Fig. 7
Fig. 7
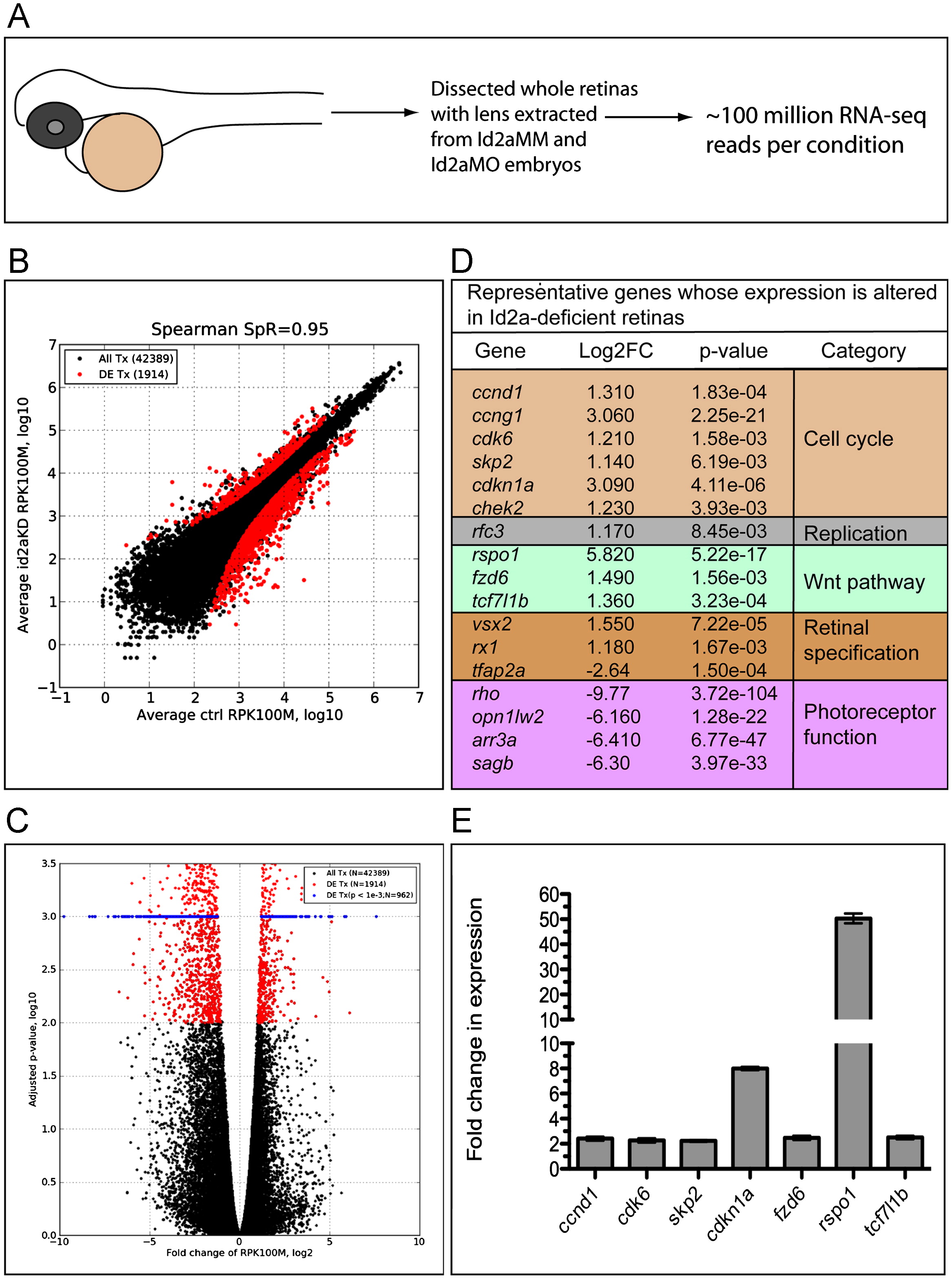
RNA-Seq analysis of differential retinal gene expression resulting from Id2a-deficiency. (A) Schematic of RNA-Seq experiment. Whole retinas were dissected from Id2aMM and Id2aMO embryos, their lenses were removed and total retinal RNA was extracted and used for Illumina RNA sequencing. ∼100 million Illumina reads were obtained for each condition, and the experiment was repeated in two biological replicates for each condition (see the Materials and methods section for details). (B) The number of reads per each transcript was normalized with total number of mapped reads and transcript length, converting all raw read counts to ‘number of reads per 1000 bases per 100 million reads’ (RPK100M). ‘100 million reads’ were chosen to get positive values of log10-transformed normalized values. A scatter plot shows the correlation between Id2aMO and Id2aMM control normalized reads (Spearman=0.95). Differentially expressed transcripts with fold changes greater than 2 and adjusted p-value less than 0.01 are indicated with red dots. (C) Volcano plot illustrating that out of 42,389 mapped transcripts, 1914 were significantly differentially expressed (DE), p<0.01 (red dots), and, for visualization purposes, of those 962 were highly significant, with an adjusted p-value <0.001 (blue dots). (D) A table depicting representative genes that exhibit significant changes in gene expression between Id2aMM and Id2aMO retinas; genes were categorized based upon known pathways and are color coded. (E) qRT-PCR validation of RNA-Seq data for a subset of DE genes. Transcript levels of ccnd1, cdk6, skp2, cdkn1a, fzd6, rspo1 and tcf7l1b in Id2aMO retinae compared to Id2aMM retinae at 48hpf. Transcript levels were normalized to tubulin and the fold-change in expression in Id2aMO retinae compared to Id2aMM retinae presented. Error bars represent SEM, **p<0.05, n=3 biological replicates.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 371(2), Uribe, R.A., Kwon, T., Marcotte, E.M., and Gross, J.M., Id2a functions to limit Notch pathway activity and thereby influence the transition from proliferation to differentiation of retinoblasts during zebrafish retinogenesis, 280-292, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.