- Title
-
Maternal control of vertebrate dorsoventral axis formation and epiboly by the POU domain protein Spg/Pou2/Oct4
- Authors
- Reim, G., and Brand, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
Live morphology of MZspg and Mspg mutant embryos. (A,A') Until sphere stage, mutants are indistinguishable from wild-type embryos. (B,B') Doming and epiboly is inefficient in MZspg embryos and (C,C') the blastoderm fails to flatten. (C-D') The shield forms on time, but the blastoderm has only reached 40% E in MZspg embryos. Shield and germring are thicker when compared with the wild type. (E-H') Epiboly of the YSL and EVL (yellow arrows) is uncoupled from epiboly of the blastoderm (red arrows) in MZspg embryos, which is stalled when the blastoderm covers around 60% of the yolk. (I) The notochord is split in MZspg embryos (I') and the somites fuse on the opposite site (I''). (J-N) After 1 day of development. (K,L) MZspg embryos display severe morphological abnormalities compared with wild type (J) and exhibit massive cell death (arrow in K indicates the split notochord; arrowhead in K and L indicates ventrally fused somites). (E''-H'') Mspg embryos recover completely from their initial epiboly defect until the end of gastrulation. Expressivity of the Mspg phenotype is variable: `strong' Mspg embryos (M) are dorsalized (H'',N) whereas `mild' Mspg embryos are hardly dorsalized. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
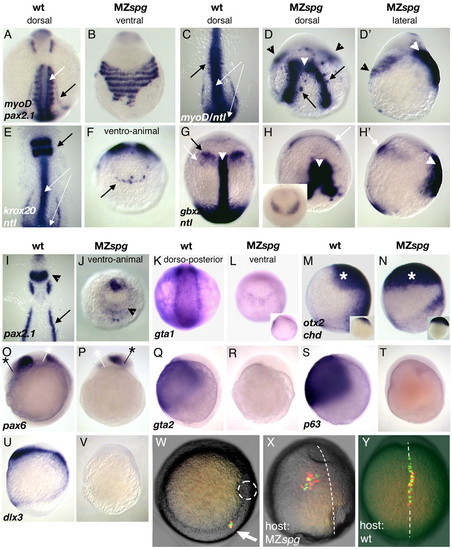
Meso- and ectodermal gene expression in MZspg embryos.(A,C) myod is expressed in wild-type somites at the eight-somite stage (white arrow). (B,D,D') Somitic myod expression is displaced and fuses ventrally in MZspg (black arrowheads in D,D'). (A,B,I,J) Pronephric pax2.1 expression (black arrows in A,I) is missing in MZspg. (C,E white arrows; G white arrowhead) ntl is expressed in the notochord and tb in wild-type embryos. (D,D',H,H', white arrowheads) ntl expression is broadened and variably split in MZspg embryos. Single ntl expressing cells are found in close proximity to the notochord (black arrows in D). (E,F) krox20 expression in rhombomere 3 and 5 (arrow) is severely reduced, and residual expression fuses at the ventral side. (G,H,H') gbx2 expression is absent at the MHB in MZspg. Mesodermal gbx2 expression (white arrows) fuses at the ventral side in MZspg. Inset in H shows ventro-animal view of MZspg solely expressing gbx2, which fuses at the ventral side. (I,J) pax2.1 expression at the MHB (arrowhead) is strongly reduced and fuses at the ventral side. (K,L) gata1 is normally expressed in blood progenitor cells. gata1 is strongly reduced in MZspg. Inset shows a lateral view of the same embryo. (M-V) Lateral views. (M,N) At tb stage otx2 (asterisk) is expressed in the wild-type forebrain and is strongly expanded to the ventral side in MZspg, manifested already at the initial phase of its expression (insets, 40-50% E). (O,P) pax6 is expressed within the wild-type forebrain and hindbrain at tb stage. pax6 domains are radialized in MZspg as indicated by white and black asterisks. (Q-V) MZspg embryos lack gata2, p63 and dlx3 expression at the end of gastrulation. (W-Y) Cell movement behavior. Bright-field images of transplanted living embryos were merged with fluorescent images taken at the same focal plane. Transplanted wild-type and MZspg cells are visualized by red or green fluorescence, respectively. (W) Animal view of a chimeric embryo transplanted at the shield stage carrying wild-type and MZspg cells in the dorsolateral germring (white arrow). A broken circle outlines the shield. (X,Y) Dorsal views of tb stage host embryos, which were transplanted as the embryo depicted in W. Broken lines indicate dorsal AP axes, anterior is towards the top. (X,Y) MZspg mutant cells are indistinguishable in their movement behavior from co-transplanted wild-type cells. (X) In MZspg embryos, convergence towards the dorsal midline and extension along the AP axis is affected in both transplanted MZspg and wild-type cells. (Y) Convergence-extension of transplanted MZspg and wild-type cells is normal in wild-type embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
