- Title
-
Essential requirement for zebrafish anosmin-1a in the migration of the posterior lateral line primordium
- Authors
- Yanicostas, C., Ernest, S., Dayraud, C., Petit, C., and Soussi-Yanicostas, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
Transcription of the kal1a and kal1b genes and accumulation of anosmin-1a and anosmin-1b, throughout PLLP migration. In situ detection of kal1a (A–F and J) and kal1b (G–I and K) transcripts in 22 to 38 hpf whole-mount embryos. Magnified views of the primordium at 32 hpf (J and K). The direction of migration is from anterior to posterior. Whole-mount immunodetection of anosmin-1a (L–N) and anosmin-1b (M–O) in 30 hpf embryos. Magnified views of the embryos shown in panels L (N) and M (O). Prim: PLLP; L2: neuromast 2; pL2, pL3: proneuromasts 2 and 3. neu: differentiated neuromasts. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Morpholino-mediated kal1a, but not kal1b, inactivation impairs PLL neuromast deposition as visualized by DASPEI staining. Wild-type (WT) embryo (A), MO kal1a (0.25 mM) (B) or (0.5 mM) (C), mmMO kal1a (0.5 mM) (D), MO kal1b (0.5 mM) morphants (E) and MO kal1a (0.5 mM) morphant co-injected with MO kal1a-insensitive kal1a RNA (1 μM) (F). Time course of neuromast deposition in WT embryos (n = 48), kal1a (0.5 mM) (n = 53) and kal1b (0.5 mM) morphants (n = 45) from 3 to 8 dpf (G). Values are means ± s.e.m. Western blot analysis of anosmin-1a accumulation (H) in 3 dpf WT embryos (1), mmMO kal1a (0.5 mM) (2), MO kal1a (0.5 mM) (3) and (0.1 mM) morphants (4) and anosmin-1b accumulation (I) in 3 dpf WT embryos (1), MO control (2) and MO kal1b (0.5 mM) morphants (3). Neuromast organization in wild-type embryos (J–J″ and L) and intermediate MO kal1a (0.25 mM) morphant (K–K″ and M) visualized by DASPEI staining of hair cells on ClaudinB::GFP embryos (J–K″) and in situ detection of tacstd transcripts in neuromast support cells (L, M). L1–L6: neuromasts lined up along the flanks of embryos; ter: neuromasts clustered in the tail region. Arrows indicate neuromasts. n: neuromast. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
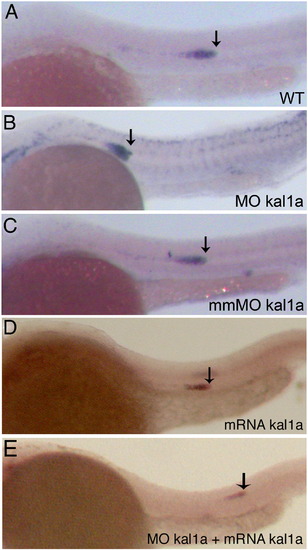
