- Title
-
Two endothelin 1 effectors, hand2 and bapx1, pattern ventral pharyngeal cartilage and the jaw joint
- Authors
- Miller, C.T., Yelon, D., Stainier, D.Y., and Kimmel, C.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
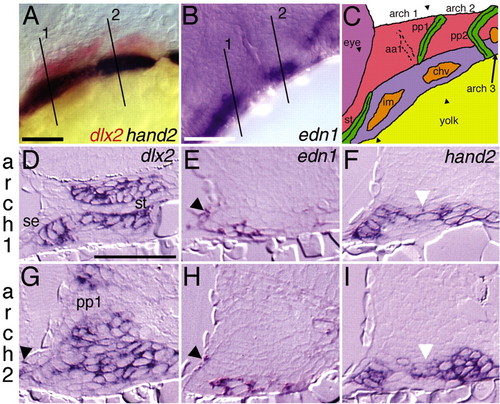
edn1 pharyngeal arch expression is ventrally confined. Lateral views of (A) dlx2 and hand2 expression in red and blue, respectively, at 28 hpf and (B) edn1 expression at 36 hpf. (C) Schematic of zebrafish pharyngeal arch primordia from 28-36 hpf at a slightly dorsal-oblique lateral view. The first and second arch ventral myogenic arch cores (intermandibularis and constrictor hyoideus ventralis; shown in orange) (see Kimmel et al., 2001b) express edn1 (Miller et al., 2000). The third arch myogenic core also expresses edn1. Pharyngeal epithelia, the stomodeum and pharyngeal pouches, are colored green. The first and second arches are labeled over the arches, with the postmigratory cranial neural crest (CNC) colored in red (dlx2+dHAND-) or blue (dlx2+dHAND+). Approximate section planes for the first two arches are indicated and numbered (A,B) or marked with arrowheads (C). (D-I) Transverse sections through the first two arches of 32 hpf embryos stained for dlx2 (D,G), edn1 (E,H) or hand2 (F,I). hand2-expressing cells are a ventral subset of dlx2-expressing CNC cells, including cells just dorsal (white arrowheads) to the edn1-expressing ventral arch cores. Lateral surface ectoderm expresses both dlx2 and edn1 ventrally (arrowheads). chv, constrictor hyoideus ventralis; im, intermandibularis; pp1, pharyngeal pouch 1; se, surface ectoderm; st, stomodeum. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
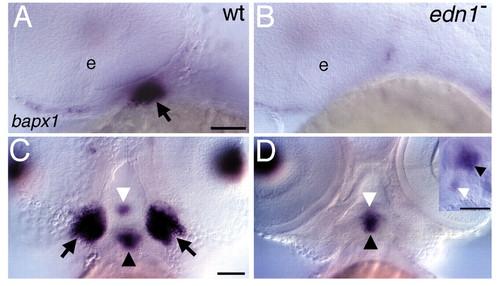
bapx1 is expressed at the developing jaw joint. (A-H) bapx1 expression in wholemount (A-D,G,H) and sectioned (E,F) wild-type embryos. (A) At 32 hpf, expression is seen in a cluster of first arch mesenchyme (arrow) as well as pharyngeal endoderm. (B) A higher magnification of A, showing that this domain appears to be at an intermediate dorsoventral position within the first arch. (C) Ventral view of 54 hpf embryo, showing bilateral first arch joint domains (arrows), first arch midline domain (white arrowhead), second arch midline domain (black arrowhead). (D) High magnification ventral-lateral oblique view of 54 hpf embryo showing the posterior end of the lower jaw (M) is surrounded by bapx-1-expressing cells, with apparent expression in cells in the posterior end of Meckel′s cartilage (outlined with broken line). The jaw joint appears to be filled with and surrounded by bapx1-expressing cells. The second arch midline domain (arrowhead) and pharyngeal endoderm domains are also present. (E,F) Horizontal sections of bapx1 expression at 48 hpf showing (E) first