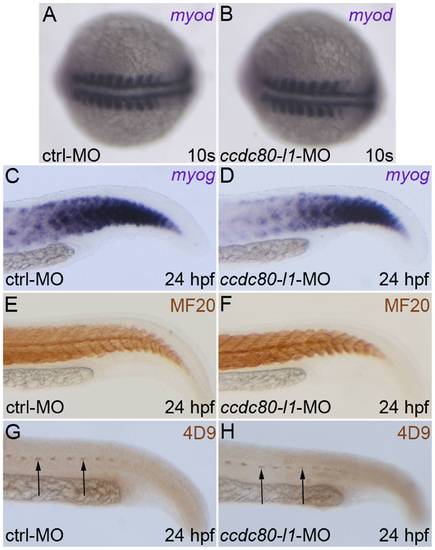
Analysis of myogenic markers expression and muscle pioneers in ccdc80-l1 morphant embryos. (A–D) The myogenic markers myod (A, B) and myog (C, D) were correctly expressed both in control and morphants embryos at 10 s stage (A, B) and 24 hpf (C, D), respectively. (E, F) The MF20 antibody staining showed that both slow and fast twitch fibers were correctly formed and distributed in control and in knocked-down embryos at 24 hpf. (G, H) At the same developmental stage, muscle pioneers resulted unaffected after ccdc80-l1 loss-of-function, as shown by the labeling with 4D9 antibody (anti-engrailed) (arrows). (A, B) Dorsal views, anterior is left; (C–H) lateral views of the tails, dorsal is up and anterior is left. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
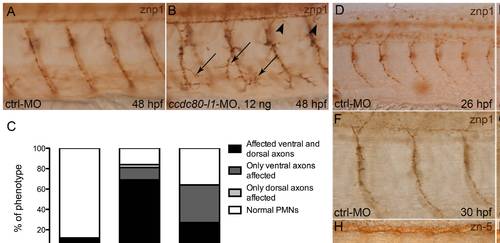
Analysis of motoneurons morphology by means of znp1- and zn-5-immunohistochemistry. (A, B) At 48 hpf, using 12 ng/embryo of morpholino, both ventral (arrows) and dorsal axons (arrowheads) were mis-orientated and over-branched in morphants (B) in comparison to control embryos (A). (C) Statistical analysis showing the percentages of the different phenotypes (affected ventral axons, dorsal axons or both) occurring in control embryos and in morphants, when different doses of ccdc80-l1-MO were injected (12 ng/embryo and 8 ng/embryo). Using a lower dose of morpholino (8 ng/embryo), we observed that in a significant percentage of embryos only ventral axons were defective. (D–G) Immunohistochemistry performed at 26 hpf (D, E) and 30 hpf (F, G) confirmed that loss-of-ccdc80-l1-function affects both CaPs (arrows) and MiPs (arrowheads) axonal migration. (H, I) The same analysis performed at 48 hpf using zn-5 antibody revealed that also SMNs axonal migration is impaired in morphants (arrows in I) in comparison to control embryos (H). (A, B; D–I) Lateral flat-mount preparation was applied for a better visualization of the motoneurons. Lateral views of the trunk region overhanging the yolk extension, dorsal is up and anterior is left. |
|
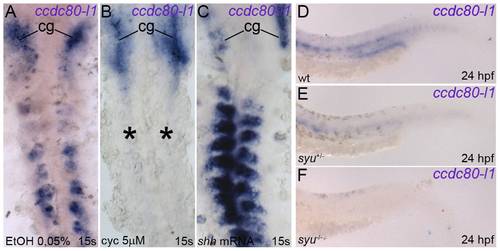
ccdc80-l1 is positively regulated by shh. (A–C) ccdc80-l1 expression in somites and myoseptum resulted strongly inhibited in embryos treated with 5 μM cyclopamine (asterisks in B), in comparison to control embryos at the same developmental stage (A). By converse, over-expression of shh led to an up-regulation of ccdc80-l1 in muscular territories (C). Expression in cranial ganglia (cg) was never perturbed. (D–F) ccdc80-l1 resulted slightly down-regulated in the muscles of heterozygous syu+/- mutants (E) in comparison to wild type siblings (D). A strikingly down-regulation was observed in homozygous syu-/- mutants (F). (A–C) Dorsal flat-mount preparations, anterior is up. (D–F) Lateral views of the tails, anterior is left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
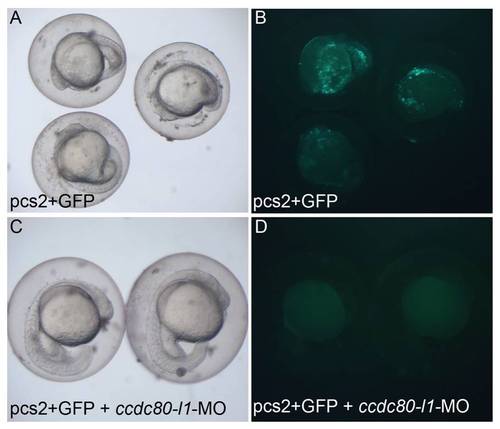
ccdc80-l1 morpholino is capable to inhibit the expression of the fluorescent protein GFP. This assay was performed in order to verify the in vivo efficiency of ccdc80-l1-MO. (A, B) In the 70% of embryos injected with the ccdc80-l1-GFP sensor plasmid, the presence of fluorescent GFP signal was detected (N = 20). (C, D) When the plasmid was injected together with the morpholino, the transcription of GFP protein was inhibited and the percentage of fluorescent embryos decreased to 51% (N = 93). In A and C embryos are visualized under normal light, in B and D under fluorescent light. |
|
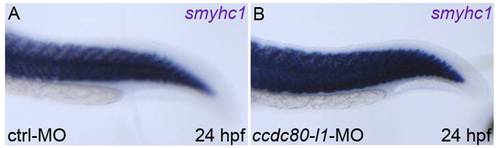
The expression pattern of the slow-myosin marker smyhc1 is unaffected in ccdc80-l1 knocked-down embryos. (A, B) Loss-of-ccdc80-l1-function did not perturb the expression of smyhc1, as morphant embryos (B) are indistinguishable from control embryos (A). Lateral views of the tails, dorsal is up, anterior is left. |
|
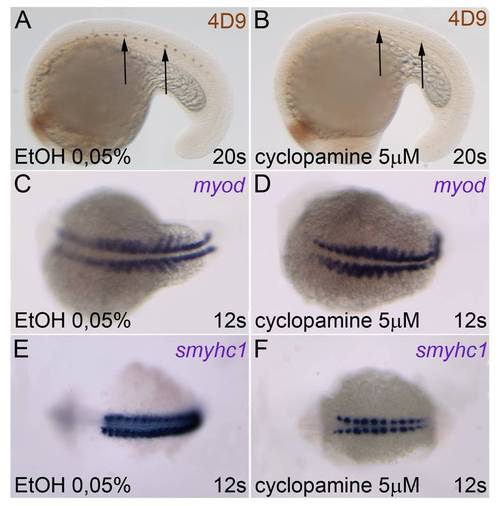
Muscle pioneers and adaxial cells are present after 5 μM cyclopamine treatment. (A, B) Labeling with 4D9 antibody (anti-engrailed) showed that muscle pioneers are not missing after pharmacological inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway (arrows). (C–F) Also adaxial cells are still present, as shown by the expression of the markers myod (C, D) and smyhc1 (E, F). (A, B) Lateral views, dorsal is up. (C–F) Dorsal views, anterior is left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
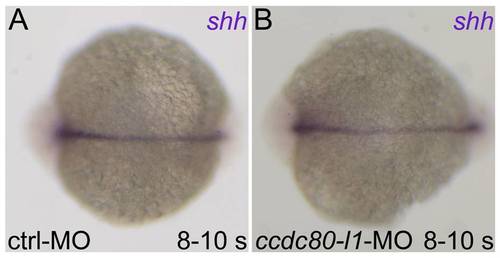
shh expression is not perturbed by loss-of-ccdc80-l1-function. (A, B) shh resulted correctly expressed both in control embryos (A) and in morphants (B). (A, B) Dorsal views, anterior is left. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements |