- Title
-
The role of stat1b in zebrafish hematopoiesis
- Authors
- Song, H., Yan, Y.L., Titus, T., He, X., and Postlethwait, J.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Mech. Dev.
|
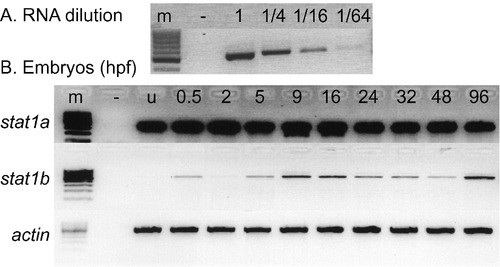
stat1 gene expression assayed by RT-PCR. A. Calibration series. A gradient of RNA dilutions and 21 amplification cycles with stat1b primers verified a semi-quantitative analysis of target mRNAs. B. Detection of stat1a and stat1b expression using RT-PCR at various stages of development using beta actin expression as loading control. RNA samples were extracted from zebrafish embryos at the indicated ages. Abbreviations: -, negative control with no RNA added; u, unfertilized eggs; 0.5, 2, etc., ages at hours post fertilization (hpf). |
|
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization shows specific expression pattern of stat1b in zebrafish hematopoietic regions. A, B. 3 and 9 hpf embryos, respectively, did not show specific expression of stat1b. C and D. At 11 hpf (2 somites), stat1b was expressed in stripes flanking the paraxial mesoderm, shown in lateral and dorsal views, respectively. E and F. At 17 hpf (18 somites), stat1b was expressed in the intermediate cell mass, shown in lateral and dorsal views, respectively. G. By 24 hpf, stat1b expression stripes had merged centrally. H. At 32 hpf, the stat1b expression compartment had spread from the intermediate cell mass to the heart and ducts of Cuvier on the yolk. I. At 48 hpf, the expression of stat1b continued in hematopoietic regions and veins. Abbreviations: dc, ducts of Cuvier; h, heart; icm, intermediate cell mass; IOC, inner optic circle; MCeV, middle cerebral vein ( Isogai et al., 2001); s, stripes flanking the paraxial mesoderm. |
|
Gene knockdowns investigate the roles of stat1a and stat1b in hematopoiesis. In situ hybridization with probes for scl (A-G), gata1 (H-N), spi1 (O-U), and mpo (V-Y) in 16 hpf embryos (A-C, H-J, O-Q) and 32 hpf embryos (D-F, K-M, R-T, V-X) injected with control sequence MO (A, D, H, K, O, R, V), stat1a MO (B, E, I, L, W), and stat1b MO (C, F, J, M, X). Quantitative PCR experiments (G, N, U, Y). Knockdown of stat1a did not alter the expression of the genes tested, but knockdown of stat1b led to increased expression of scl and gata1, markers of HSCs and erythrocytes, and to depressed expression of spi1 and mpo, markers of the myelocyte lineage. These results would be expected if normal stat1b activity helped promote a lineage switch from the erythroid to the myeloid lineage. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Histochemical staining of hemoglobin with o-dianisidine. A. Embryos stained with o-dianisidine: uninjected controls (UIC, 1-3), control MO injected embryos (CMO, 4-6), stat1a MO treated embryos (7-9), and stat1b MO treated embryos (10-12). Knockdown of stat1b caused an increase in hemoglobin staining in the trunk compared to controls and stat1a MO injected embryos. B. Quantitative analysis of o-dianisidine-stained embryos, ten individuals scored for each of the four conditions. Pixels of o-dianisidine positive cells were counted and summed. Compared to the uninjected control using a t-test (single tailed), P values for significant only for stat1b MO (p = 0.0014), and were not significant for control MO (0.337) or stat1a MO (0.108). PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 128(7-10), Song, H., Yan, Y.L., Titus, T., He, X., and Postlethwait, J.H., The role of stat1b in zebrafish hematopoiesis, 442-56, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.