Migration of the PLLP is defective following inactivation of the kal1a, but not kal1b, gene as visualized by whole-mount in situ detection of cxcr4b RNAs at 28 hpf. Wild-type (WT) embryo (A), MO kal1a (0.5 mM) (B) and mmMO kal1a morphants (0.5 mM) (C), embryo injected with MO kal1a-insensitive kal1a RNA (1 μM) alone (D) and MO kal1a (0.5 mM) morphant injected with MO kal1a-insensitive kal1a RNA (1 μM) (E). Arrows indicate the leading edge of the migrating PLLP. |
|
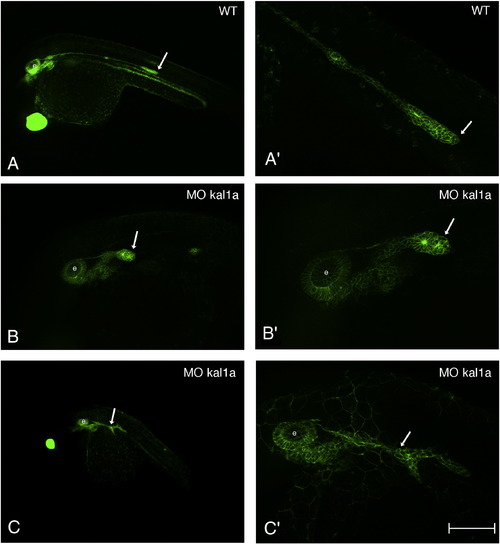
Kal1a inactivation affects the morphology of the PLLP. 28 hpf ClaudinB::GFP embryo (A and A′) and ClaudinB::GFP embryos injected with MO kal1a (0.5 mM) (B to C′). Magnified views of the primordium of the embryos shown in panels A (A′), B (B′) and C (C′). Arrows indicate the PLLP. e: ear. Scale bar = 200 μm in panels A, C, 100 μm in panel B and 50 μm in panels A′–C′. |
|
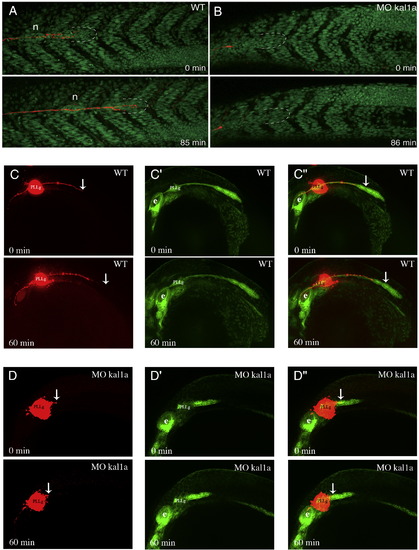
Kal1a inactivation severely compromises PLLP migration as shown by DiI labelling of the axon of PLL sensory neurons in H2A.F/Z::GFP (A and B) and ClaudinB::GFP (C to D″) embryos. In vivo imaging of PLLP migration by time-lapse confocal microscopy from 32 to 33.5 hpf in a H2A.F/Z::GFP embryo (A) and a H2A.F/Z::GFP MO kal1a (0.5 mM) morphant (B), and apotome microscopy from 26 to 27 hpf in a ClaudinB::GFP embryo (C to C″) and a ClaudinB::GFP MO kal1a (0.5 mM) morphant (D to D″) following DiI injection into the PLLP ganglion. Dashed lines: PLLP leading edge; n: recently deposited neuromast. PLLg: posterior lateral line ganglion, e: ear, WT: wild-type. Arrows indicate the tip of the PLLP nerve. Anterio-posterior axis is from left to right. |
|
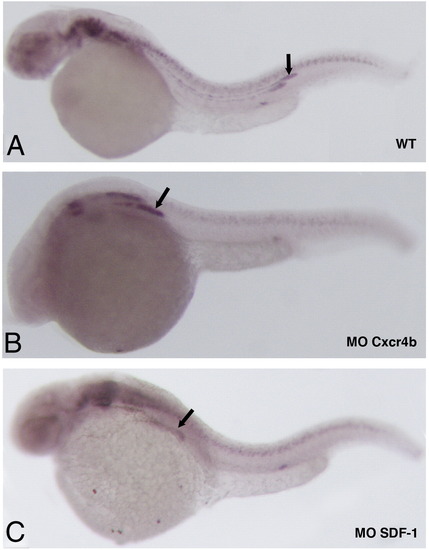
Kal1a transcription in the PLLP is independent of CXCR4b/SDF1a signalling. In situ detection of kal1a transcripts on whole-mount 28 hpf wild-type embryo (A) and cxcr4b (B) and sdf1a morphants (C). Arrows indicate the PLLP. |
|
Moderate depletion of both anosmin-1a and SDF1a markedly affects PLLP migration. 26 hpf ClaudinB::GFP embryo (A) and ClaudinB::GFP embryos injected with MO sdf1a (0.1 mM) (B), MO kal1a (0.1 mM) (C) or co-injected with a mix of MO sdf1a and MO kal1a (0.1 mM each) (D). Magnified views the primordium of the embryo shown in panel D (D′ and D″). Arrows indicate the PLLP. e: ear. Scale bar = 200 ′m in panels A–C, 300 ′m in panel D, 100 μm in panel D′ and 50 μm in panel D″. |
|
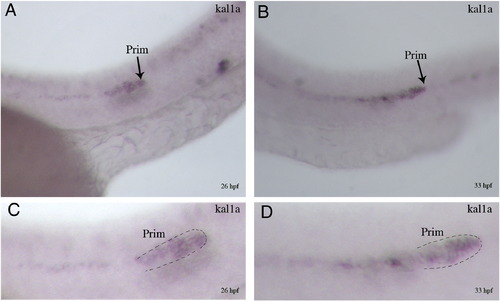
Pattern of kal1a transcript accumulation in primordia of 26 (A, C) and 33 hpf (B, D) whole-mount embryos. Magnified views of the primordium of the embryos shown in A (C) and B (D). Arrows (A and B) and dashed lines (C and D) indicate the leading edge of primordia. Prim: primordium. |
|
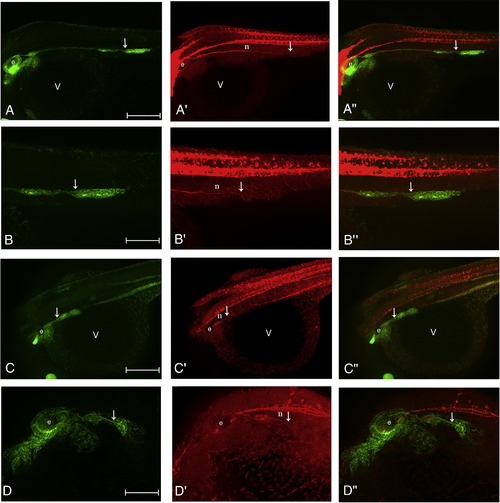
Localisation of anosmin-1a in the anterior lateral line primordium (ALLP) and head neuromast hair cells. Pattern of accumulation of anosmin-1a (A′–A″) in the head region (A–D) and head neuromast hair cells (C, D) of 26 hpf ClaudinB::GFP embryos. Merge image of the photographs shown in A and A′ (A″). White arrows indicate the ALLP. e: ear; v: vitellus; n: neuromast; ALLP: anterior lateral line primordium. |
|
Embryonic development is not delayed following kal1a inactivation. Pigmentation pattern and morphology of 3 (A–B′) and 4 dpf (C–D′) wild-type embryos (A, A′, C and C′) and MO kal1a (0.5 mM) morphants (B, B′, D and D′). Magnified views of the head of the embryos shown in A (A′), B (B′), C (C′) and D (D′). Arrows indicate the mouth. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Kal1a inactivation compromises terminal elongation of the PLLP nerve within the migrating primordium. DiI labelling of the axon of PLL sensory neurons in control H2A.F/Z::GFP embryos (A) and following injection of MO kal1a (0.25 mM) (B) and (0.5 mM) (C). Dashed lines: PLLP leading edge. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Kal1a inactivation compromises terminal elongation of the PLLP nerve within the migrating primordium. Acetylated β-tubulin immunostaining of the PLLP nerve (A′, B′, C′ and D′) in ClaudinB::GFP embryos (A, B) and following injection of MO kal1a (0.5 mM) (C, D). Magnified views of the primordium shown in A (B), A′ (B′), A″ (B″), C (D), C′ (D′) and C″ (D″). Merge images of the photographs shown in A and A′ (A″), B and B′ (B″), C and C′ (C″) and D and D′ (D″). Arrows indicate the distal edge of the PLLP nerve. v: vitellus, e: ear. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 320(2), Yanicostas, C., Ernest, S., Dayraud, C., Petit, C., and Soussi-Yanicostas, N., Essential requirement for zebrafish anosmin-1a in the migration of the posterior lateral line primordium, 469-479, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.