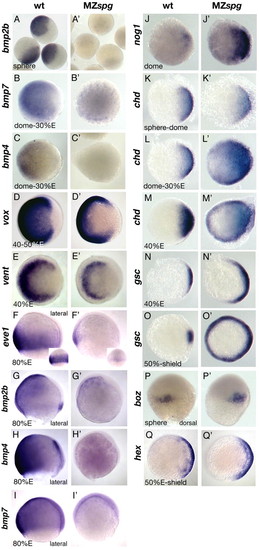
Establishment of DV patterning is disturbed in MZspg. Embryos are shown in animal views, if not indicated otherwise. (A) bmp2b initiates at the sphere stage in the wild type. (A') bmp2b is absent in MZspg at sphere stage. (B) bmp7 initiates like bmp2b at sphere stage. (B') bmp7 is strongly reduced at its initiation in MZspg.(C) bmp4 is initiated slightly later than bmp2b and bmp7 within the wild type. (C') bmp4 fails to be initiated in MZspg. (D) vox is strongly expressed during blastula stages within the wild type and is absent from the dorsal-most region. (D') vox is lost in animal regions in MZspg; however, expression remains at the ventrolateral margin. (E) vent is similarly expressed as vox in the wild type during blastula stages. (E') vent is strongly reduced in MZspg; however, ventrolateral expression remains. (F,F') During gastrulation, eve1 expression is severely reduced in MZspg. Insets show ventral views. (G,G') bmp2, (H,H') bmp4 and (I,I') bmp7 fail to be expressed in MZspg. (G') bmp2 expression in the YSL is unchanged in MZspg. (J) nog1 is faintly initiated at the dorsal side in the wild type at sphere stage and similarly expressed at dome stage. (J') nog1 is strongly expressed in MZspg and expands ectopically to ventrolateral regions by dome stage. (K,K') chd initiates at sphere stage, similar to MZspg embryos. (L,M) chd is similarly expressed slightly later in the wild type. (L') In MZspg chd is nearly ubiquitously expressed shortly after initiation. (M') Ectopic expression persists until beginning of gastrulation. (N,O) gsc is expressed at the dorsal margin in the wild-type at blastula stages, and is dorsally confined when the shield forms. (N',O') gsc is expanded ventrally within the germ ring by 30-40% E, and is ectopically expressed within the entire germ ring by beginning of shield stage. (P,P') boz expression in the presumptive dorsal organizer is normal in MZspg embryos. (Q,Q') hhex expression in the dorso-marginal YSL is normal in MZspg. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Epistasis experiments by mRNA misexpression. (A-B') Misexpression of ca-alk8 leads to a spherical embryonic shape in wild-type and MZspg embryos at the end of gastrulation, indicating ventralization. (C,C') A similar ventralization is seen after bmp2b misexpression in wild-type and MZspg embryos. (D-G) In situ hybridization analysis for pax2.1, krox20, ntl and myod expression. (D) Dorsal view of a non injected wild-type embryo. (D') Non-injected MZspg embryo, dorsal view shows ntl expression; inset shows ventral view with somitic myod expression in MZspg. (E,E') Expression of neuroectodermal genes such as krox20 and pax2.1, and of axial or paraxial markers such as ntl and myod is repressed or lost in MZspg embryos at the end of gastrulation. (F,F') A similar repression of neuroectodermal and paraxial markers is observed in bmp2b misexpressing wild-type and MZspg embryos. (G) bmp4 misexpression leads to a similar ventralization of MZspg as obtained by bmp2b misexpression. (H) Injection of bmp2b mRNA is not able to rescue endodermal sox17 expression in MZspg at tb stage. (I) Wild-type bmp2b expression. (J,K,M,N) Embryos injected with c.a.alk8-mRNA. (J) ca-alk8 misexpression slightly enhances bmp2b expression in the wild type and restores bmp2b initiation in MZspg to the wild-type expression level (K). (L) bmp4 is not expressed at sphere stage in the wild type. (M) ca-alk8 misexpression causes slight ectopic bmp4 expression at oblong-sphere stage in wild-type and MZspg embryos (N). (O-R) Embryos injected with XFD-mRNA. (O) XFD misexpression in the wild type leads to upregulation of bmp2b when compared with bmp2b expression of non-injected wild-type embryos (inset; upper embryo, 50% epiboly; lower embryo, shield stage). (P) bmp2b expression fully restores in XFD-injected MZspg embryos. (Q) bmp4 expression is not sensitive to XFD misexpression in wild-type embryos (inset shows non-injected wild-type embryos; upper embryo, 50% epiboly; lower embryo, shield stage). (R) bmp4 is not restored in XFD-injected MZspg embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The fate of dorsalized MZspg cells. (A-E) Bright field images of transplanted living larvae. (A'-E') UV images merged with bright field images. Wild-type cells (A,A') and MZspg cells (B-E') transplanted into the ventral side of wild-type host embryos can be found at pharyngula stages in locations of ventral derivatives, like blood precursors (B',C') and ventral tail tissue (D'-E'). |
|
Spatial requirement for pou2. Animal views, if not noted otherwise. (A-M) An asterisk indicates the shield. (F',H,J,L,N) Upper half with and lower half without phase contrast to show the shield, or expression, respectively. (A'-M') Bright-field images of injected living embryos were merged with UV images taken with the same adjustment. (A''-M'') UV images show EGFP expression, corresponding to A'-M'. (A-J) pou2 mRNA injection into ventro-marginal blastomeres of MZspg embryos at early cleavage stages can restore bmp4 expression. (B') bmp4 expression at beginning of shield stage in the wild-type embryo. (K-N) pou2 mRNA injection into dorsal or animal blastomeres of MZspg embryos at early cleavage stages cannot restore bmp4 expression. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

(A-F′) Mspg embryos are dorsalized. (A-C′) Lateral views. (D-E′) Dorsal views. (A,A′) bmp7 is strongly reduced in Mspg embryos. (B,B′) gta2 is strongly reduced in Mspg embryos. (C,C′) bmp4 is strongly reduced in Mspg embryos. (D,D′) ntl expression is normal in Mspg embryos. (E-F′) Expression of neuroectodermal genes is ventrally expanded (E′) or circumferential (F′) in Mspg, reflecting variable expressivity of the dorsalization phenotype among Mspg embryos. (G-K′) Fgf signaling is not affected in MZspg embryos. (G-I′) Animal views. (G-H′) Expression of the Fgf ligands fgf8 and fgf3 is normal in MZspg embryos. (I-K′) Target genes of Fgf signaling are normally expressed in MZspg. (L-R) Epiboly of YSL and EVL is normal in MZspg embryos at the tb stage. (L,M) Embryos injected at sphere/dome-stage with rhodamine-dextrane are subjected at the tb stage to pax2.1 in situ hybridization and antibody staining for rhodamine-detection to visualize the YSL (neuroectodermal and pronephric pax2.1 expression is absent in MZspg embryos). The rhodamine-dye fills the entire YSL in the wild-tyep and the MZspg embryo. (N-P) EGFP expression within nuclei of the YSL shows that the YSL completely covers the wild-type and the MZspg embryo along their animal-vegetal axis. (P) Vegetal view of an MZspg embryo focusing on the yolk-plug closure. (Q,R) The EVL (black arrow indicates its vegetal leading edge) is lagging behind the YSL (red arrow indicates its vegetal leading edge) with (the same) little distance in the wild-type and MZspg embryo. The EVL/YSL cover the same level of the yolk (80-90% E) in both the wild-type and the MZspg embryo. White arrowheads indicate the leading edge of the blastoderm in the wild-type and MZspg embryo (not in focus). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|