Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240729-113
- Publication
- Brennan et al., 2024 - A zebrafish gephyrinb mutant distinguishes synaptic and enzymatic functions of Gephyrin
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
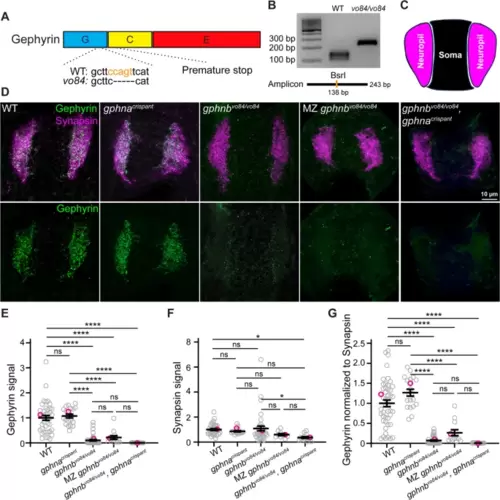
Generation and validation of gphnbvo84 mutants. A Schematic of Gephyrin protein showing its three domains and the 5 bp deletion in gphnbvo84 causing a frameshift and premature stop. The BsrI recognition site used for genotyping was indicated in orange. B Representative gel images for genotyping gphnbvo84. A BsrI recognition site is disrupted by gphnbvo84 mutation in the middle of the amplicon. C Schematic of neuropil (magenta) and soma (black) regions in transverse spinal cord section of zebrafish at 5 dpf. D Representative transverse sections in the spinal cord at 5 dpf with Gephyrin (green) and Synapsin (magenta) staining from the following conditions: wildtype (WT); gphnacrispant, gphnbvo84/vo84; maternal zygotic (MZ) gphnbvo84/vo84; and gphnbvo84/vo84, gphnacrispant. E–G Gephyrin signal (E), Synapsin signal (F) and Gephyrin normalized to Synapsin (G) from the spinal sections. nWT = 19 fish, 41 sections, 3 technical replicates; ngphna = 12 fish, 20 sections, 1 technical replicate; ngphnb = 18 fish, 42 sections, 3 technical replicates; nMZ gphnb = 7 fish, 13 sections, 1 technical replicate; and n = 8 fish, 15 sections, 1 technical replicate. E, F[4, 126] = 45.29; F, F[4, 116] = 3.303; G, F[4, 129] = 56.29. All data are represented as mean ± SEM; ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05; ****, p < 0.0001; the data points corresponding to the representative images are noted in pink; ns, not significant; (E–G) one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test; scale bars 10 μm |