- Title
-
A screen for hoxb1-regulated genes identifies ppp1r14al as a regulator of the rhombomere 4 Fgf-signaling center
- Authors
- Choe, S.K., Zhang, X., Hirsch, N., Straubhaar, J., and Sagerström, C.G.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
An ectopic expression/dissection strategy to identify hoxb1b-regulated genes. (A–C) Uninjected (A), meis3 + βgal mRNA-injected (B) or meis3 + hoxb1b mRNA-injected (C) embryos were analyzed by in situ hybridization for expression of krox20. The position of r5 is indicated by arrows and the site where the anterior embryo was dissected is indicated by black lines in A–C. (D–E) Quantitative RT-PCR was used to assay expression of tubulin (D) and krox20 (E) in meis3-injected and meis3 + hoxb1b-injected embryos. Two independent injections are shown in E. Embryos in A–C were flat mounted at 14hpf and are shown in dorsal view with anterior to the top. |
|
Expression patterns of hoxb1b-regulated genes. 30 genes identified as up-regulated by hoxb1b (see Table 1 and Table S1) were assayed by in situ hybridization to determine their expression patterns. All embryos are at 14hpf and are shown as whole mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. The Unigene ID for each gene is given in the lower right of each panel and corresponds to the Unigene IDs in Table 1 and Table S1. Expression patterns of hoxb1b-regulated genes. 30 genes identified as up-regulated by hoxb1b (see Table 1 and Table S1) were assayed by in situ hybridization to determine their expression patterns. All embryos are at 14hpf and are shown as whole mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. The Unigene ID for each gene is given in the lower right of each panel and corresponds to the Unigene IDs in Table 1 and Table S1. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Hindbrain expression patterns of hoxb1b-regulated genes. 18 hoxb1b-regulated genes identified as expressed in the hindbrain were assayed by themselves (1st and 3rd column) or as double in situ hybridization together with krox20 (2nd and 4th column; krox20 is expressed in r3 and r5 and is detected in red). Based on the double in situ hybridizations, it was determined which rhombomeres express each of the novel genes and this is indicated in each panel in columns 1 and 3. All embryos are at 14hpf and are shown as whole mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. In situ panels in columns 1 and 3 are duplicated from Fig. 2 for ease of comparison. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
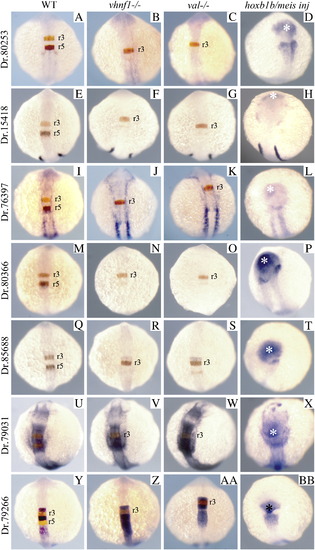
Expression of hoxb1b-regulated genes in vhnf1 mutant, valentino mutant and hoxb1b/meis3-injected embryos. Seven hoxb1b-regulated genes were analyzed for their expression in wild type (A, E, I, M, Q, U, Y), vhnf1 mutant (B, F, J, N, R, V, Z), valentino mutant (C, G, K, O, S, W, AA) or hoxb1b + meis3-injected (D, H, L, P, T, X, BB) embryos. Genes were analyzed as double in situ hybridizations with krox20 (A–C, E–G, I–K, M–O, Q–S, U–W, Y–AA; krox20 detected in red) or as single in situ hybridizations (D, H, L, P, T, X, BB). All embryos are at 14hpf and are shown as whole mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. In situ panels in the left-hand column are duplicated from Fig. 3 for ease of comparison. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
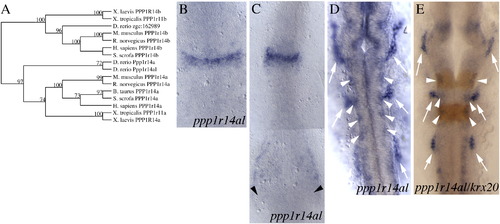
Sequence and expression analysis of the ppp1r14al gene. (A) Phylogenetic tree demonstrating that zebrafish ppp1r14al groups with other ppp1r14a genes, not with ppp1r14b genes. (B–E) ppp1r14al expression pattern at 9hpf (B), 11hpf (C) and 20hpf (D, E). Arrows indicate cranial placodes (D, E) and arrowheads indicate staining in ventral mesoderm (C) and in the lateral neural tube (D, E). E is a double in situ hybridization with krox20 detected in red. Embryos in B–E are shown as flat mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Disruption of ppp1r14al leads to loss of fgf3 expression. (A–N) Control (A, C, E, G, I, K, M) and ppp1r14al MO-injected (B, D, F, H, J, L, N) embryos were assayed for expression of fgf3 at 10.5hpf (A, B), DUSP2 at 10.5hpf (C, D), hoxb1a at 11.5hpf (E, F) krox20 at 10.5hpf (G, H) and at 12hpf (I, J), pea3 at 12hpf (K, L) and valentino at 12.5hpf (M, N). (O–R) Analysis of fgf3 expression in control (O), ppp1r14al MO-injected (P), ppp1r14al MO + ppp1r14al mRNA injected (Q; note that mRNA is mutated to resist MO effect) reveals rescue of the ppp1r14al MO phenotype at 10.5hpf. Actual data is given in R. Phenotypes were scored as severe (similar to panel P), or mild (similar to panel B). Embryos in A–Q are shown as flat mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
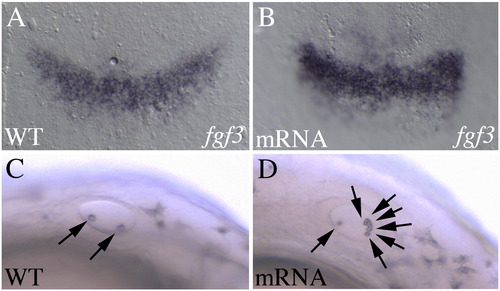
Overexpression of ppp1r14al leads to elevated fgf3 expression. Control (A, C) or ppp1r14al mRNA-injected (B, D) embryos were assayed for fgf3 expression (A, B), or observed under brightfield for the presence of otoliths (C, D). A, B are shown as flat mounts in dorsal view with anterior to the top. C, D are live embryos in lateral view with anterior to the left. Arrows in C, D indicate otoliths. |
|
Combined loss of ppp1r14al and fgf8 function leads to disruption of the r4 signaling center. Uninjected (A, E, I), fgf8 MO-injected (B, F, J), ppp1r14al MO-injected (C, G, K) or fgf8 + ppp1r14al MO-injected embryos (D, H, L) were assayed for expression of krox20 (A–D), pea3 (E–H) or valentino (I–L) by in situ hybridization. All embryos are dorsal views at 11hpf with anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
ppp1r14al is regulated by Hoxb1b together with Pbx and Meis cofactors. (A–C) ppp1r14al expression was analyzed in control (A), dominant negative Meis-injected (B) and hoxb1b/pbx4/meis3-injected (C) embryos. Embryos in A–C are flat mounts at 11hpf in dorsal view with anterior to the top. (D) Chromatin immunoprecipitation from 11hpf zebrafish embryos revealed binding of Hoxb1b (top panel), Meis and Pbx (bottom panel) proteins to the regulatory region of ppp1r14al. Asterisks indicate values that are statistically different (p < 0.05) from the control value based on Student′s T-test. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 358(2), Choe, S.K., Zhang, X., Hirsch, N., Straubhaar, J., and Sagerström, C.G., A screen for hoxb1-regulated genes identifies ppp1r14al as a regulator of the rhombomere 4 Fgf-signaling center, 356-67, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.