- Title
-
Zebrafish as a potential model organism for drug test against hepatitis C virus
- Authors
- Ding, C.B., Zhang, J.P., Zhao, Y., Peng, Z.G., Song, D.Q., and Jiang, J.D.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
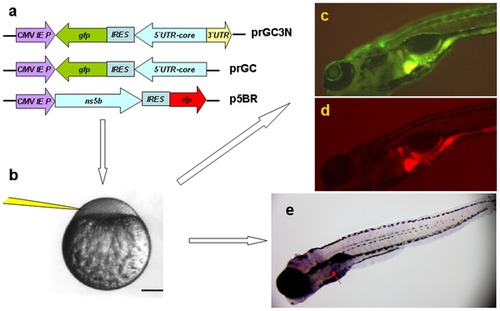
Zebrafish as a model organism for HCV sub-replicon amplification. a. The HCV sub-replicon was created with prGC3N and p5BR vectors. Cartoons are for vector prGC3N, prGC and p5BR. CMV promoter was for transcription. prGC3N has a gfp-IRES(EMCV)-core-52UTR sequence that was reversely inserted at the downstream of CMV promoter and followed by a HCV 32UTR sequence in a forward direction; prGC has no HCV 32UTR; the p5BR is a functional vector carrying HCV RNA polymerase (NS5B) and RFP. b. Co-injection of the sub-replicon into zebrafish zygote blastomere. c. Fluorescent microscopy examination for HCV core protein amplification in zebrafish liver using a GFP filter (480 nm excitation, 505 nm emission; image, 100X). d. Fluorescent RFP filter (556 nm excitation, 586 nm emission) was used to detect liver HCV NS5B protein signal in red. e. The whole mount in situ nucleic acid hybridization was used to detect the positive strand of HCV core RNA, in order to confirm the green fluorescent signal for the replication of the HCV sub-replicon. |
|
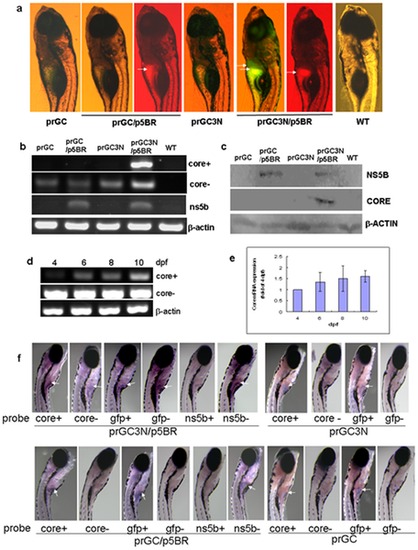
Amplification of the HCV sub-replicon in liver of the zebrafish larvae. a. HCV sub-replicon amplified in those co-injected with prGC3N and p5BR vectors. Green fluorescence represents the NS5B-dependent HCV core protein products of the sub-replicon (prGC3N/p5BR); red fluorescence indicates the presence of the NS5B enzyme. Arrows point the positive signals in liver area. WT, untreated control. b. RT-PCR measurement for the amplification of the study genes in the sub-replicon. Core+, the positive strand of HCV core RNA; core-, the negative strand of HCV core RNA; ns5b, HCV ns5b from p5BR; and beta-actin, loading control. WT, wild type. c. Western blot for HCV core and NS5B proteins with anti-core or anti-NS5B antibody, respectively. Beta-actin was loaded as a control. d. Amplification of the HCV sub-replicon exhibits a time–dependent increase from 4- to 10-dpf in zebrafish larvae for the positive strand of core RNA; negative strand core RNA and beta-actin remains to be constant. dpf, day post fertilization. e. Confirmation of the time–dependent amplification of the HCV sub-replicon with quantitative real time RT-PCR for the positive strand of HCV core RNA. f. Whole mount in situ hybridization of the co-injected zebrafish. Whole mount in situ hybridizations were carried out on 10-dpf larvae using antisense or sense RNA probes. The presented are original microscopy images of the zebrafish larvae (80X). dpf, day post fertilization. |
|
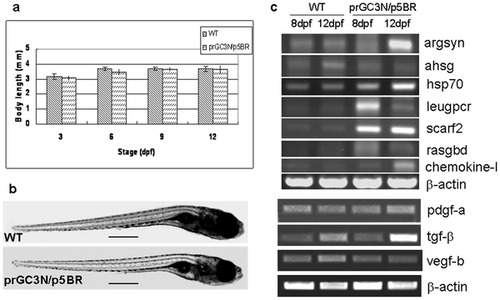
Biological effects on zebrafish larvae after injection of the HCV sub-replicon. a. Body length of the wild type larvae and those co-injected with prGC3N/p5BR. b. Phenotype of wild type larvae and those co-injected with prGC3N/p5BR. The scales represent 500 um. c. Expression of the HCV-associated genes in zebrafish larvae. The mRNA level of the study genes were examined with RT-PCR reaction in wild-type and the prGC3N/p5BR co-injection larvae (8 dpf and 12 dpf). |