- Title
-
Characterisation of expression patterns and functional role of Cactin in early zebrafish development
- Authors
- Atzei, P., Yang, F., Collery, R., Kennedy, B.N., and Moynagh, P.N.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
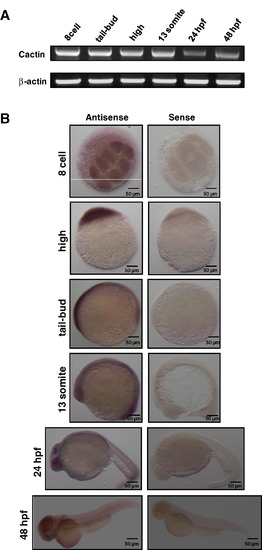
Expression of zCactin during early embryonic developmental stages. (A) Total RNA (50 ng) was isolated from staged embryos and analyzed by RT-PCR using specific primers for zCactin. β-actin mRNA expression was determined as a control housekeeping gene. Sizes of zCactin and β-Actin fragments are 500 and 322 bp, respectively. Results are indicative of three independent experiments. (B) In situ hybridisation shows zCactin mRNA expression at a variety of embryonic developmental stages. zCactin is expressed from 8-cell stage to 48 hpf, where it strongly presents in the eyes. The sense probe was used as a negative control. Images were acquired using a Zeiss Axioplan II microscope and processed using Adobe Photoshop. |
|
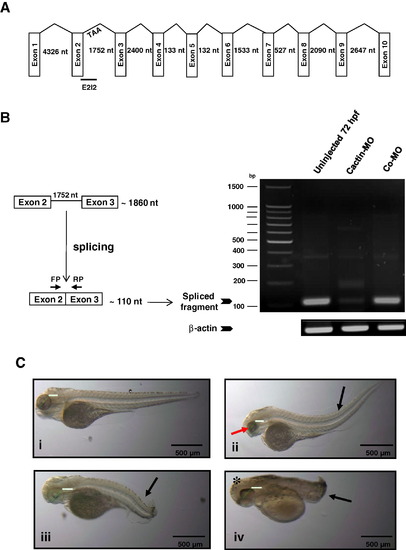
Knockdown of zCactin by specific morpholino antisense oligonucleotide causes developmental abnormalities. (A) Schematic representation shows the genomic organisation of the zCactin gene (not in scale). Splice site targeted by E2I2 morpholino is shown. Stop codon in intron 2 is indicated (TAA). (B) The efficacy of the morpholino was validated by RT-PCR using a forward primer (FP) and reverse primer (RP) as indicated in uninjected embryos, Cactin morpholino (Cactin-MO) and control morpholino (Co-MO) injected embryos. The PCR products of the spliced form are illustrated together with a PCR fragment of the β-actin housekeeping gene. (C) Representative images of embryos (72 hpf) injected with control morpholino (Co-MO) (i) or Cactin morpholino (Cactin-MO) (ii–iv) (300μM) are demonstrated and are representative of three independent experiments. Each experiment comprised of two groups of embryos injected with each morpholino (98, 112 and 74 embryos for Cactin-MO and 90, 152 and 88 embryos for Co-MO). Black arrows indicate bent body characteristics, the red arrow points to smaller eye size and the asterisk shows the more rounded head phenotype. Eye size was measured (green line); for Co-MO: 736.42μm; for Cactin-MO: 558.77, 597.26 and 808.78 μm. Images were acquired using a Zeiss Axioplan II microscope and processed using Adobe Photoshop. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
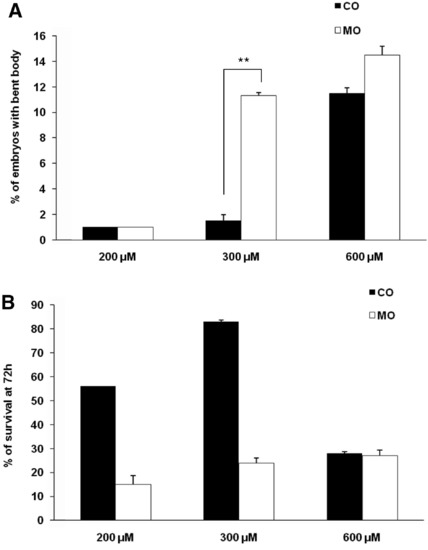
Specificity of effects of zCactin morpholino oligonucleotides. Embryos were injected with 200, 300 and 600 μM of Cactin morpholino (MO) and control morpholino (Co) and monitored from day 0 to 72 hpf. Embryos were scored for (A) bent body phenotype and (B) viability from at least three independent experiments. **p < 0.01 paired Students t test. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
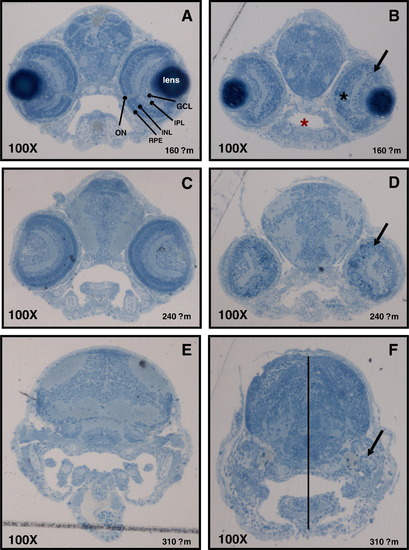
Characterisation of developmental defects associated with zCactin knockdown. The control morpholino (A, C and E) and Cactin morpholino embryos (B, D and F) at 72 hpf were processed for light microscopy sectioning. Sections at depths of 160, 240, 310 μm into the anterior embryo were obtained using a diamond knife mounted on a Leica EMUC6 ultramicrotome. For histological examination the sections were stained lightly with 1% toludine blue. Distinct layers stratify ganglion, amacrine, bipolar, horizontal and Muller cells as well as rod and cone photoreceptors cells (A). ON, optic nerve; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigmented epithelium. Black arrows indicate the dysmorphic layer of the eye (panel C, F and I). Red asterisk shows the smaller oral cavity in the morphant section (panel C), while black asterisk indicates the more spherical shape of the eye (panel C). Dotted line shows the reduced distance between the crown and the mandibular arch (panel F). Microscopical images were captured using a Leica DM LB microscope equipped with a Leica DFC 480 digital camera. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 10(4-5), Atzei, P., Yang, F., Collery, R., Kennedy, B.N., and Moynagh, P.N., Characterisation of expression patterns and functional role of Cactin in early zebrafish development, 199-206, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns