- Title
-
Polaris and Polycystin-2 in dorsal forerunner cells and Kupffer's vesicle are required for specification of the zebrafish left-right axis
- Authors
- Bisgrove, B.W., Snarr, B.S., Emrazian, A., and Yost, H.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
Polaris and pkd2 are expressed in multiple ciliated tissues during early development. In situ localization of polaris (A–I) and pkd2 (J–R) transcripts at early cleavage through 72 hpf (all panels are lateral views except panels C, G, I, and P, dorsal views, and panel R, ventral view). Maternal polaris RNA is present in cleavage stage embryos (A) and becomes undetectable by early gastrula stages (B). At late gastrula stages (C), polaris expression is restricted to dorsal forerunner cells (dfc) which later aggregate to form the primordium of Kupffer′s vesicle (Kv) at the end of gastrulation (D). Polaris expression is ubiquitous at later stages with high levels detected in the otic vesicle (ov) (F), the pronephric duct primordia (pnd) and floorplate (fp) (G). At 24 hpf, polaris is expressed in the brain and in the caudal floorplate (H). At 3 dpf, polaris is expressed in the brain (I). Maternal pkd2 message is not detected by in situ hybridization (J). At 40% epiboly, zygotic expression is detected in a band of 3–4 cell diameters at the blastoderm margin (K). Pkd2 RNA is localized to the hypoblast of the dorsal midline and to DFCs during gastrulation (L). From tailbud stage through 24 hpf, pkd2 is ubiquitous with higher levels of expression in KV (M) that persist to the 6 somite stage (N). pkd2 message is also detected in the pronephric duct primordia and floorplate (P) and at 24 hpf is highly expressed in the brain (Q). At 3 dpf, pkd2 is expressed in the pharyngeal arches (pa) and pectoral fins (pf) (R). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
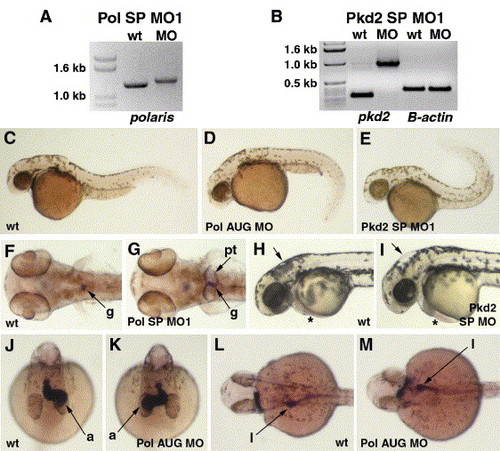
Knock-down of polaris and pkd2 gene function leads to several morphological phenotypes. Pol SP MO1 (A) and Pkd2 SP MO1 (B) morpholinos interfere with splicing of polaris and pkd2 message, respectively. RT-PCR products produced from gene-specific primers from RNA extracted from uninjected wild-type (wt) embryos versus morpholino-injected embryos are increased in size reflecting incorporation of intron sequences into the mRNAs. As an RT-PCR control, B-actin primers give the same size products from cDNAs prepared from wt and morpholino-injected embryos (B). Body shape is altered in 40 hpf morphant embryos (C–D). Polaris morphants exhibit a ventrally curved trunk and tail (D) while pkd2 morphants exhibit a dorsally curved trunk and tail (E) compared to uninjected wt embryos (C). Kidney cysts are evident in polaris and pkd2 morphants at 3 dpf (F, G). In uninjected wt embryos, wt1 expression identifies the glomerulus (g) of the pronephric kidney, while in morphants (Pol SP MO1 shown), the glomerulus appears enlarged and the pronephric tubules (pt) are distended (G). Polaris and pkd2 morphants exhibit hydrocephalus and cardiac edema at 2 dpf (H, I). Expansion of the hindbrain (single arrow) and pericardium (asterisk) is evident in morphants (Pkd2 SP MO shown, I) compared to an uninjected wt embryo (H). The direction of heart and gut looping is often reversed in 40 hpf polaris and pkd2 morphants (J–M). In a wt embryo (J), the atrium (a) of the heart loops toward the left side of the embryo while in morphants (Pol AUG MO shown) the atrium often loops toward the right side (K). In wt embryos, the liver (l) and intestinal bulb are located on the left side of the embryo (L) while in morphants (Pol AUG MO shown) these organs are often on the right side (M). |
|
Polaris and pkd2 morpholinos cause randomized expression of spaw (A–E). Polaris and pkd2 morphants show left-sided (A), right-sided (B), bilateral (C) or an absence (D) of spaw expression in the LPM (Pol AUG MO morphants shown). MyoD expression in somites was used to stage embryos. (E) Histogram showing the percentage of control and morphant embryos with left-sided (L), right-sided (R), bilateral (B) or absent (A) spaw expression. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Polaris and pkd2 morpholinos cause randomized expression of lft1 and lft2 in 22–24 somite zebrafish embryos (A–E). Polaris and pkd2 morphants show left-sided (A), right-sided (B), bilateral (C) or absent (D) lft1 expression in the diencephalon and lft2 expression in the LPM (Pol AUG MO morphants shown). MyoD expression in somites was used to stage embryos. (E, F) Histograms show the percentage of control and morphant embryos with left-sided (L), right-sided (R), bilateral (B) or absent (A) lft1 and lft2 expression. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
KV cilia are shorter in polaris morphant embryos. Anti-acetylated tubulin staining of KV cilia in 8 somite embryos. (A) Uninjected wt control embryo; cilia average 3.5 μm in length. (B) Embryo injected with 4.5 ng Pol AUG MO; cilia average 2.2 μm in length. |

Unillustrated author statements |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 287(2), Bisgrove, B.W., Snarr, B.S., Emrazian, A., and Yost, H.J., Polaris and Polycystin-2 in dorsal forerunner cells and Kupffer's vesicle are required for specification of the zebrafish left-right axis, 274-288, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.