arch jaw joint (arrow) and second arch midline domain (arrowhead), and (F) pharyngeal endoderm expression in pouches 2 through 6. (G,H) Two-colored in situ hybridization of expression of (G) dlx2 in red and bapx1 in blue at 32 hpf and (H) bapx1 in red and hand2 in blue at 30 hpf. bapx1 expression is ventral to a portion of dlx2 expression and dorsal to hand2 expression. The outline of the eye in the upper left, the first pharyngeal pouch in the upper-right corner, and the edge of the embryo towards the bottom are delineated. e, eye; M, Meckel′s cartilage; p, pharynx; pe, pharyngeal endoderm; pp1, pharyngeal pouch 1; pp2, pharyngeal pouch 2; st, stomodeum. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
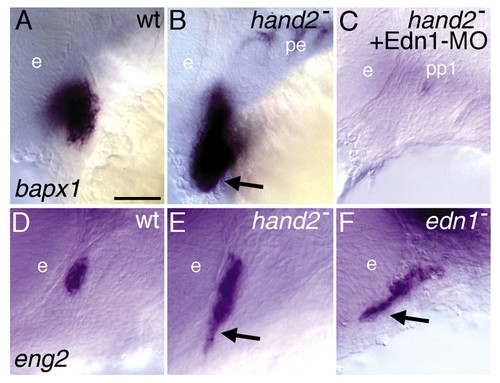
edn1 function is required for jaw joint bapx1 expression. (A-D) bapx1 expression in wild-type (A,C) and edn1 mutant larvae (B,D). (A,B) Lateral views of 36 hpf embryos, focused on the first arch joint domain (arrow in A). First arch mesenchymal expression of bapx1 is absent in edn1 mutants (B). Cells apposed to the eye and the first pharyngeal pouch express bapx1 in both wild types and mutants. (C,D) Ventral views of 54 hpf embryos. Joint domains (arrows in C,D) are abolished in edn1 mutants, whereas the first and second arch midline domains (white and black arrowheads, respectively, in C and D) are present. Inset (D) shows lateral view of same embryo, showing both midline domains are present. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
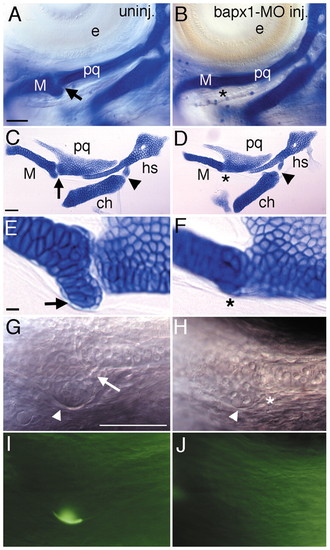
bapx1 is required for patterning the first arch joint region. Lateral views of pharyngeal cartilages (A-H) and bones (I,J) in uninjected (A,C,E,G,I) and bapx1-MO-injected (B,D,F,H,J) larvae. Wholemounted (A,B) and flat-mounted (C-F) Alcian Green-stained pharyngeal cartilages in animals at 4 days. The first arch joint (arrow in A,C) is eliminated upon bapx1 downregulation (asterisk in B,D), whereas the second arch joint is unaffected (arrowheads in C,D). Panel D is a montage of two Nomarski focal planes of the same flatmount preparation. (E,F) Higher magnification of jaw joint region showing retroarticular process (RAP) (arrow in E) is severely reduced (asterisk in F) in bapx1-MO-injected animals. (G,H) Nomarski images of live animals revealing that the jaw joint (arrow) is missing (asterisk) and the RAP of Meckel′s cartilage (arrowhead) is reduced in bapx1-MO-injected animals. (I,J) Fluorescent images of the same fish as in G,H stained with calcein, which fluorescently labels calcified bone. In uninjected animals, the retroarticular bone (RAB) has formed on the RAP of Meckel′s cartilage, and this bone is missing in bapx1-MO-injected animals. The second branchiostegal ray (BSR2) (C. B. K., unpublished), a bone that normally forms slightly later than RAB, was actually more frequently observed in bapx1-MO-injected animals (95/121 or 79% of injected animals had BSR2, whereas 29/52 or 56% of uninjected siblings had BSR2). This indicates that the loss of RAB is specific and not a result of developmental delay. ch, ceratohyal; e, eye; hs, hyosymplectic; m, Meckel′s; pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bars: 50 μm for all except (E,F): 10 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
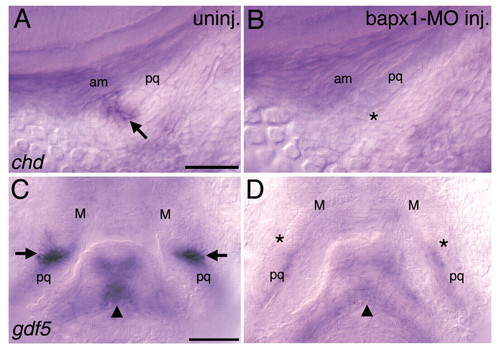
bapx1 is required for jaw joint expression of chd and gdf5. (A-B) Lateral views of wild-type wholemounted embryos at 56 hpf. (A) In uninjected animals, chd is expressed at the jaw joint (arrow) and (B) this domain appears to be absent in bapx1-MO-injected animals (asterisk). The jaw-closer muscle, the adductor mandibulae, which connects the upper and lower jaw, is present and grossly unaffected in bapx1-MO-injected animals. (C,D) Ventral views of wild-type wholemounted embryos at 78 hpf. (C) In uninjected animals, gdf5 is expressed at the first arch joint (arrows) and (D) these domains are severely downregulated in bapx1-MO-injected animals. Second arch midline expression of gdf5 (arrowheads) is also downregulated in bapx1-MO-injected animals. am, adductor mandibulae; M, Meckel′s; pq, palatoquadrate. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
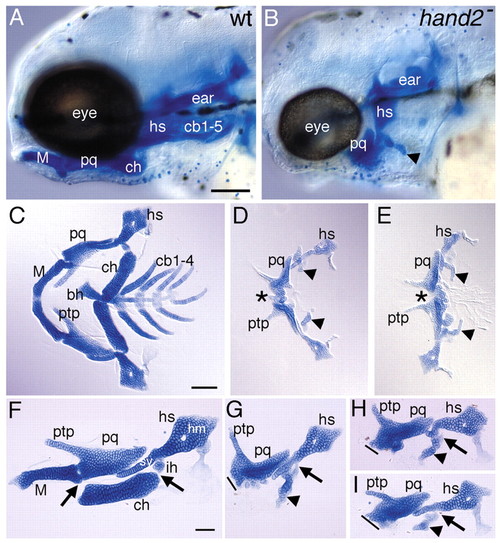
hand2 is required for ventral pharyngeal cartilage and the jaw joint but not for the second arch joint. (A,B) Lateral views of wholemount 4-day old wild type (A) and hand2 mutant (B) larvae stained with Alcian Green, revealing severe loss of ventral pharyngeal cartilage in the mutant. (C-I) Flat-mounted pharyngeal cartilages from wild type (C,F) and hand2 mutants (D,E,G-I). (C-E) Flat-mounted pharyngeal cartilages from the first six arches in wild type (C), and the entire pharynx in two different hand2 mutants (D,E). In hand2 mutants, ventral cartilages (arrowheads) are severely reduced. The two upper jaws are connected by a continuous cartilaginous bridge (asterisk), although some hints of partial jaw joint formation are evident (see Table 2). Branchial cartilages are also absent in hand2 mutants. The upper hyomandibular region of the hyosymplectic in E was slightly nicked during dissection and resembled the contralateral counterpart. (F-I) Flat-mounted pharyngeal cartilages from one side of the first and second arches. The prominent ventral cartilages (M, ch) present in wild type (F) are absent in hand2 mutants, although a small jumbled mass of ventral second arch cartilage is invariably present (arrowheads, see Table 2). (G-I). The dorsal cartilages are relatively well patterned with distinctive PTP and SY elements visible. The second arch joint (arrows) is present in hand2 mutants. Because of the highly penetrant jaw joint loss (see Table 2), the hand2 mutants in G-I were cut during dissection in order to flat-mount; the line indicates the plane of cutting and where the upper jaw was fused to its contralateral counterpart (asterisk in D,E). bh, basihyal; cb1-4, ceratobranchial 1-4; ch, ceratohyal; hm, hyomandibula; hs, hyosymplectic; ih, interhyal; M, Meckel′s; pq, palatoquadrate; ptp, pterygoid process of palatoquadrate; sy, symplectic. Scale bars: 100 μm in A-E, 50 μm in F-I. |
|
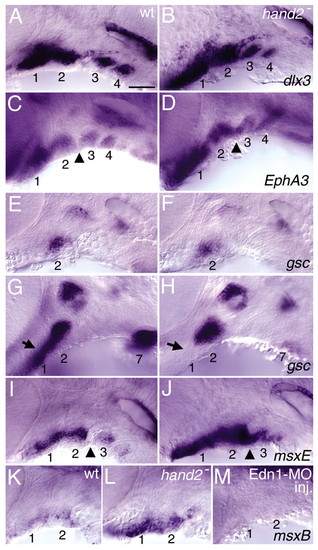
hand2 is not required for early ventral pharyngeal arch expression of edn1 targets. Lateral views of deyolked wild type (A,C,E,G,I,K), hand2 mutant (B,D,F,H,J,L) and edn1-MO-injected (M) animals. In each panel, the eye is in the upper left and the ear is in the upper right. (A,B) The ventrally restricted pharyngeal arch expression domain of dlx3 at 30 hpf (A) does not require hand2 function (B). (C,D) EphA3 expression at 32 hpf (C) also does not require hand2 function (D). (E-H) gsc expression. (E,F) Early dorsal and ventral hyoid expression domains of gsc at 32 hpf (E) are present in hand2 mutants (F). (G,H) At 38 hpf, ventral arch one expression of gsc is absent in hand2 mutants (arrows), whereas both dorsal and ventral arch two expression are still present (H). The seventh pharyngeal arch expression domain is downregulated in hand2 mutants. (I,J) msxe expression at 30 hpf. hand2 mutants have upregulated ventral arch msxe expression. (K-M) msxb expression at 30 hpf. Ventral pharyngeal arch expression of msxb (K) requires Edn1 signalling (M), but is upregulated in hand2 mutants (L). Relevant pharyngeal arches are numbered in each panel. The second pharyngeal endodermal pouch fails to completely separate the second and third arches in hand2 mutants (arrowheads in C,D and I,J). Scale bar: 50 μm. |
|
hand2 represses joint and dorsal pharyngeal fates. Lateral views of wholemount wild type (A,D), hand2 mutant (B,E), hand2 mutant injected with Edn1-MOs (C) and edn1 mutant (F). (A-C) bapx1 expression at 36 hpf is present at its normal location and expanded ventrally in hand2 mutants (arrow). This expansion of bapx1 in hand2 mutants is edn1-dependent, as hand2 mutants injected with Edn1-MOs lack all first arch mesenchymal expression of bapx1, whereas the first pharyngeal pouch expression domain is present (C). We found no evidence for the converse relationship, as hand2 expression appeared unaffected in bapx1-MO-injected animals (data not shown). (D-F) eng2 expression at 30 hpf, localized to constrictor dorsalis, the dorsal first arch mesodermal core (see Kimmel et al., 2001b) expands ventrally in both hand2 and edn1 mutants. e, eye; pe, pharyngeal endoderm; pp1, pharyngeal pouch 1. Scale bars: 50 μm. |